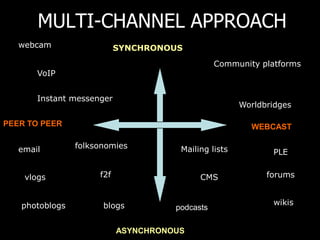
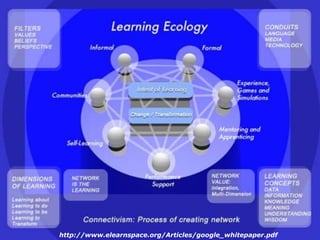
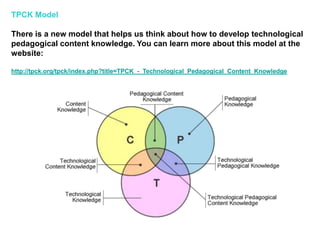
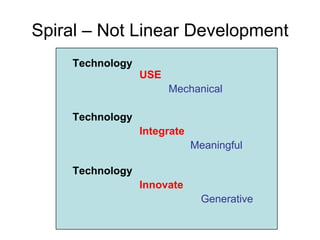
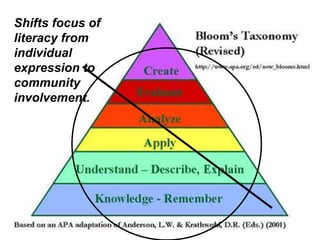
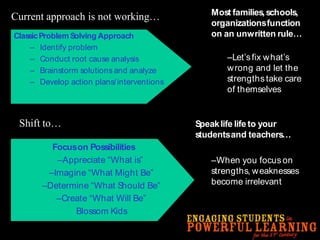
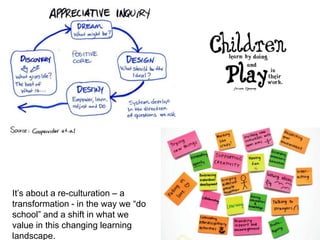
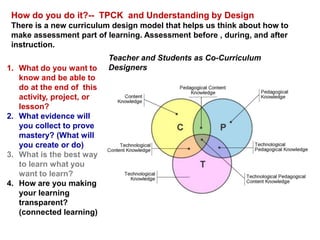
This document discusses the need to unlearn traditional approaches to teaching and learning and adopt more modern, student-centered pedagogies. It highlights moving from deficit-based to strength-based learning, collaboration both inside and outside the classroom, and using multiple channels including both synchronous and asynchronous tools. The document also emphasizes that effective technology integration depends on the teaching approaches used and that the focus should be on learning rather than the technology itself.