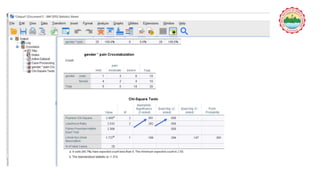
This document provides an overview of quantitative data analysis using SPSS. It discusses the objectives of analyzing how to enter data into SPSS and what statistical tests can be applied, including assessing normality, chi square, correlation coefficients, t-tests, and one-way ANOVA. It defines different types of variables that can be entered into SPSS and the three main types of data analysis: univariate, bivariate, and multivariate. Specific statistical tests are explained like independent t-tests, paired t-tests, correlation, chi square, Fisher's exact test, and one-way ANOVA. Steps for hypothesis testing and assessing normality are also outlined. Examples of transferring data from Excel and running analyses in SPSS are provided.