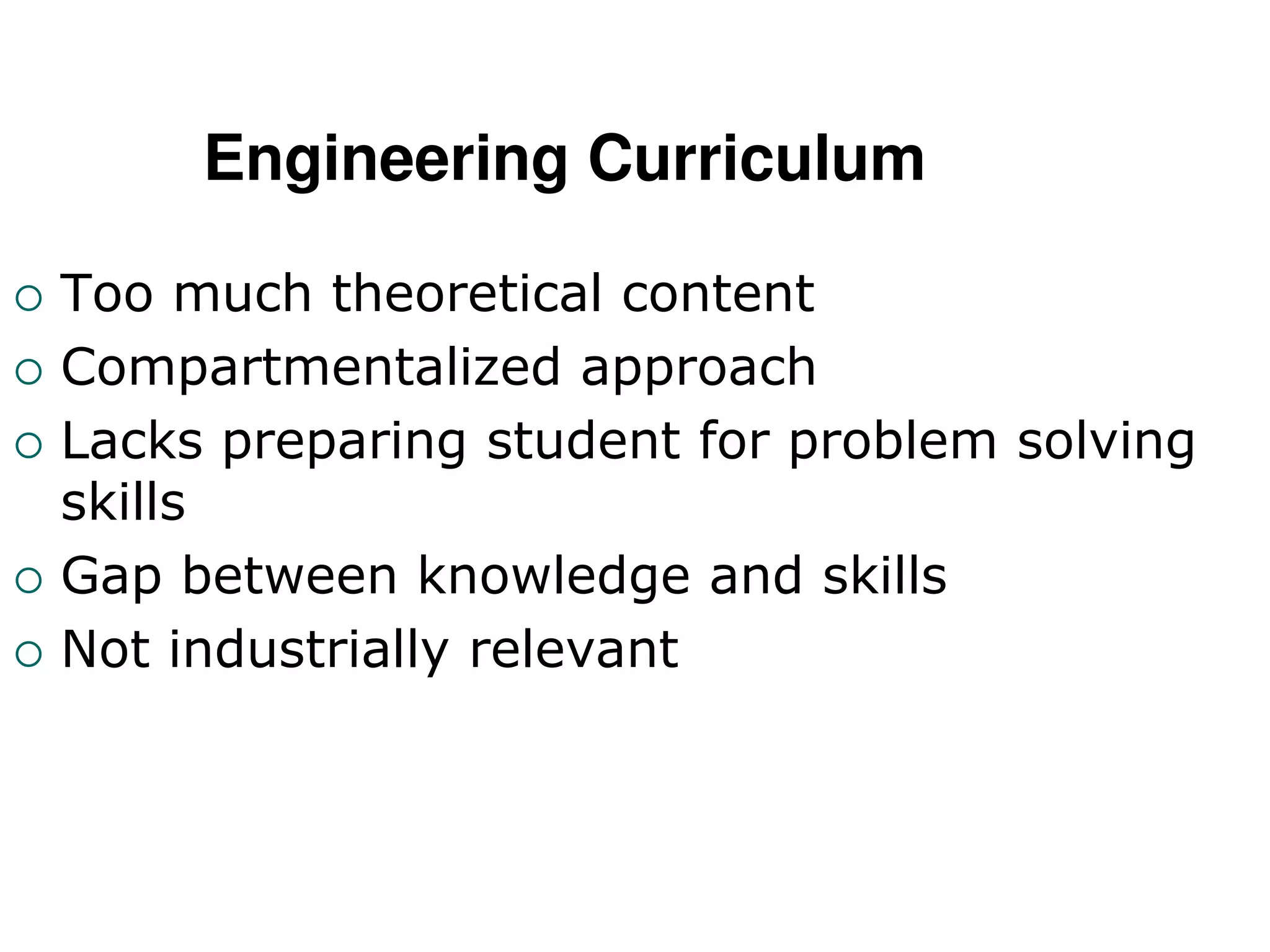
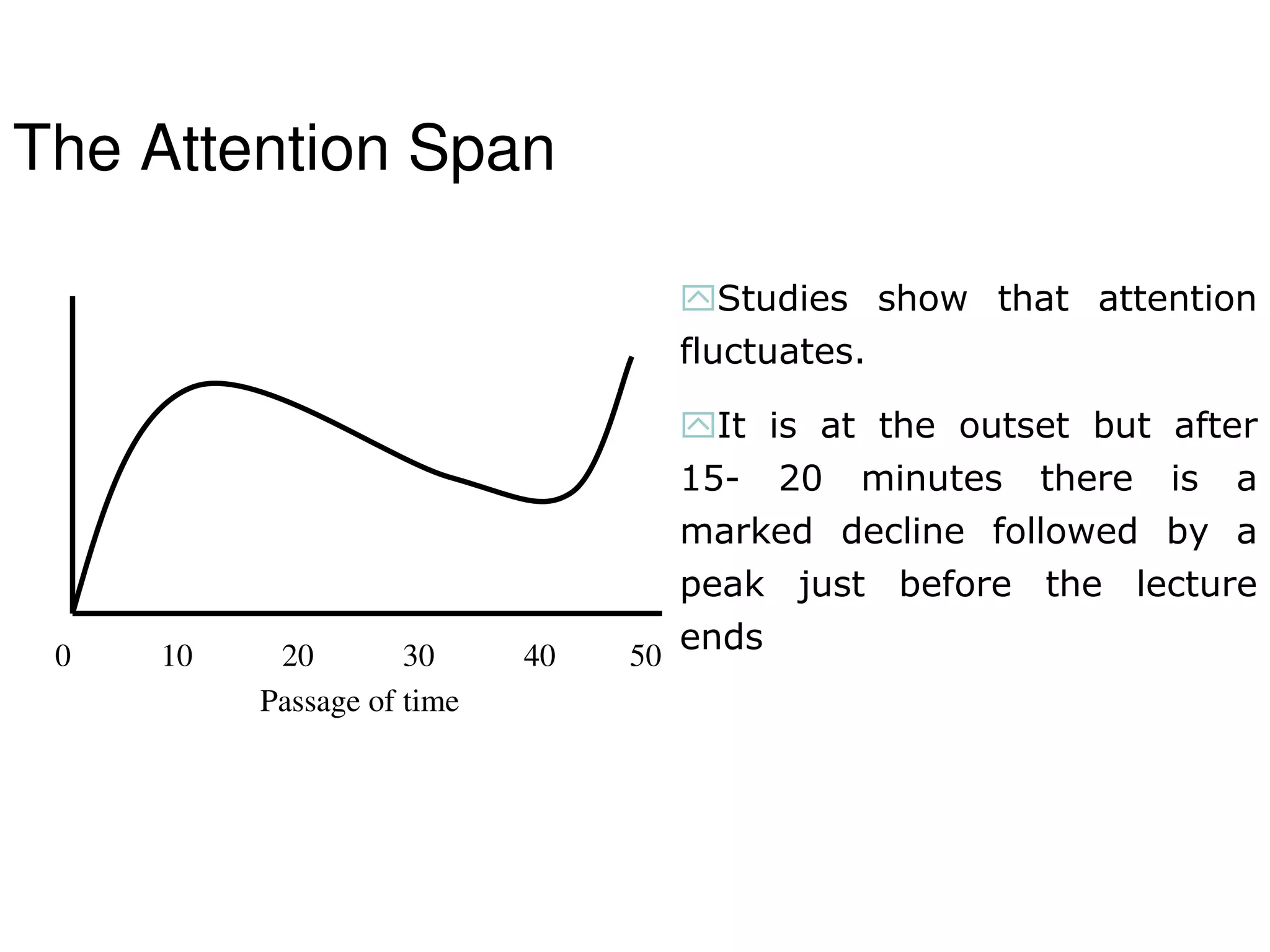
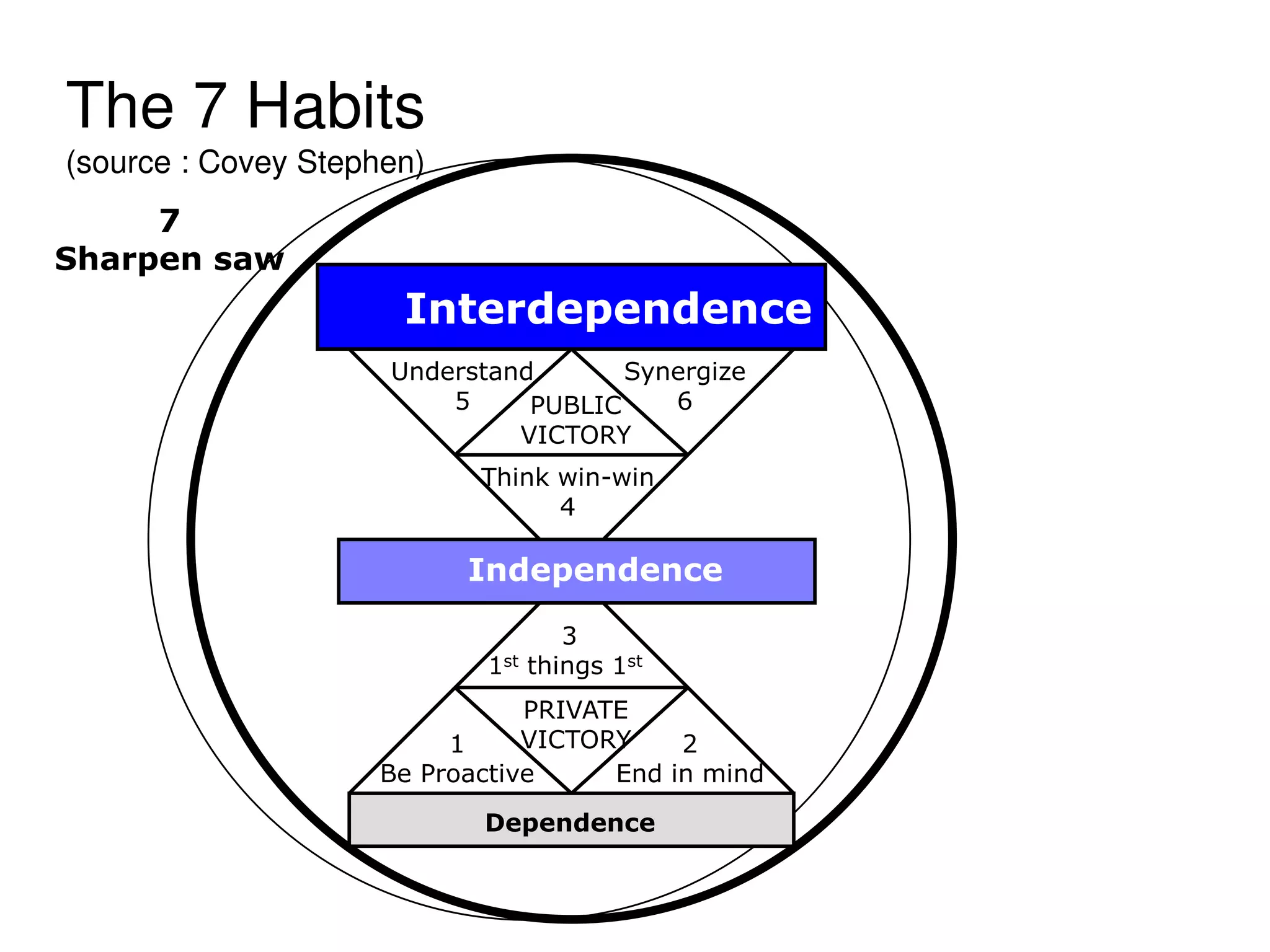
The document discusses the changing landscape of higher education and the role of teachers. It notes that quality in education is increasingly important globally. Teachers now face challenges like students with short attention spans who are used to technology. The curriculum also needs to better align with industry needs. Teachers must adapt to these changes by using new technologies, varying teaching methods, and focusing on interactive learning. They should act as facilitators and help students construct knowledge through collaboration. The key is for teachers to continuously learn and adapt their skills and teaching styles to remain relevant in the current environment.