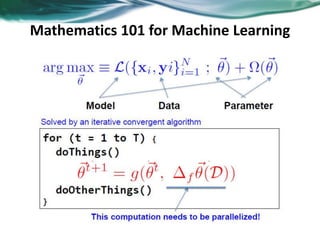
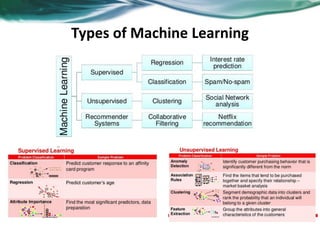
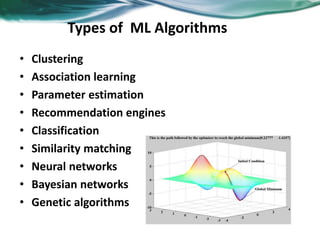
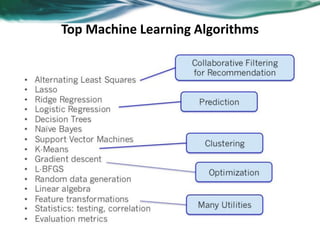
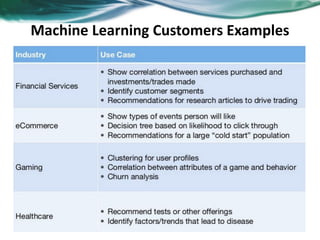
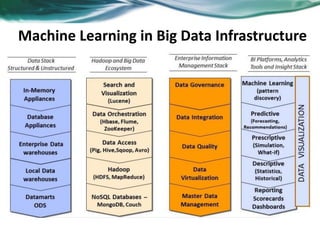
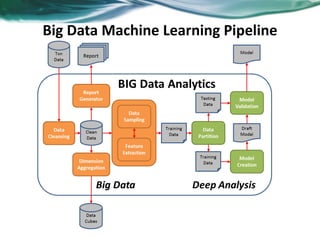
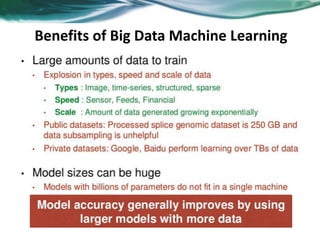
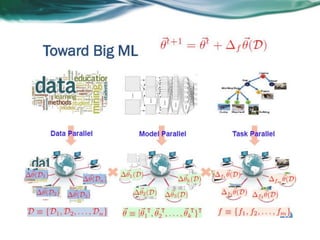
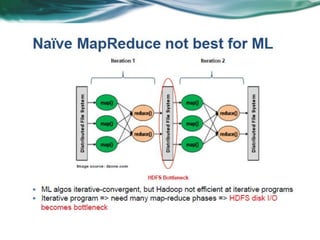
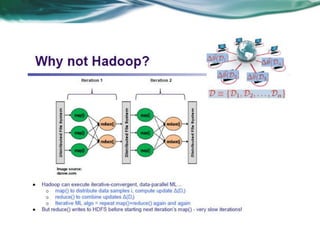
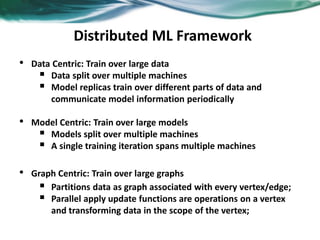
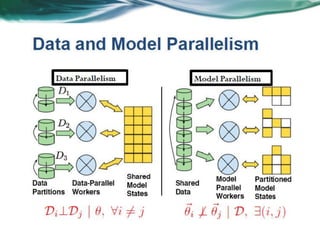
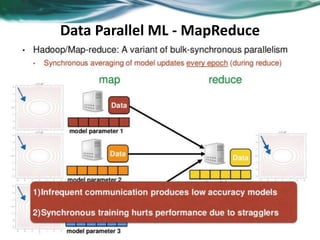
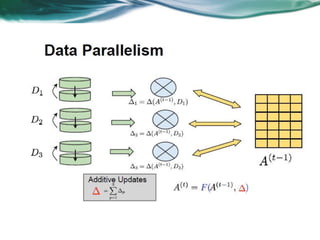
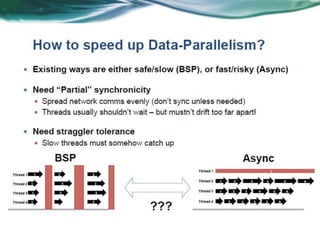
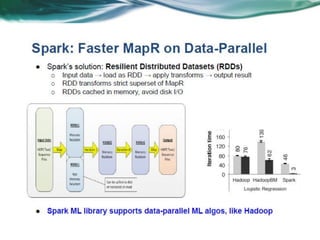
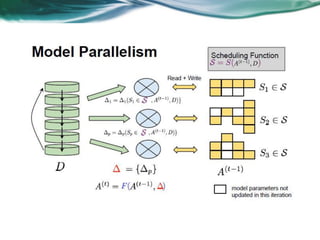
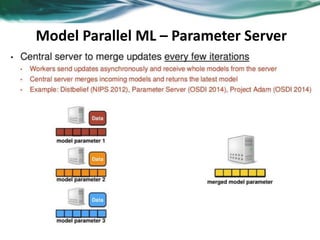
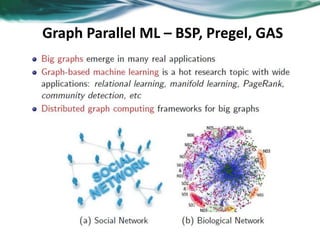
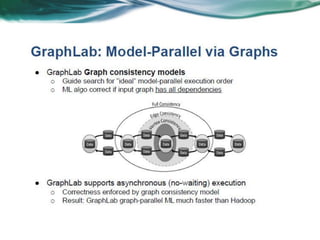
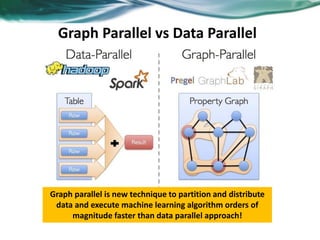
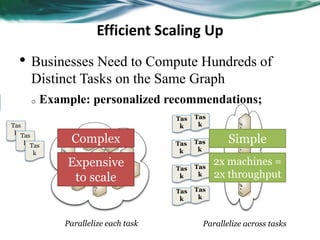
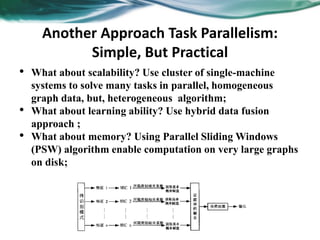
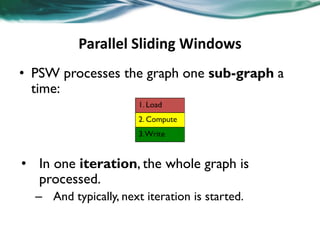
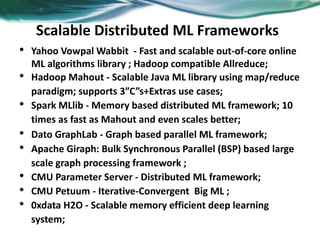
Machine learning can be distributed across multiple machines to allow for processing of large datasets and complex models. There are three main approaches to distributed machine learning: data parallel, where the data is partitioned across machines and models are replicated; model parallel, where different parts of large models are distributed; and graph parallel, where graphs and algorithms are partitioned. Distributed frameworks use these approaches to efficiently and scalably train machine learning models on big data in parallel.