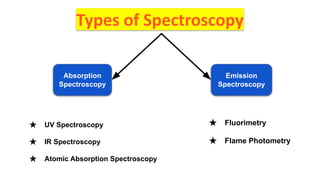
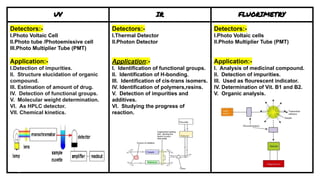
The document discusses different types of absorption and emission spectroscopy techniques. It describes UV spectroscopy, IR spectroscopy, atomic absorption spectroscopy, fluorimetry, and flame photometry. For each technique it covers the light source, filters, monochromator, detectors, and applications. Overall the document provides an overview of various spectroscopy methods, the core components used, and their uses in analyzing samples.