1. Homeostasis refers to the regulation of a stable internal environment in living things, from single-celled organisms to complex multi-cellular organisms. It involves maintaining optimal conditions like temperature, pH levels, and nutrient intake.
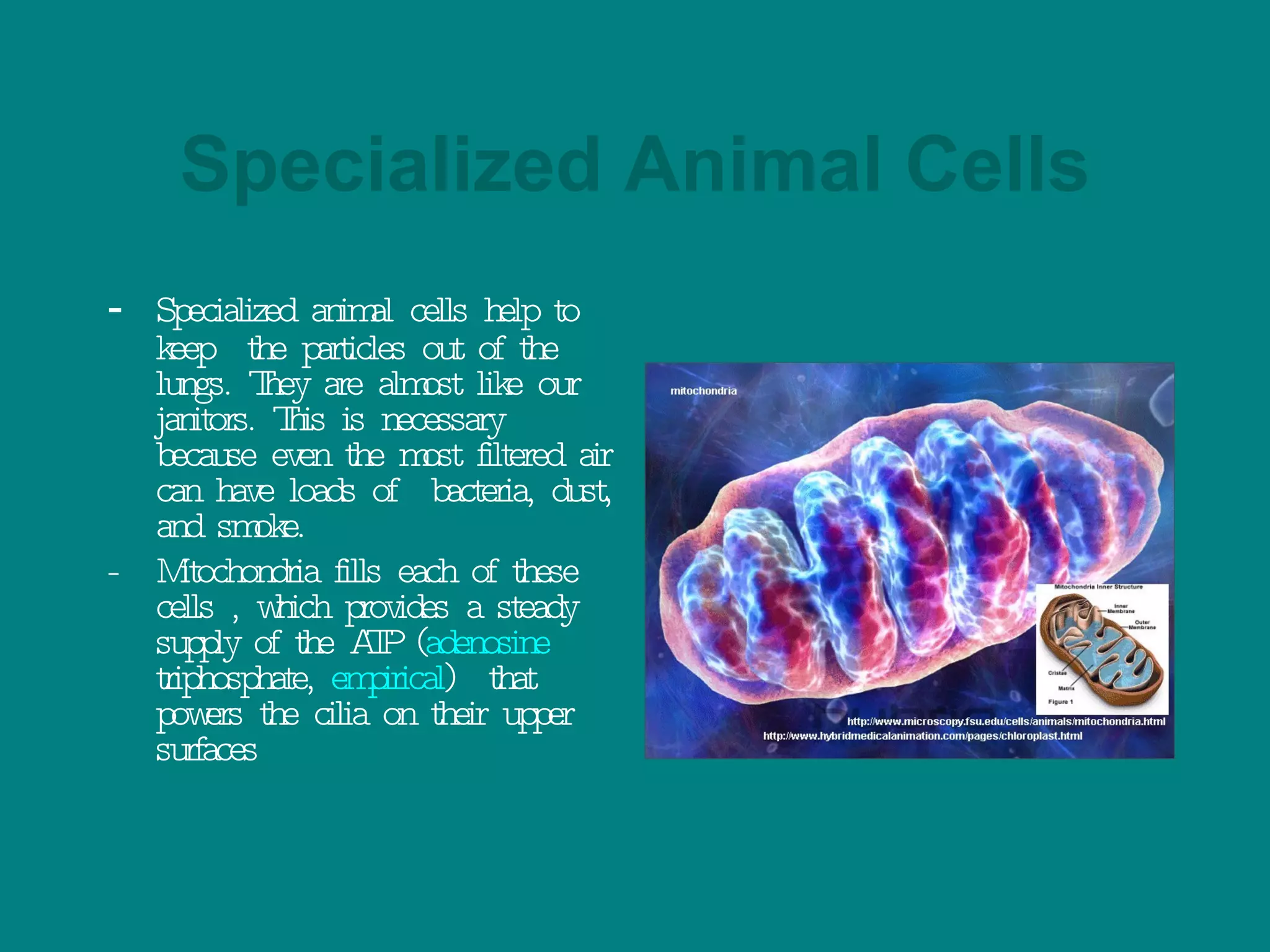
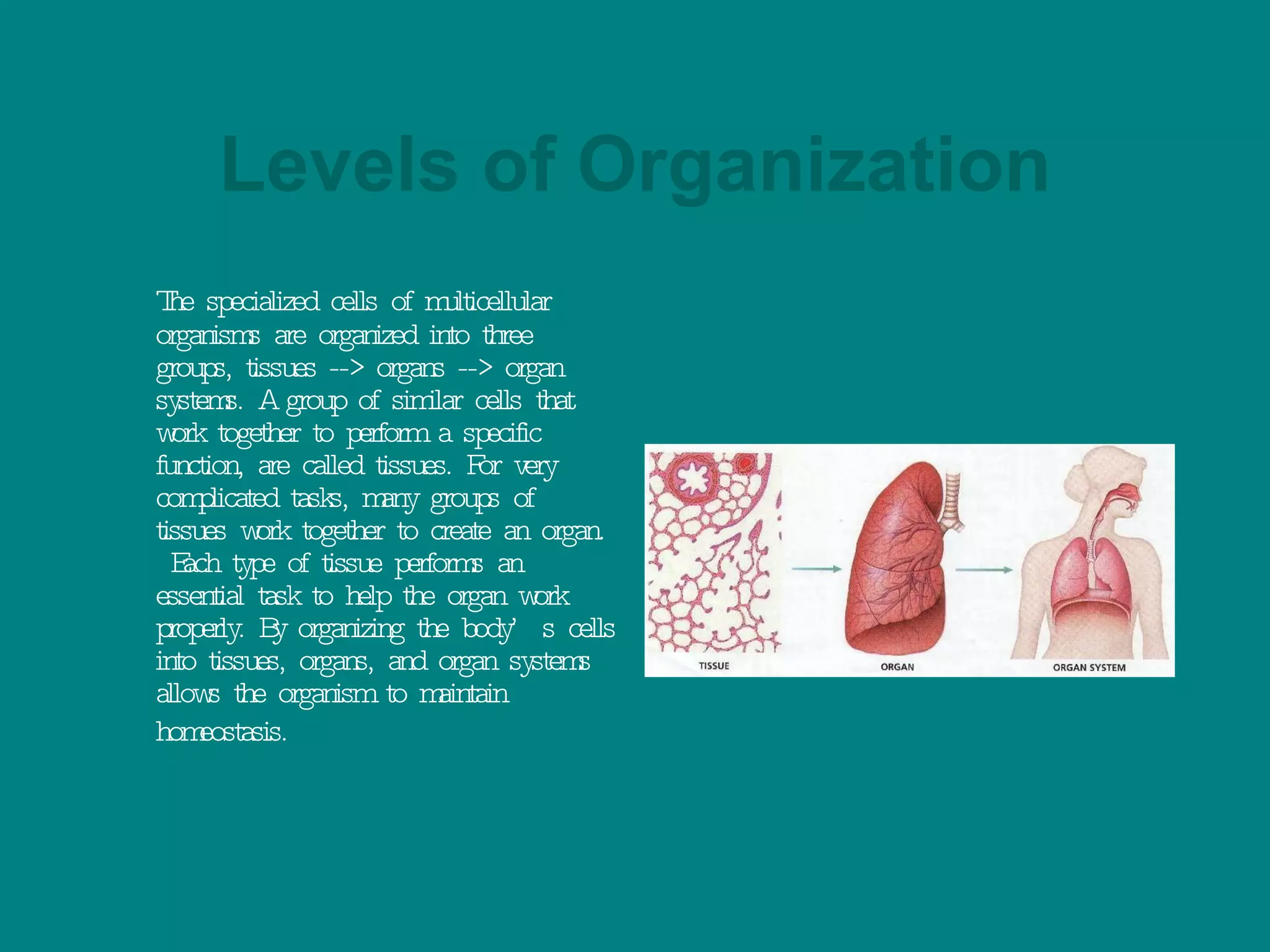
2. Both single-celled and multi-cellular organisms rely on cellular specialization and communication to maintain homeostasis. In multi-cellular organisms, specialized cells perform distinct functions that collectively support the whole organism.
3. Cellular communication allows cells to coordinate their activities through chemical signaling. This enables a dynamic response to internal or external changes and helps organisms preserve homeostasis.