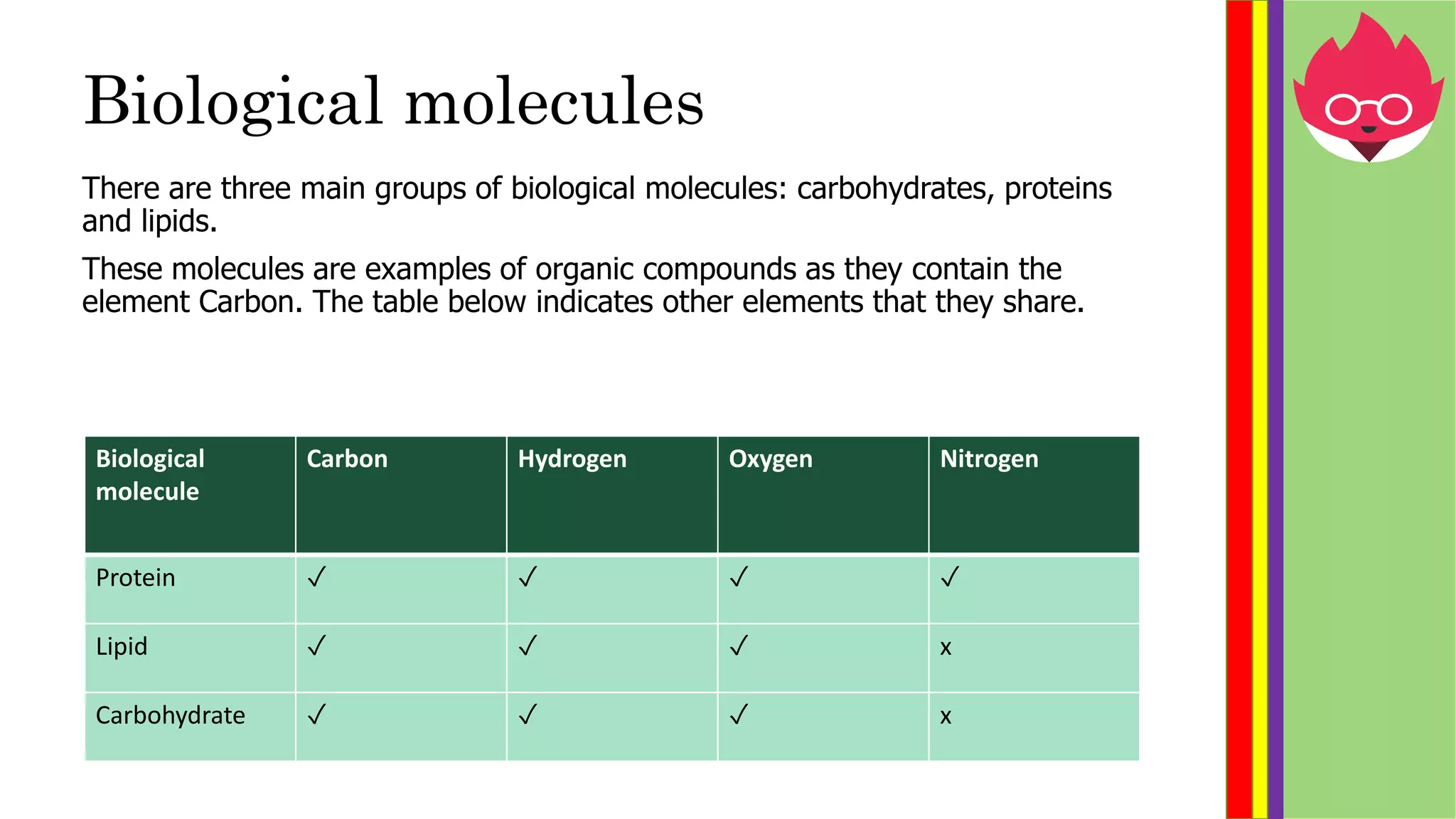
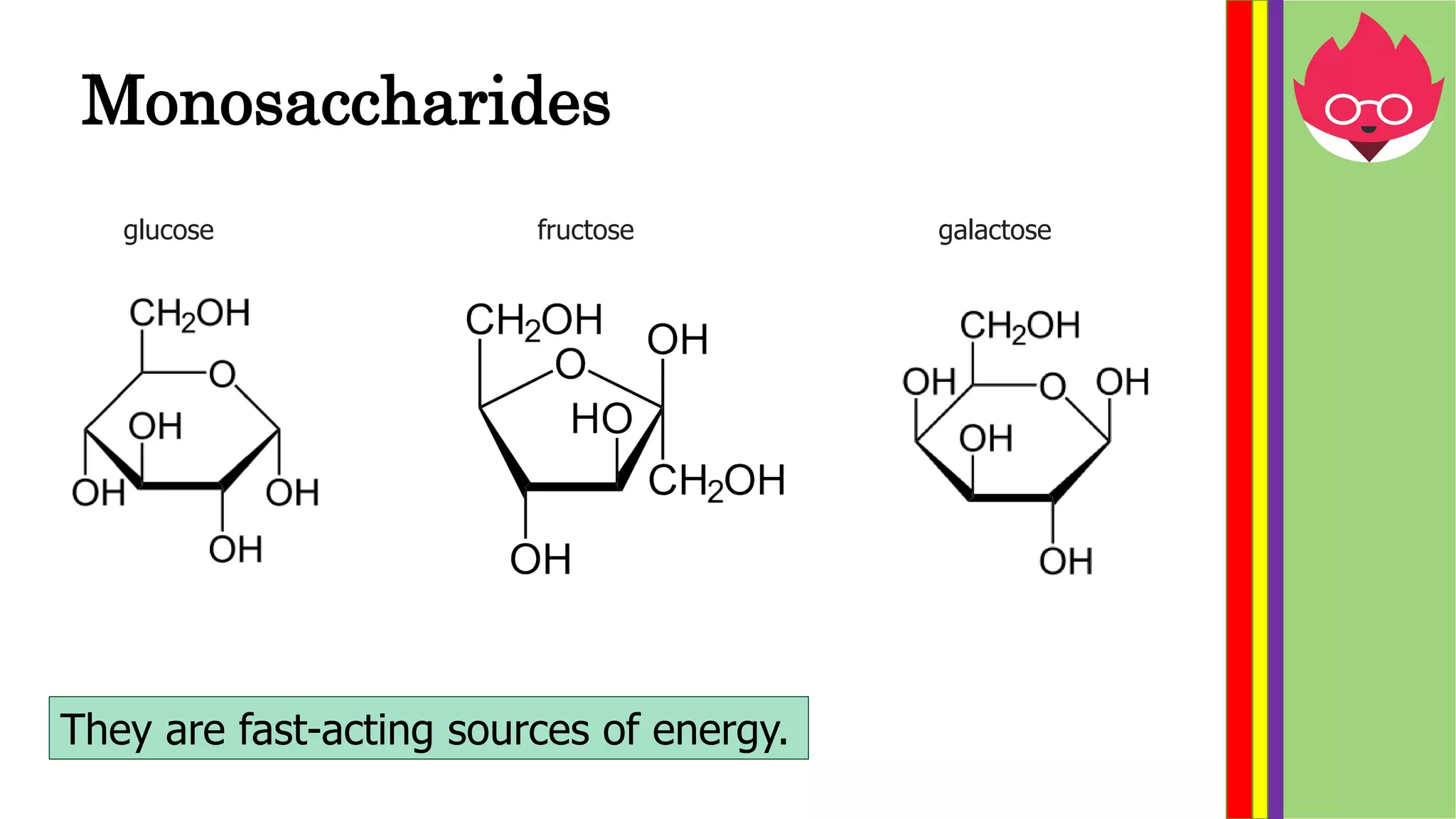
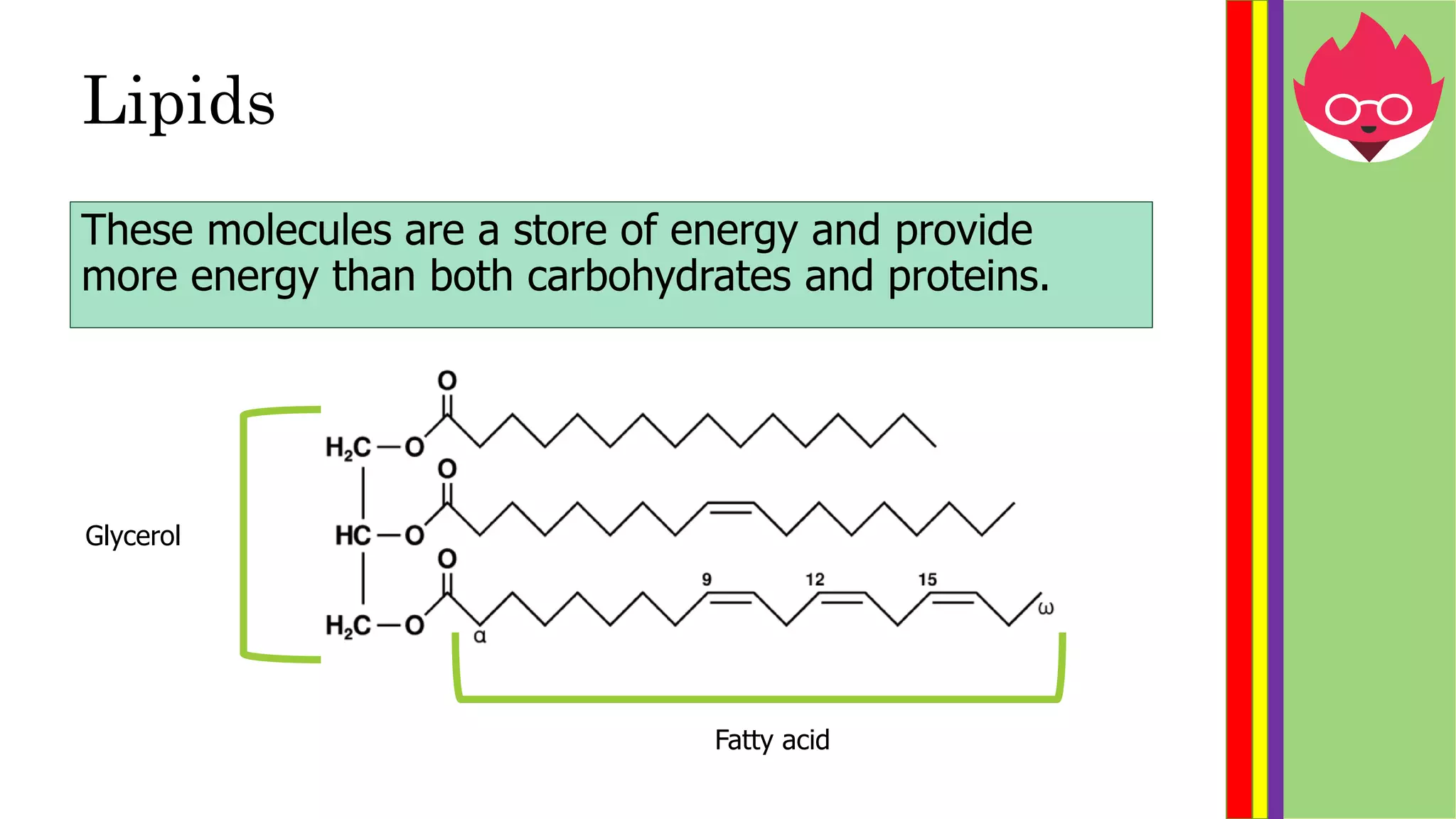
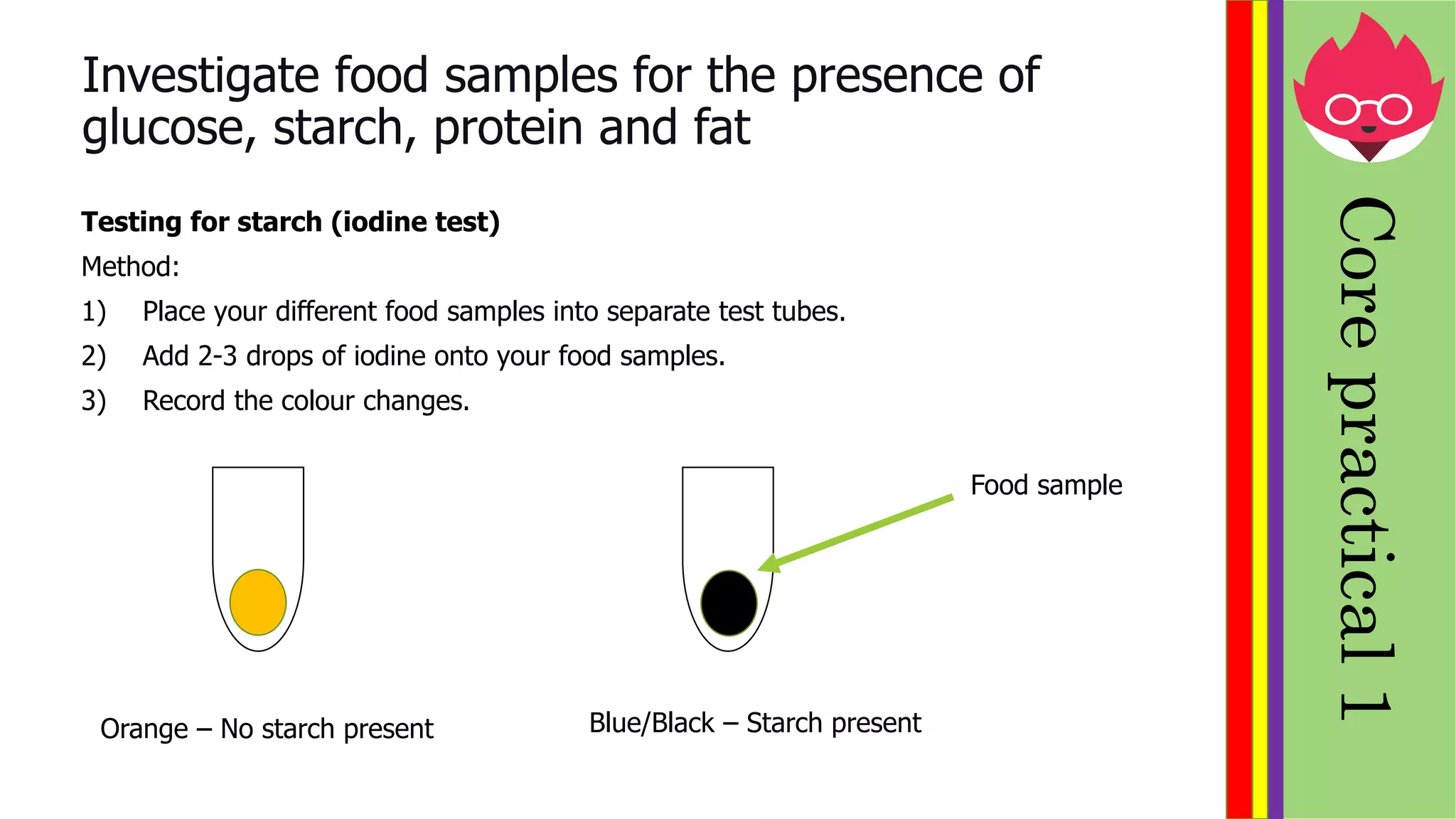
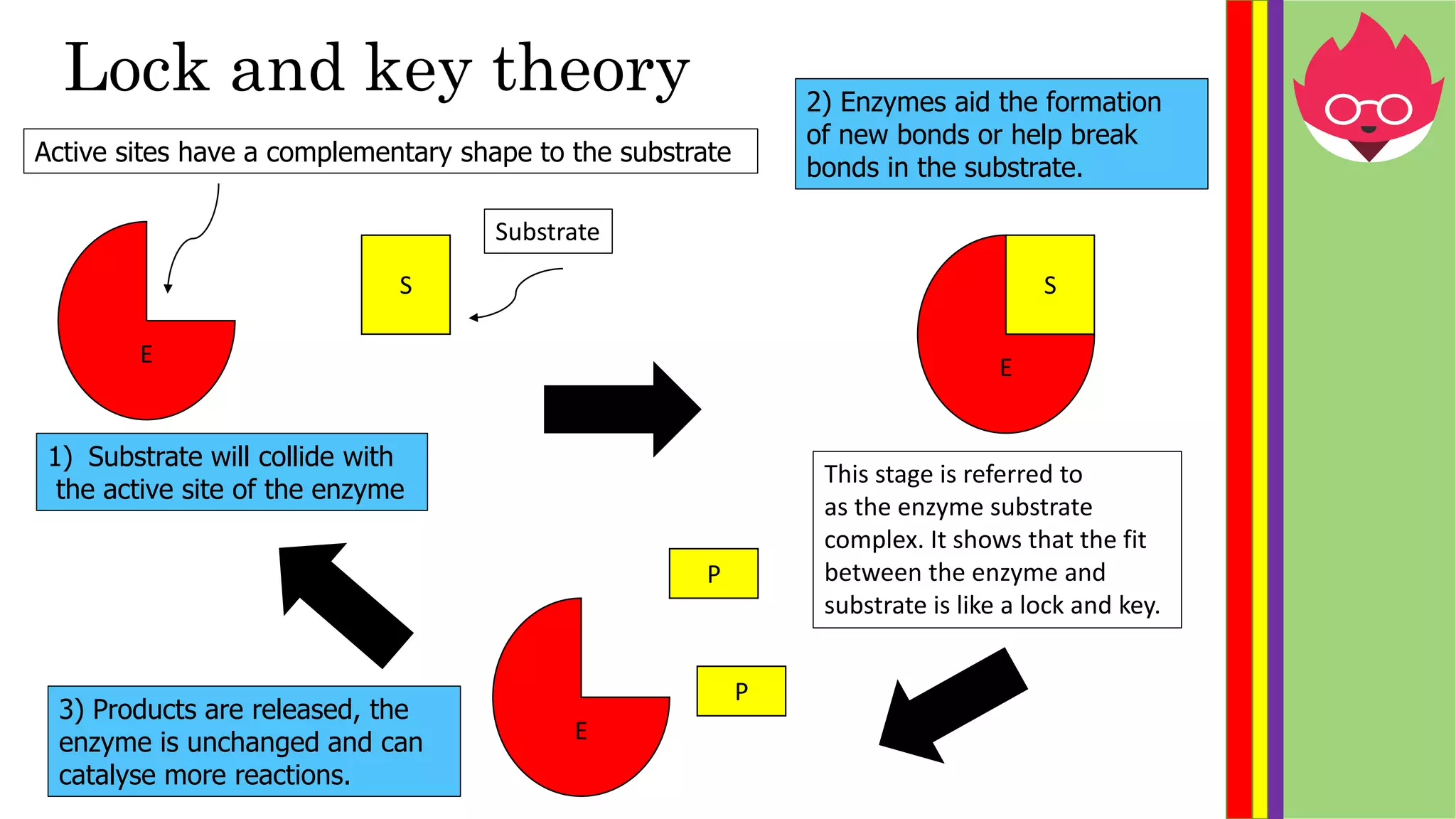
This document provides information about biological molecules and enzymes for an International GCSE Biology exam. It defines carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids as the three main types of biological molecules, and describes their structures and components. It also explains enzyme function using the lock and key theory and discusses how enzyme activity can be affected by changes in temperature and pH. Practical investigations are described for testing food samples for glucose, starch, protein and fat, as well as experiments on how enzyme activity of amylase is influenced by temperature and pH changes.