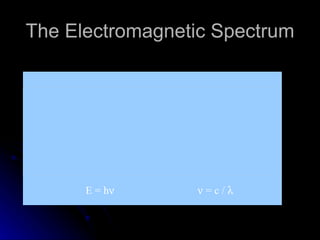
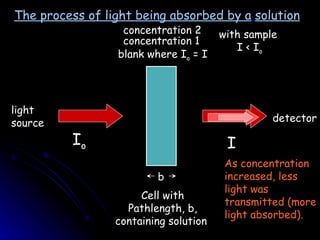
1. A spectrophotometer measures the light that passes through a liquid sample and gives readings in percent transmittance and absorbance.
2. As concentration of an absorbing substance increases, less light is transmitted through the sample according to Beer-Lambert's law.
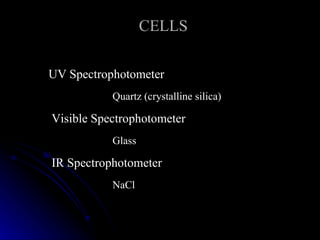
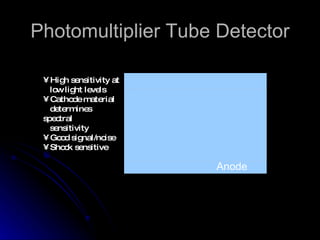
3. Key aspects of a spectrophotometer include the light source, monochromator, sample cells, detector, and associated electronics for amplification and readout. Spectrophotometers are used for a variety of applications including quantitative analysis and molecular structure determination.