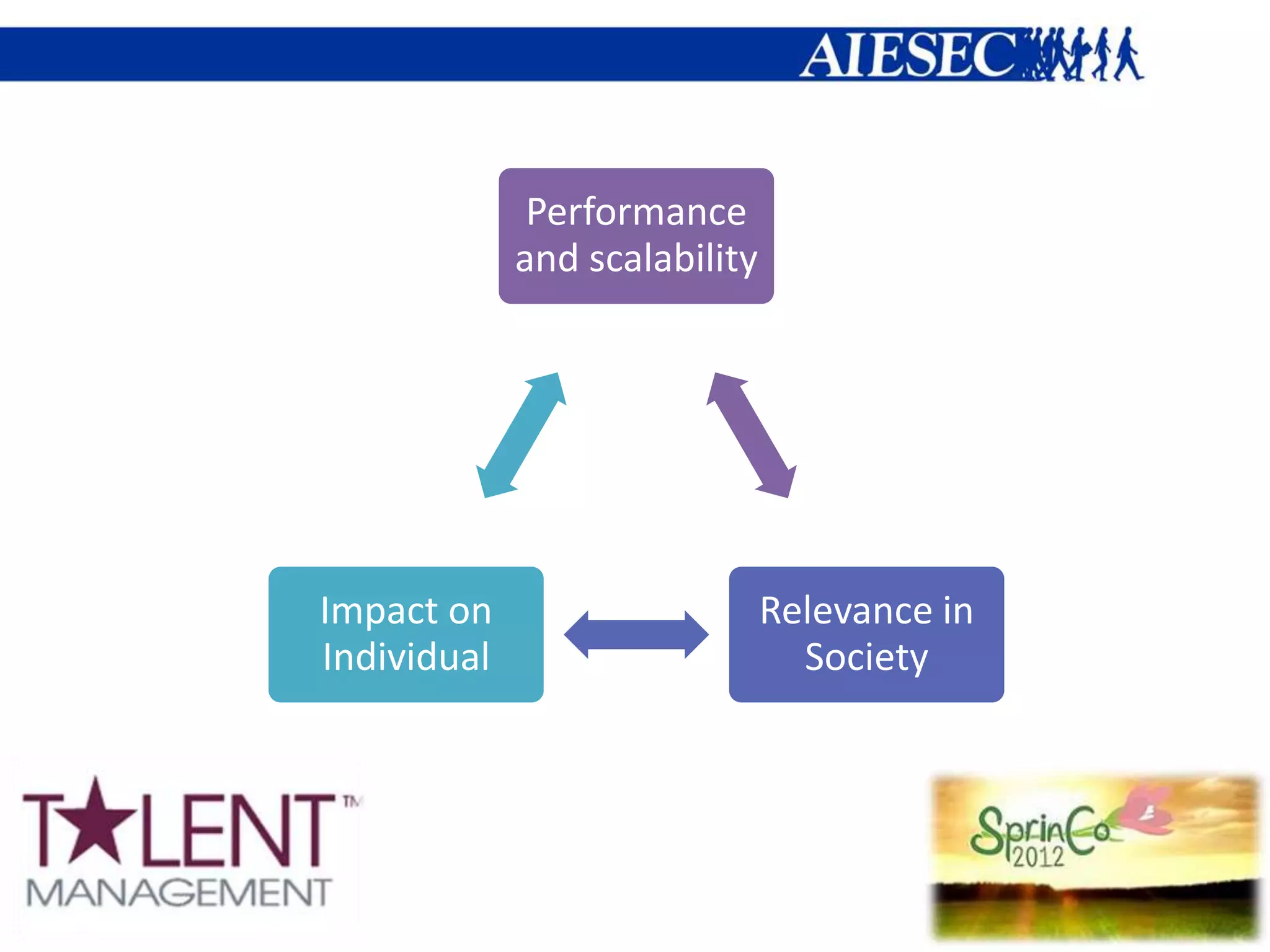
This document summarizes plans for talent management initiatives. It includes analyzing the current talent management area and planning strategies. Specific initiatives to be planned include SWOT analysis, vision, main missions and strategies, and timelines. The document also discusses key societal trends like social responsibility, emotional customers, glocalization, convergence technology, and co-creation that talent management programs and local talent programs should cater to. It emphasizes moving to less centralized structures and involving the network in decision making. The overall aim is for the talent management initiatives to be relevant to achieving goals by 2015.

![Friday Saturday Saturday Saturday
[13.04] [14.04] [14.04] [14.04]
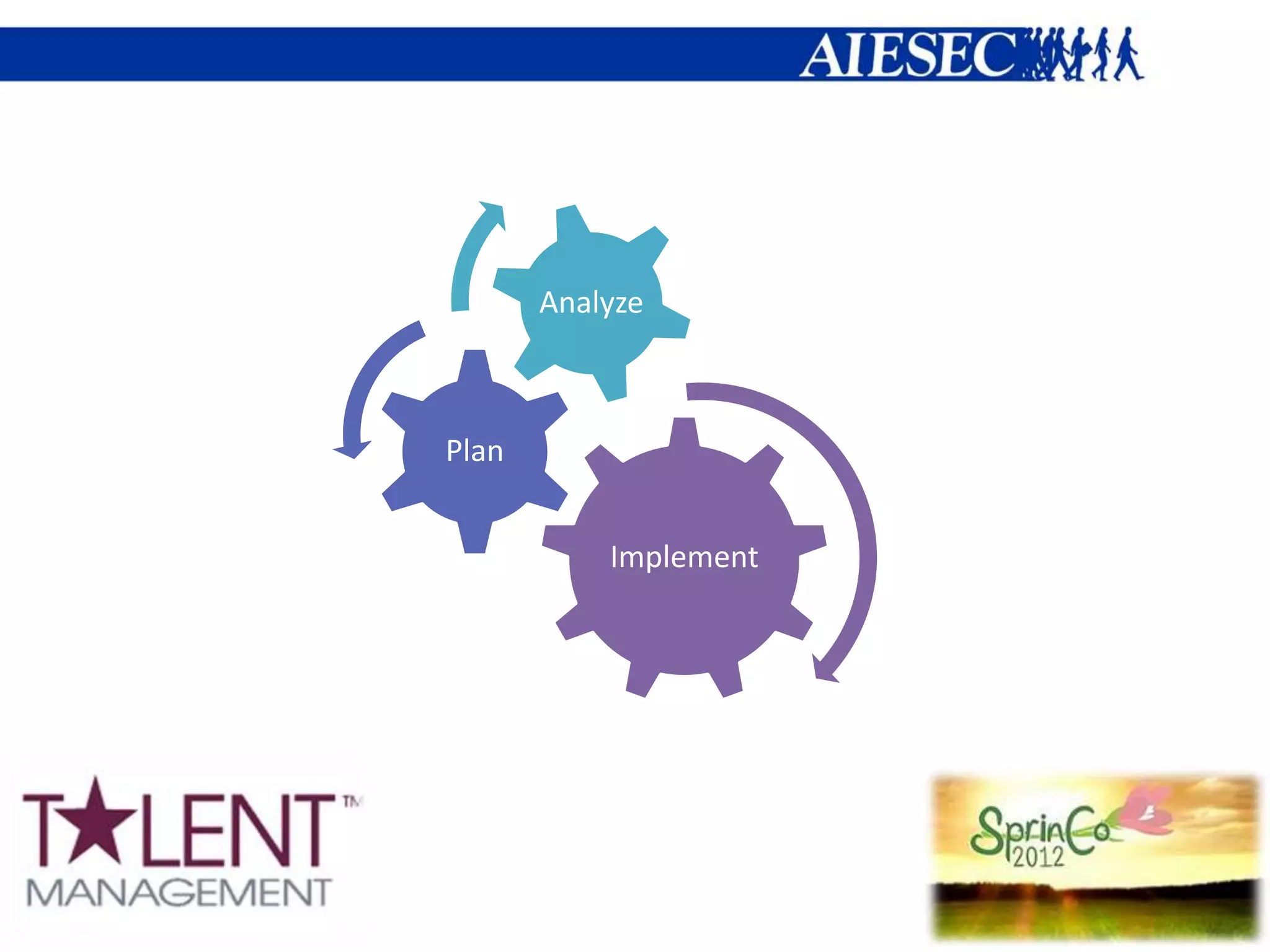
Analyze TM area Plan Initiatives Bringing home
Plan strategies
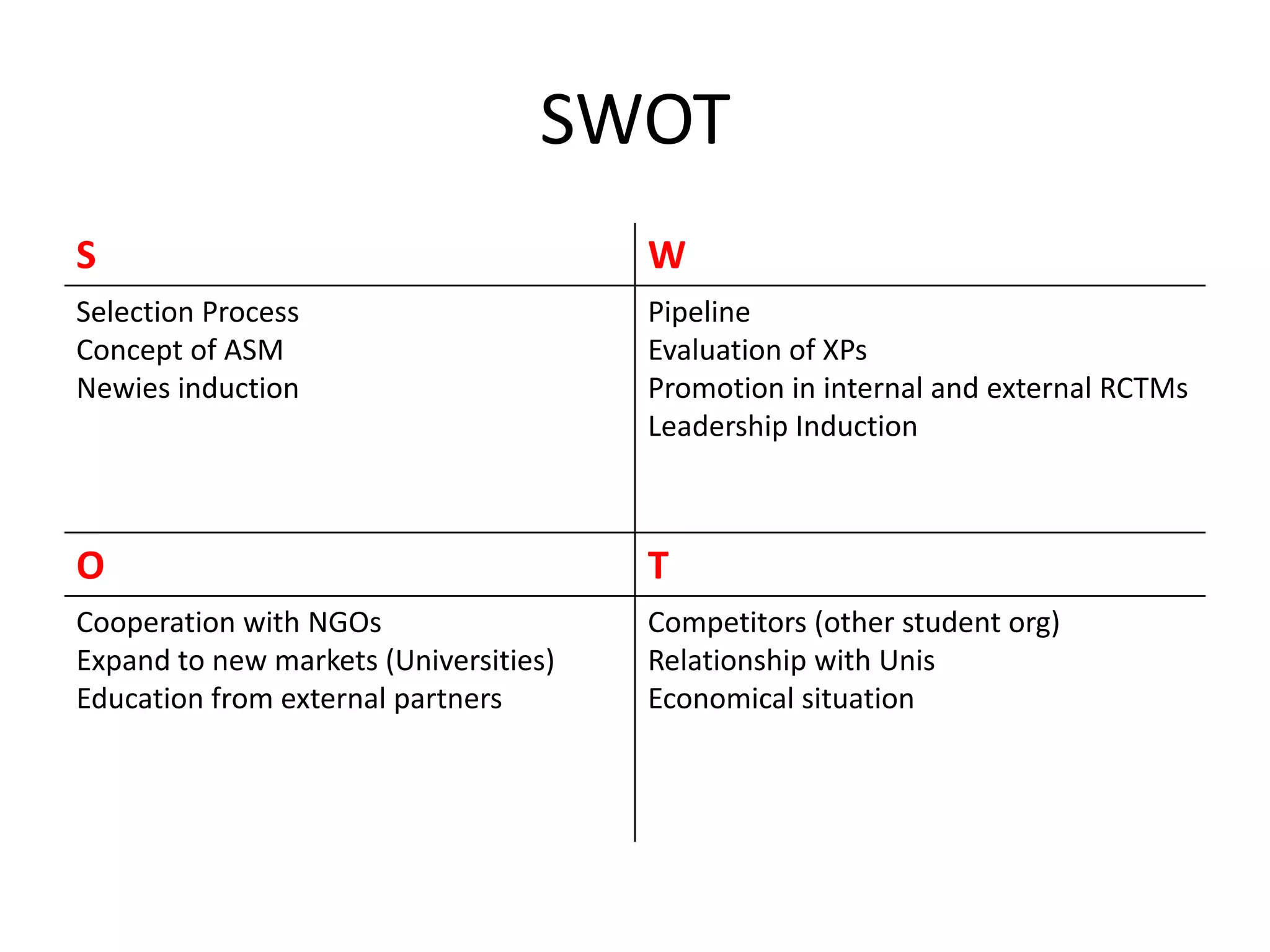
•SWOT •Sub MoSes
•Vision •Sub Strategies Update
Cross-Functional
•Main MoS •Timelines Time-Line
•TM Global •Resources needs Task Forces
Direction
•Main Strategies](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sprincotmswotglobaldirection-120416101554-phpapp02/75/Sprin-co-tm-swot-global-direction-3-2048.jpg)