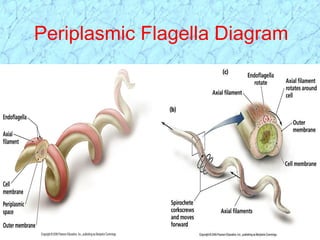
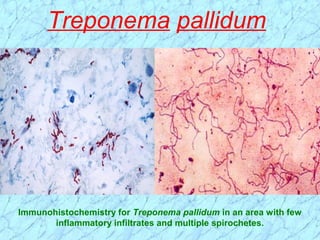
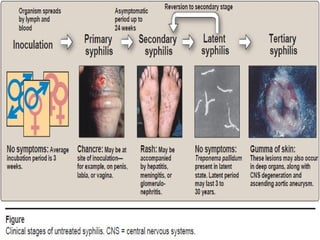
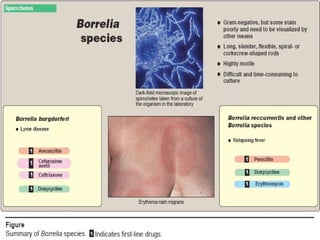
Spirochetes are a phylum of Gram-negative bacteria characterized by their spiral or corkscrew shape and motility via periplasmic flagella. The document discusses three genera of medically important spirochetes: Treponema, Borrelia, and Leptospira. Treponema pallidum causes syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection. Borrelia burgdorferi is the causative agent of Lyme disease transmitted through tick bites. Leptospira interrogans causes leptospirosis, a zoonotic disease spread through contact with infected animal urine.