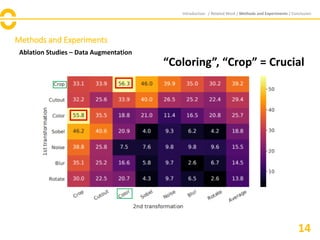
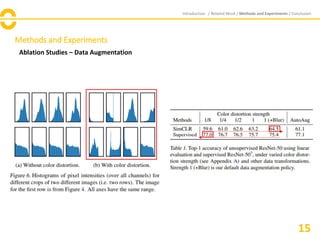
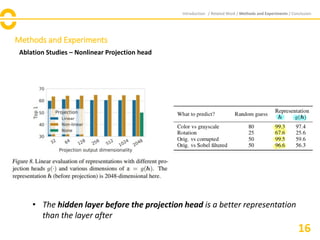
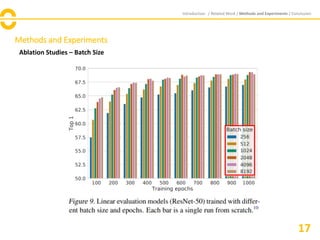
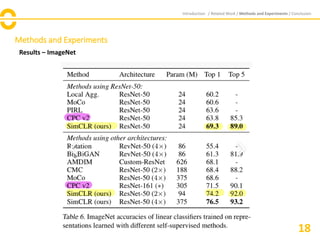
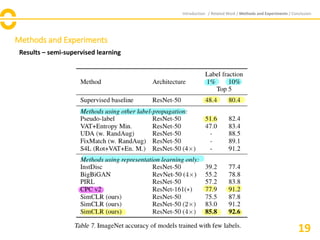
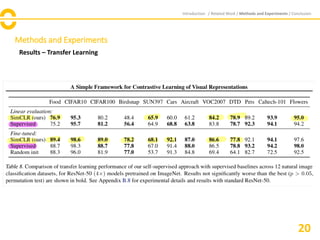
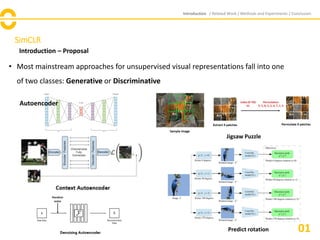
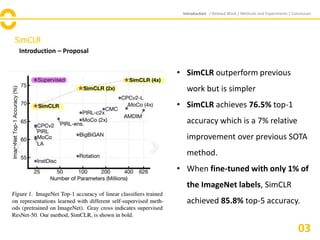
The document discusses SimCLR, a framework for contrastive learning of visual representations, which has outperformed previous methods with a 76.5% top-1 accuracy. Key insights include the importance of data augmentation, the effectiveness of larger batch sizes, and the benefits of learnable nonlinear transformations on representation quality. The conclusion emphasizes SimCLR's significant improvements across self-supervised, semi-supervised, and transfer learning tasks.

![SimCLR
Introduction – Proposal
• Discriminative approaches based on Contrastive Learning in the latent space have
recently shown state-of-the-art results.
Introduction / Related Work / Methods and Experiments / Conclusion
02[AMDIM]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/simclrreview-201025123851/85/A-Simple-Framework-for-Contrastive-Learning-of-Visual-Representations-4-320.jpg)

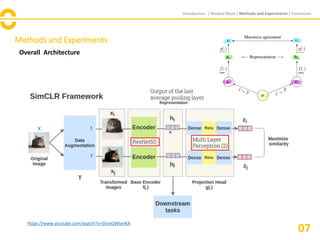
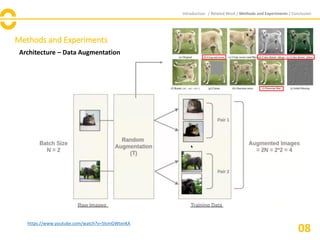
![Methods and Experiments
Introduction / Related Work / Methods and Experiments / Conclusion
10
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5lsmGWtxnKA
Final Loss
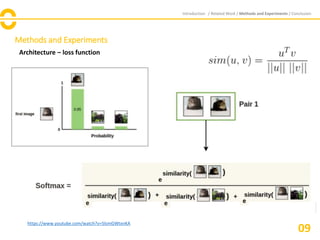
Architecture – loss function
[Normalized temperature-scaled cross entropy loss]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/simclrreview-201025123851/85/A-Simple-Framework-for-Contrastive-Learning-of-Visual-Representations-12-320.jpg)