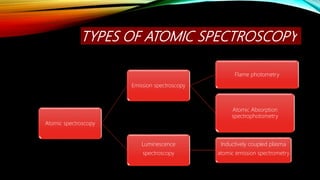
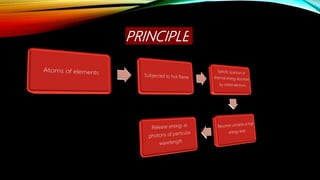
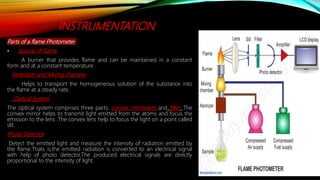
This document provides an overview of flame photometry, which is a technique used to determine the concentration of certain metal ions like sodium, potassium, calcium, and lithium. It describes the basic components and working of a flame photometer, including the nebulizer, burner, optical system, and photodetector. When a sample solution containing metal ions is introduced into the flame, the ions absorb energy and emit light of characteristic wavelengths. The intensity of emitted light can then be used for quantitative analysis of metal ion concentrations. Some applications mentioned are analysis of soils, fertilizers, drinks and other samples. Advantages include low cost and sensitivity down to ppm and ppb levels, while limitations are inability to detect non-radiating