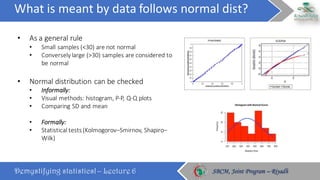
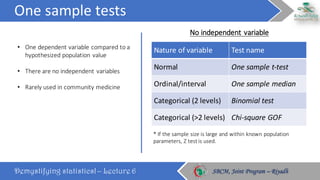
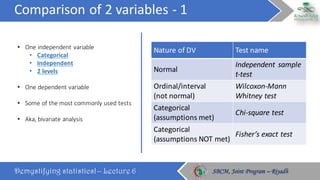
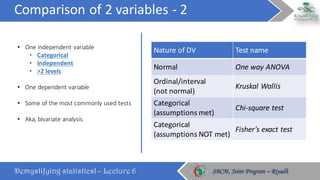
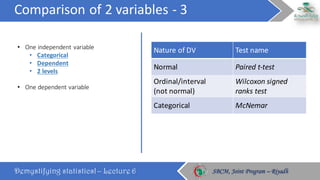
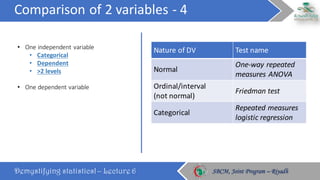
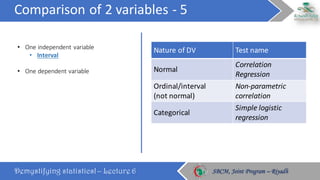
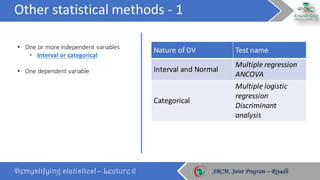
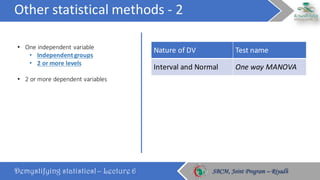
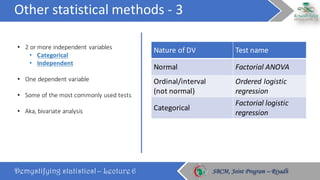
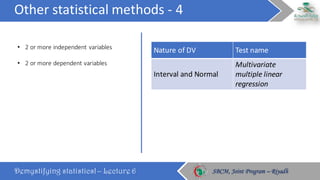
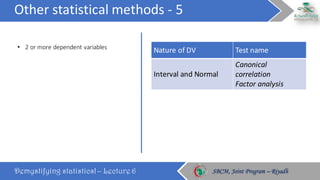
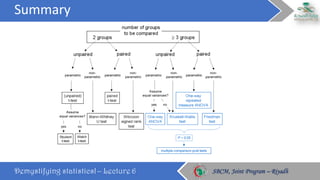
The document discusses how to choose the appropriate statistical test based on the characteristics of the data. It outlines several key considerations for selecting a test, including the number and type of variables, whether the data is paired or independent, and if the continuous variables follow a normal distribution. The document then describes many commonly used statistical tests for different types of comparisons, including onesample, bivariate, and multivariate tests. It emphasizes that the correct statistical test must be applied to ensure valid conclusions can be drawn from the data analysis.