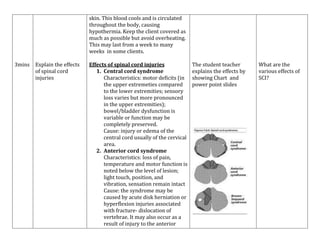
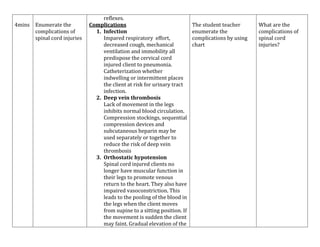
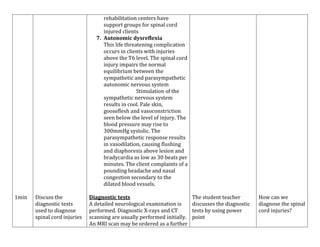
- Spinal cord injuries occur most often in males aged 16-30 and result from motor vehicle accidents, violence, falls, or sports.
- Medical management includes immobilizing the spine, administering steroids to reduce swelling, and surgery to decompress the spinal cord if needed.
- Nursing management focuses on respiratory care if needed, skin integrity, bowel and bladder care, pain management, and preventing complications like infection, blood clots, and autonomic dysreflexia.