The document describes how to plan and implement an objective structured clinical examination (OSCE) for assessing pediatric nursing students. It discusses:
- The OSCE model based on Miller's hierarchy of clinical competence using simulated practice.
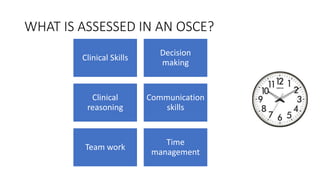
- Skills that can be assessed including clinical skills, decision making, communication, and time management.
- Locations for the OSCE including clinical areas with real patients or simulated labs.
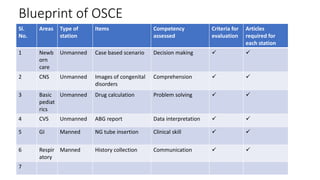
- Steps for planning including time allotted, staffing needs, station types and content, and evaluation criteria.
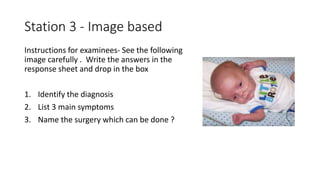
- Types of stations such as manned stations where students perform skills and unmanned stations involving cases, images, and written responses.
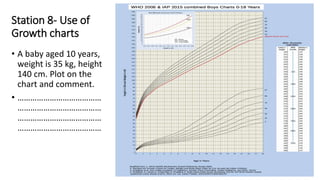
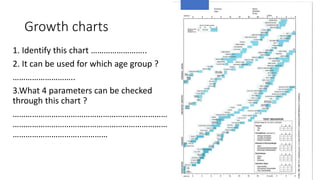
- Examples of station content covering various pediatric topics, skills