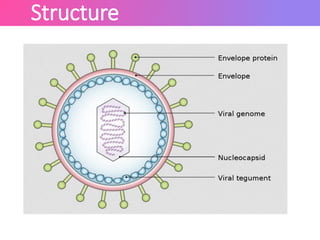
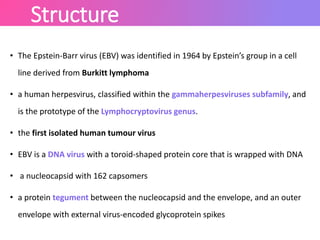
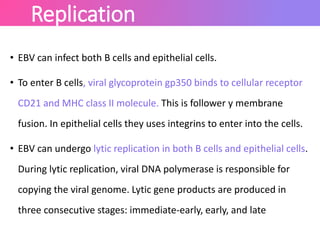
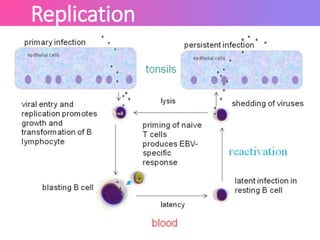
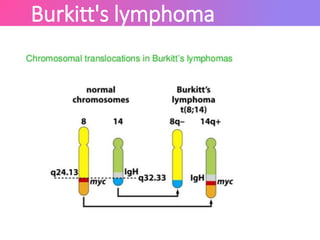
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), a common human herpesvirus, is known for causing mononucleosis and is associated with various cancers such as Burkitt's lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. EBV can infect B cells and epithelial cells, leading to lytic replication or latency; while mononucleosis symptoms include fever and sore throat, most cases resolve without treatment. Diagnosis typically involves antibody testing, and while there is no specific treatment for EBV infections, symptomatic relief is recommended.