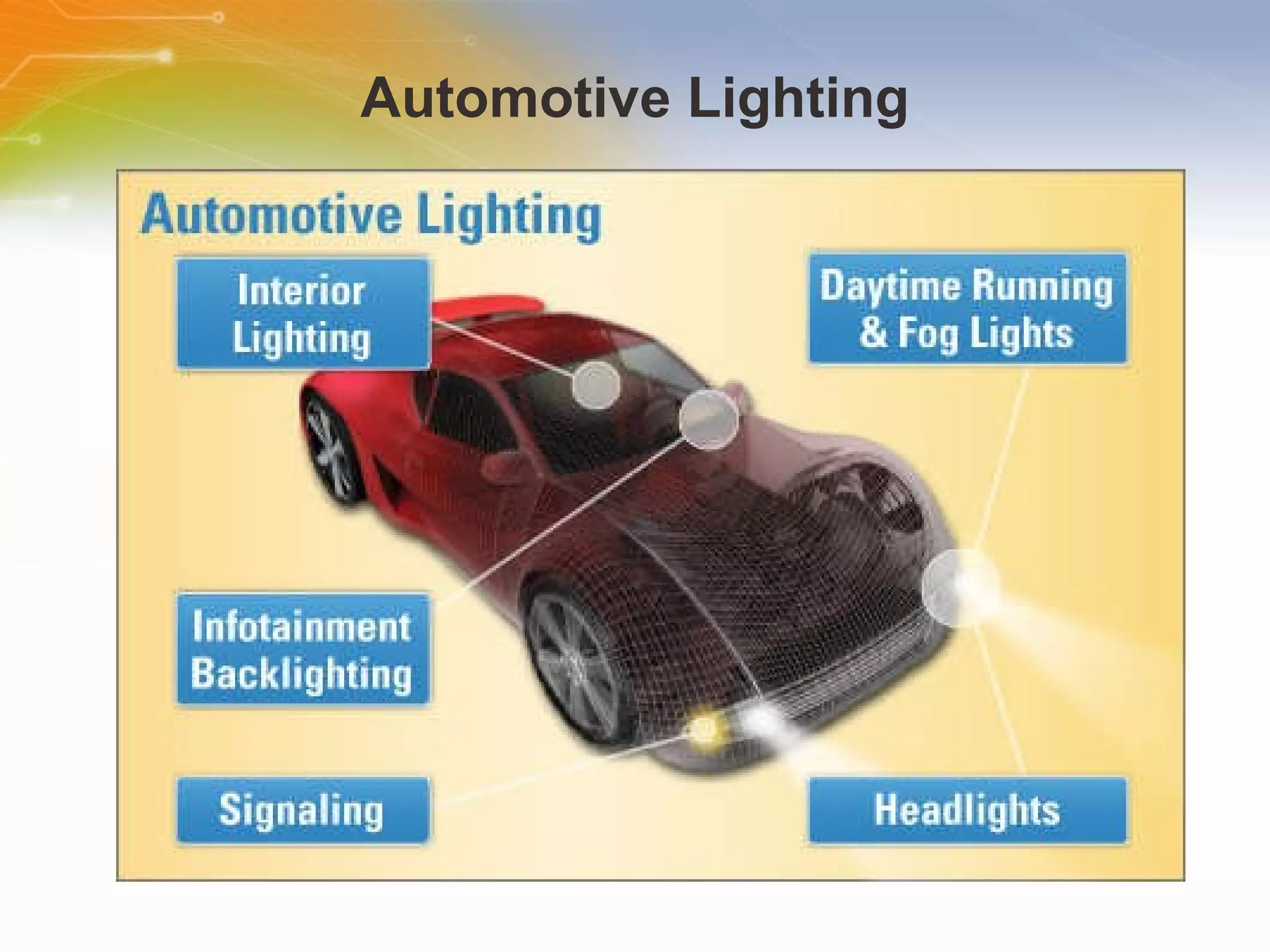
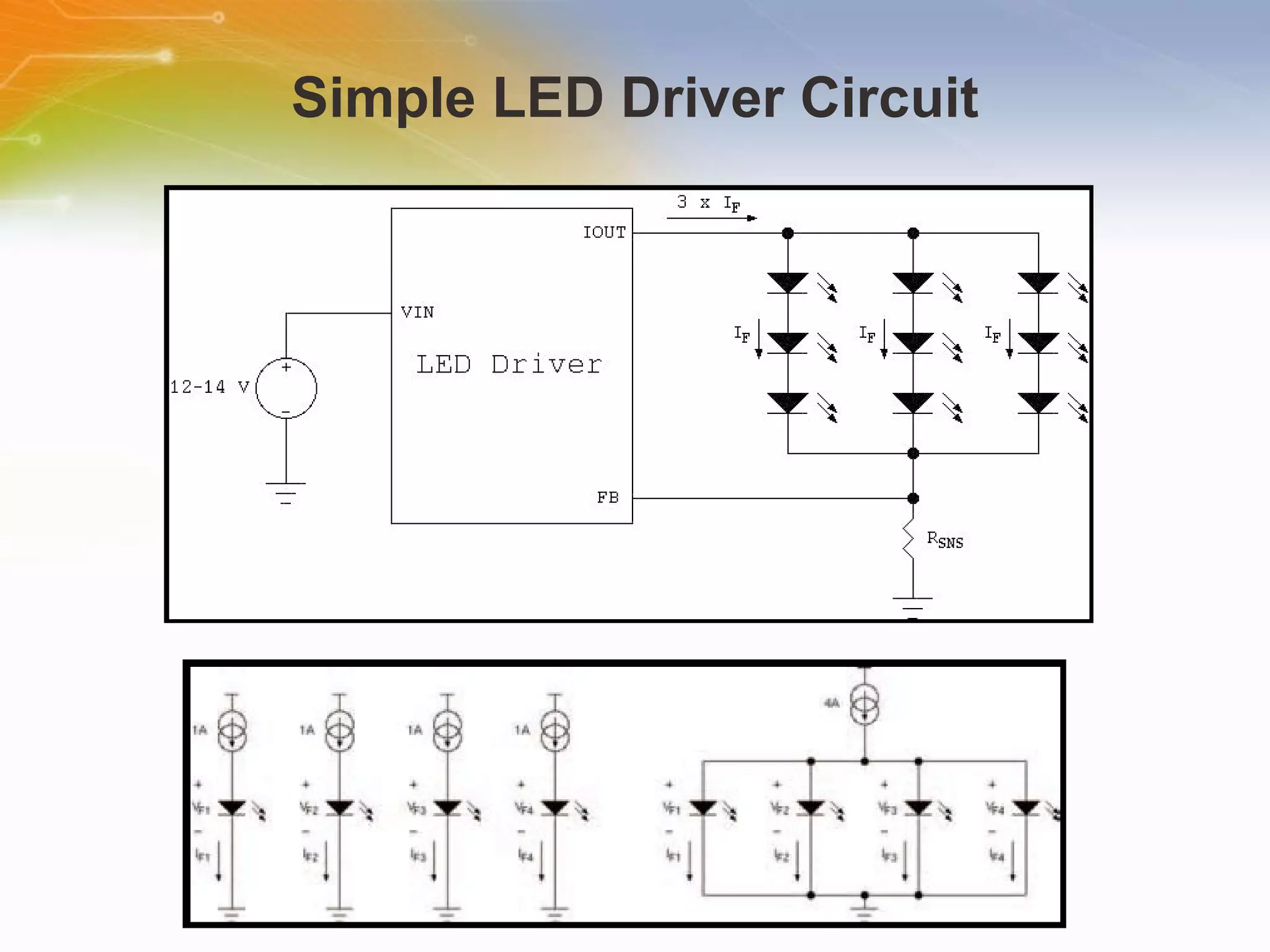
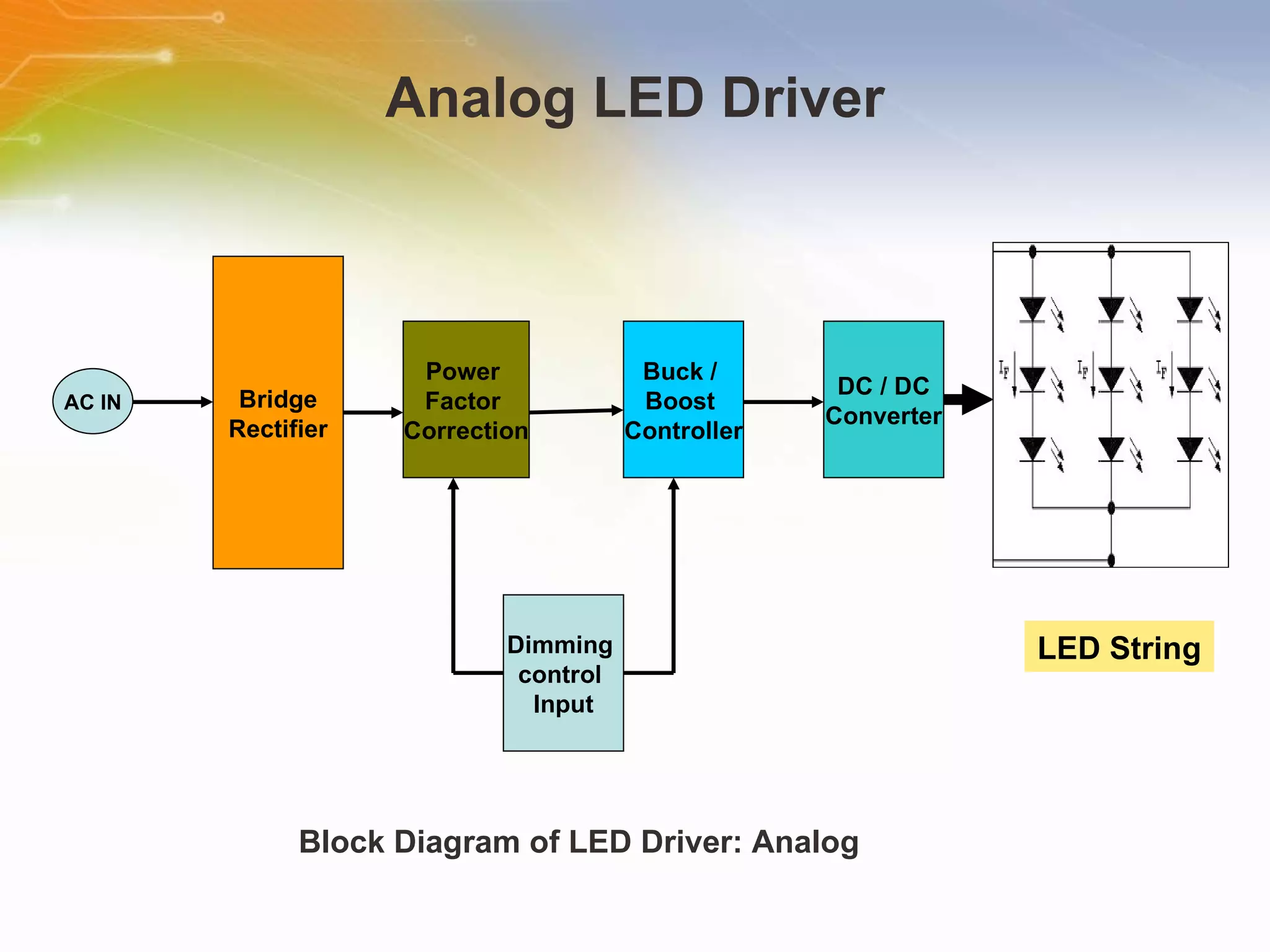
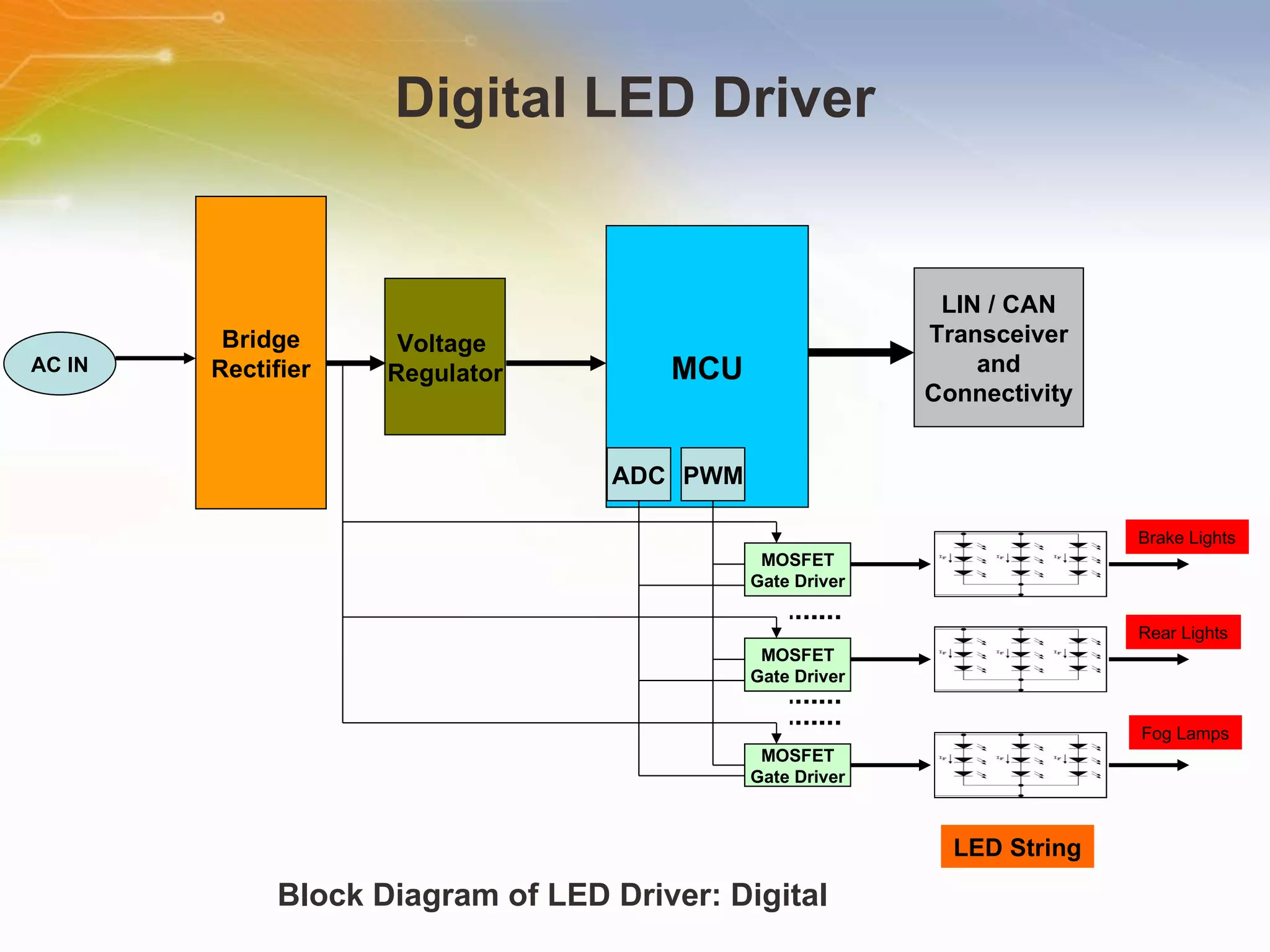
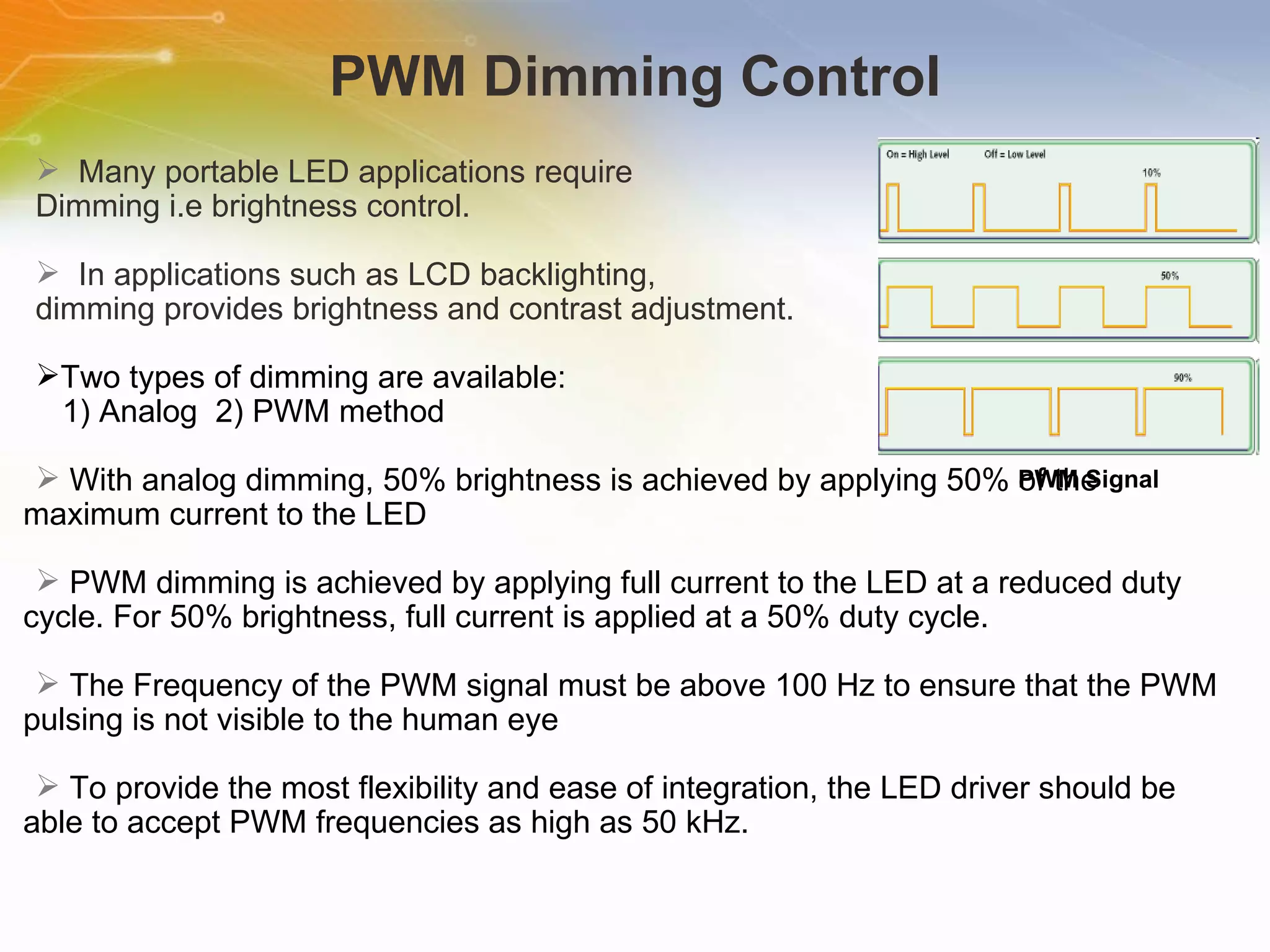
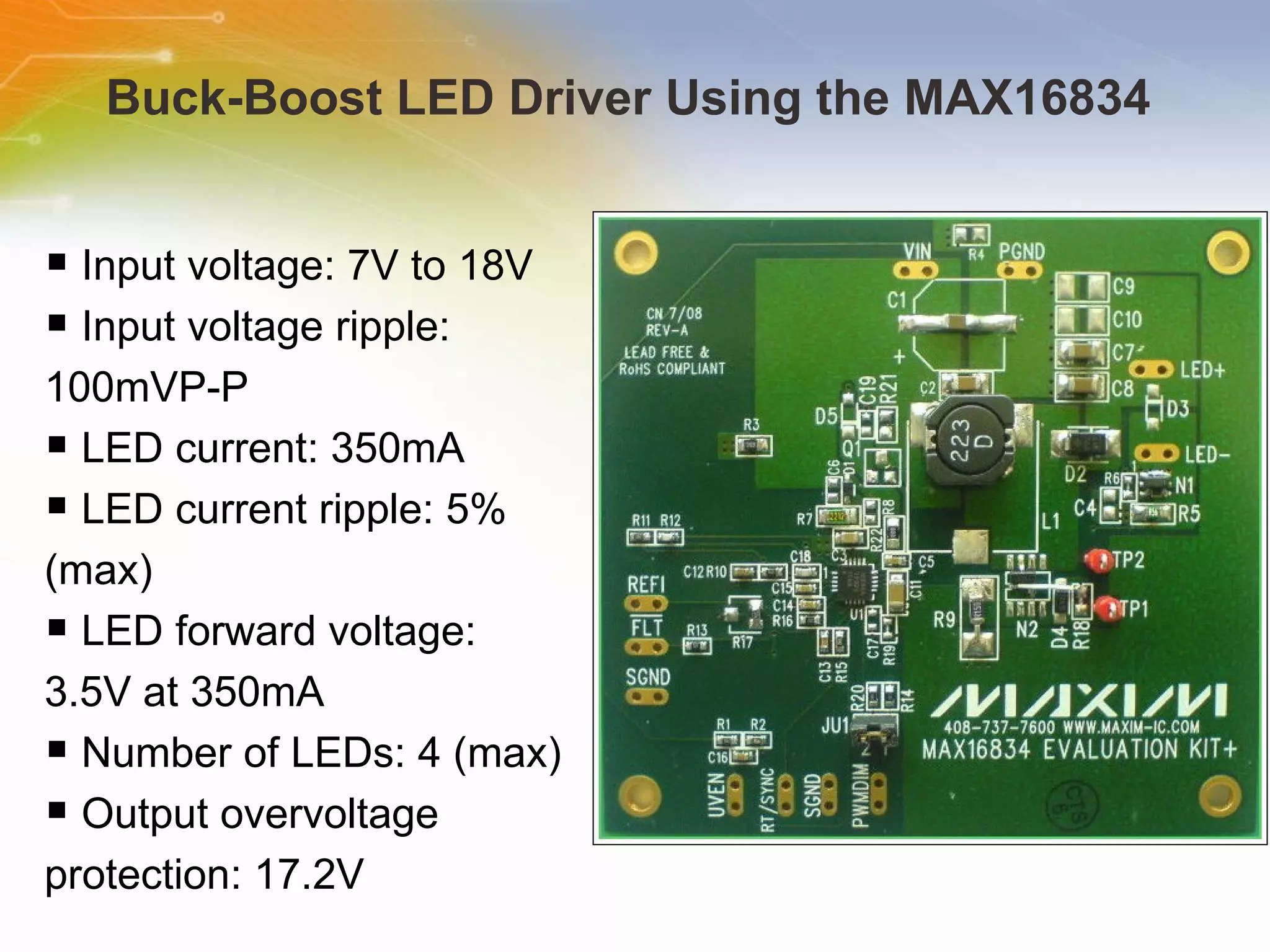
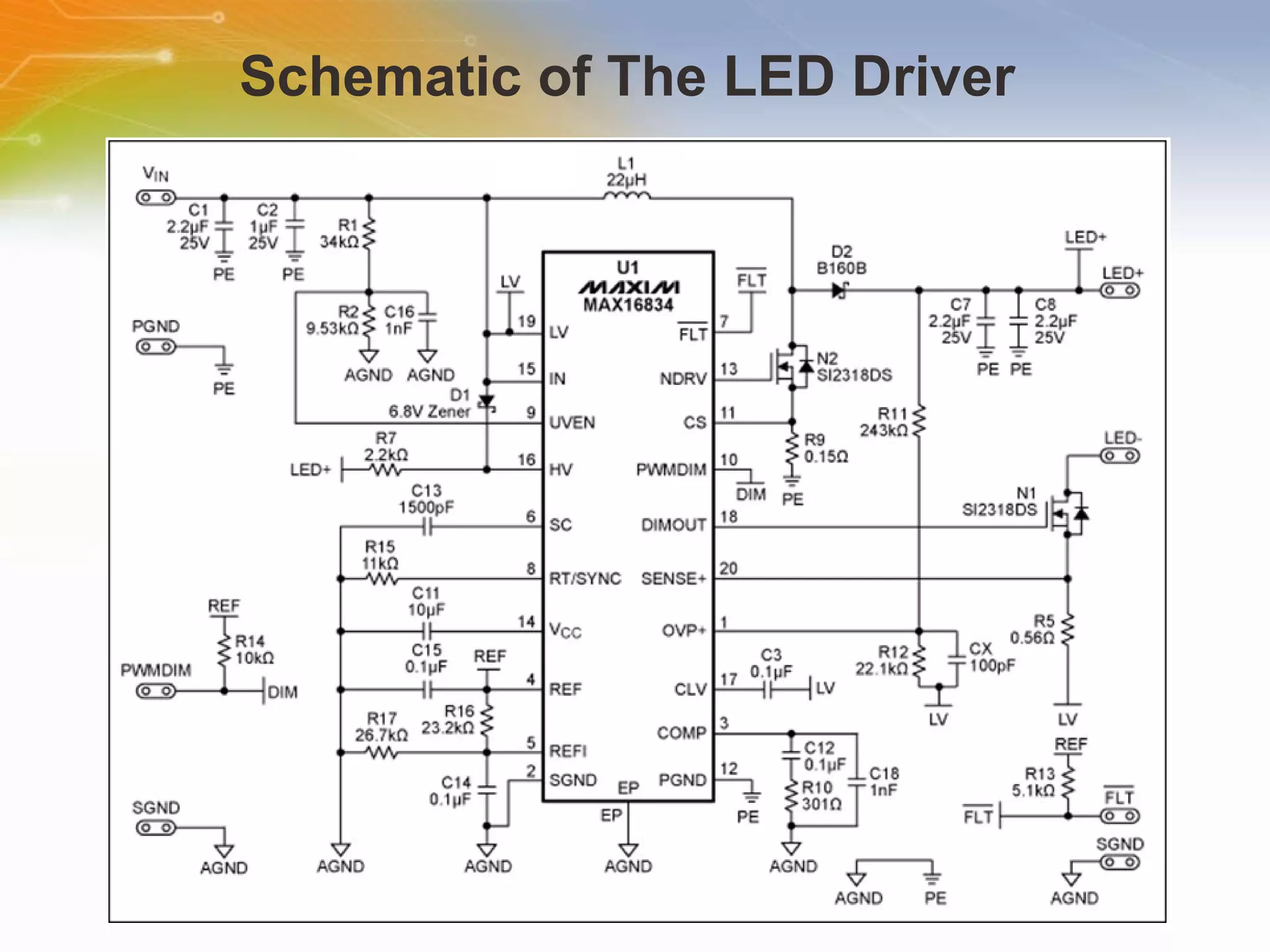
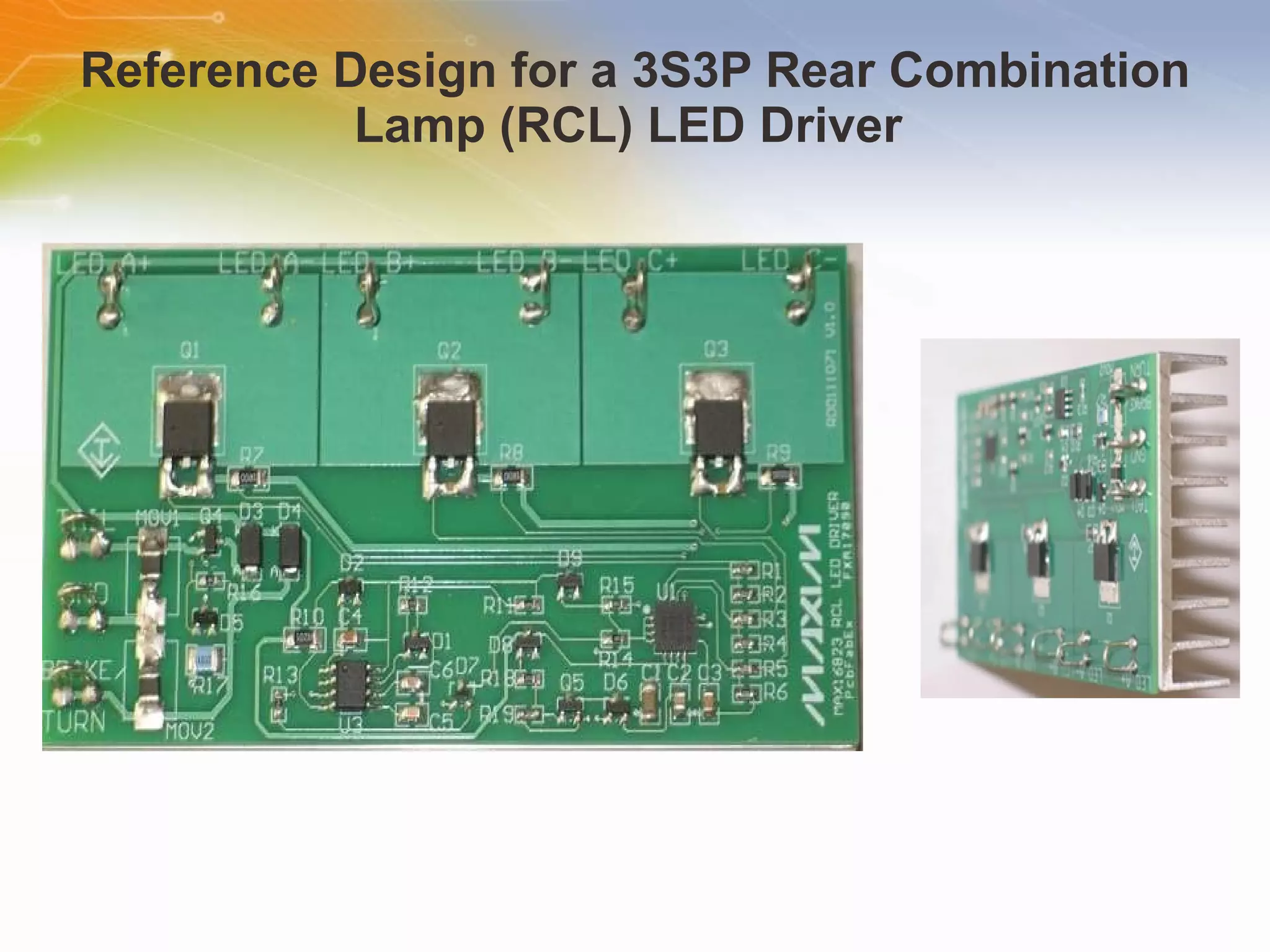
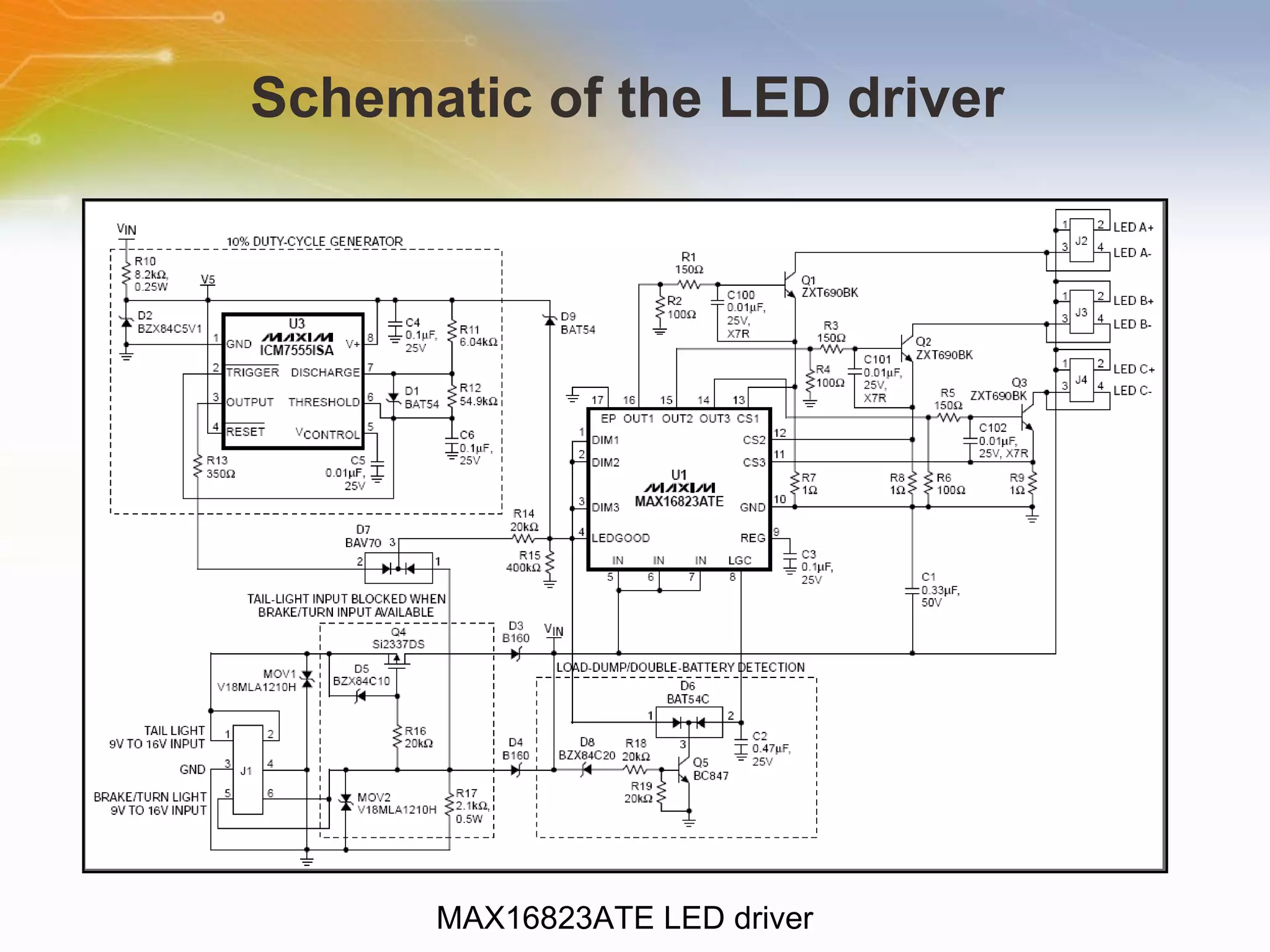
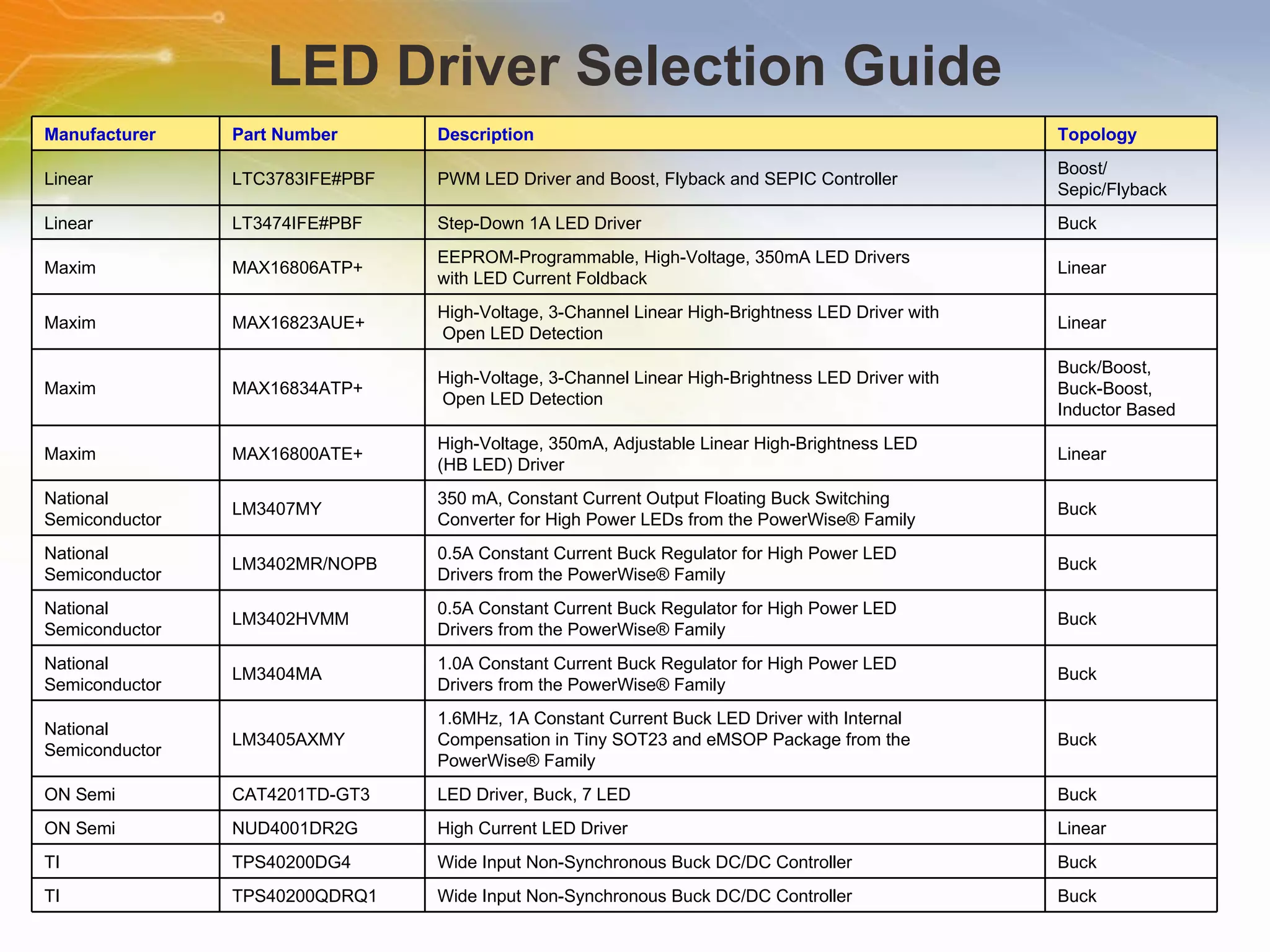
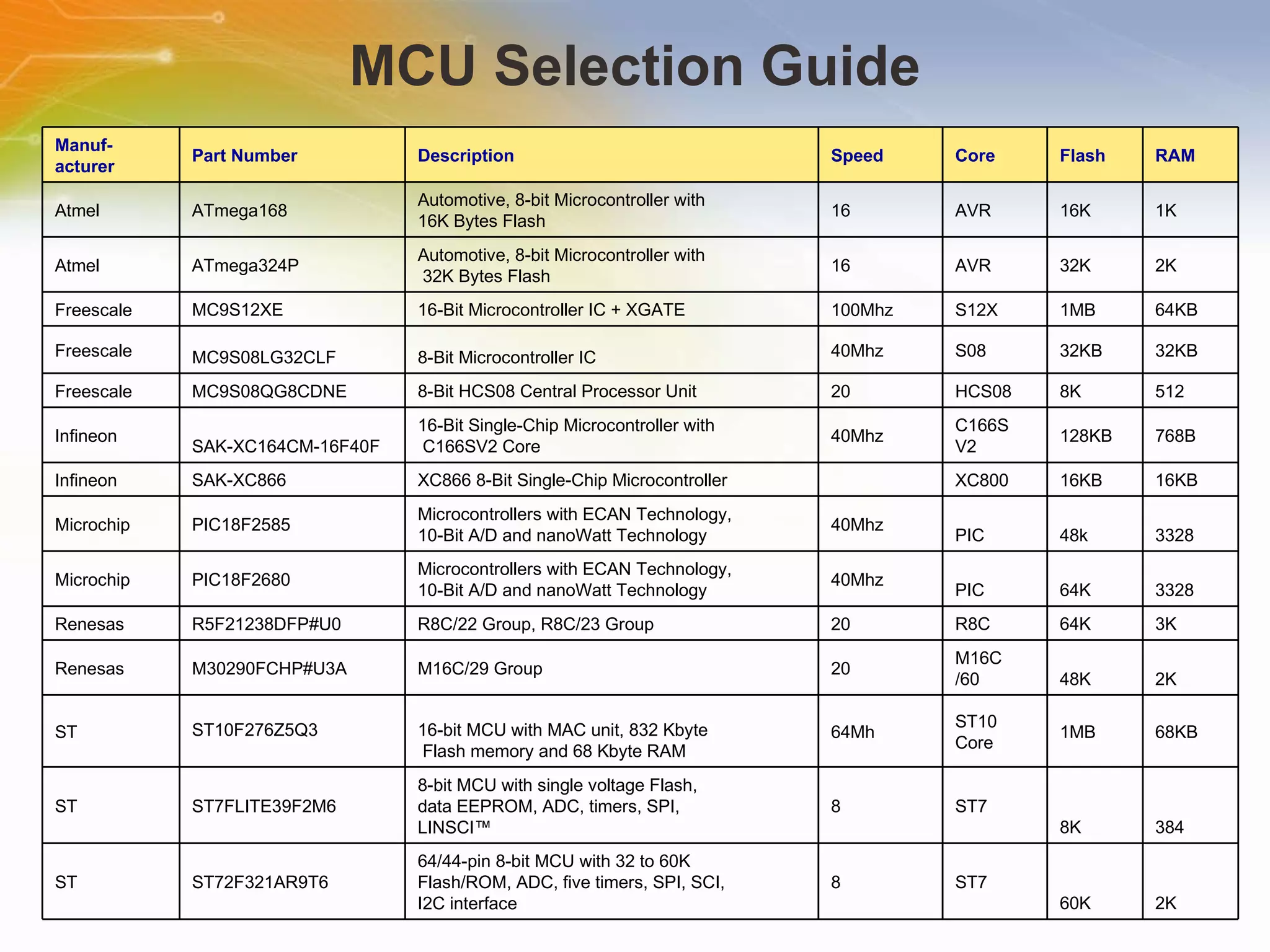
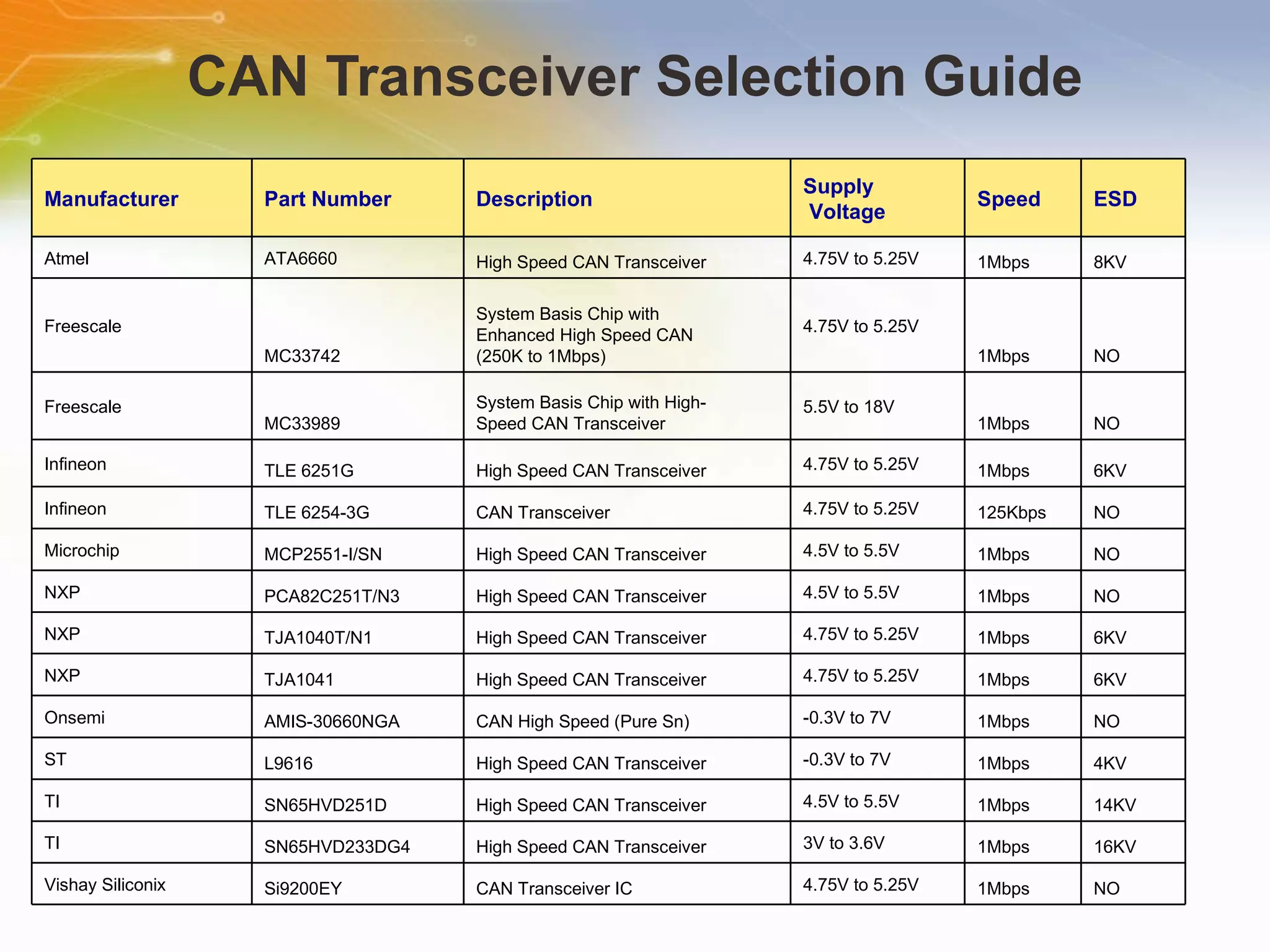
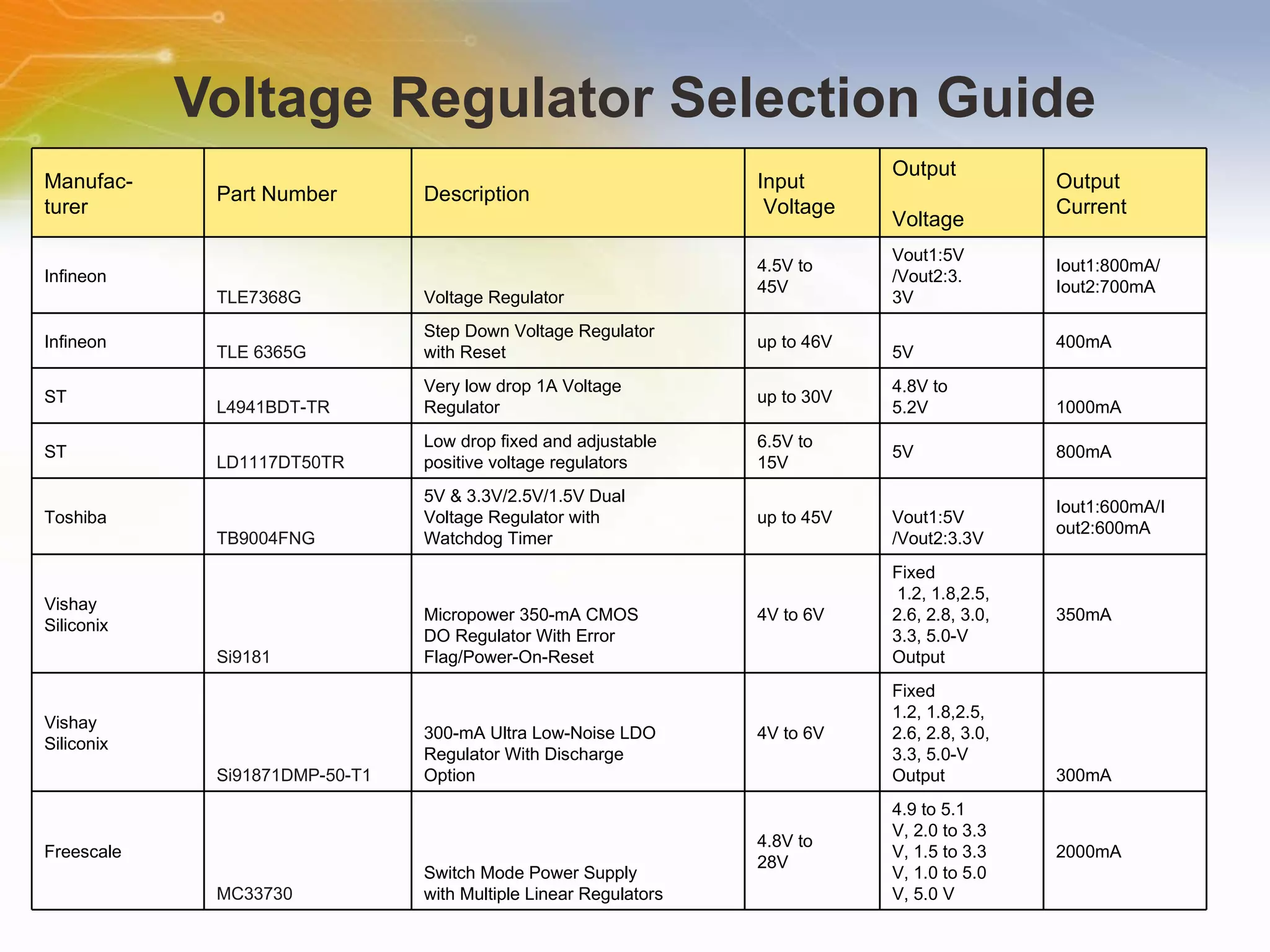
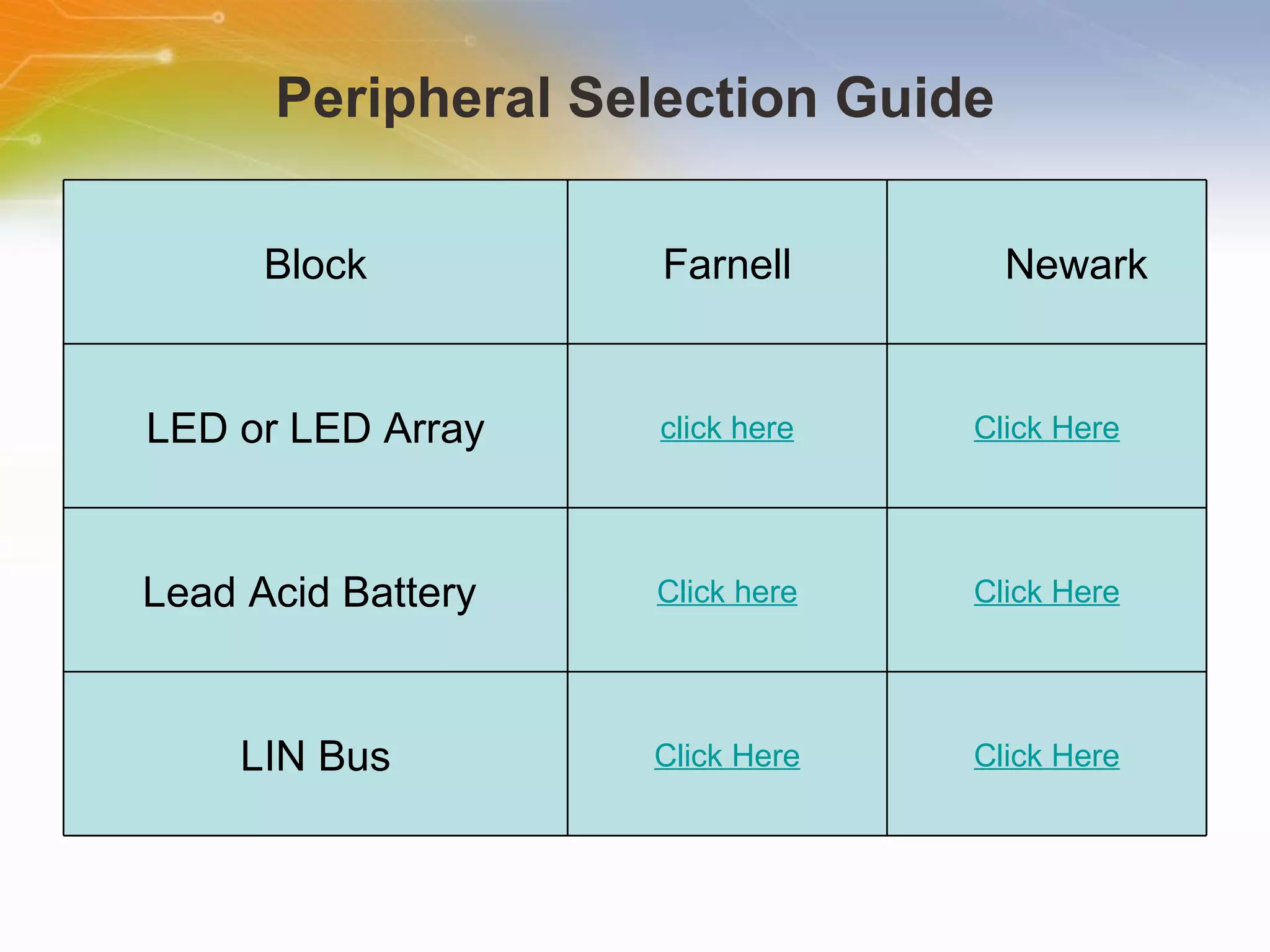
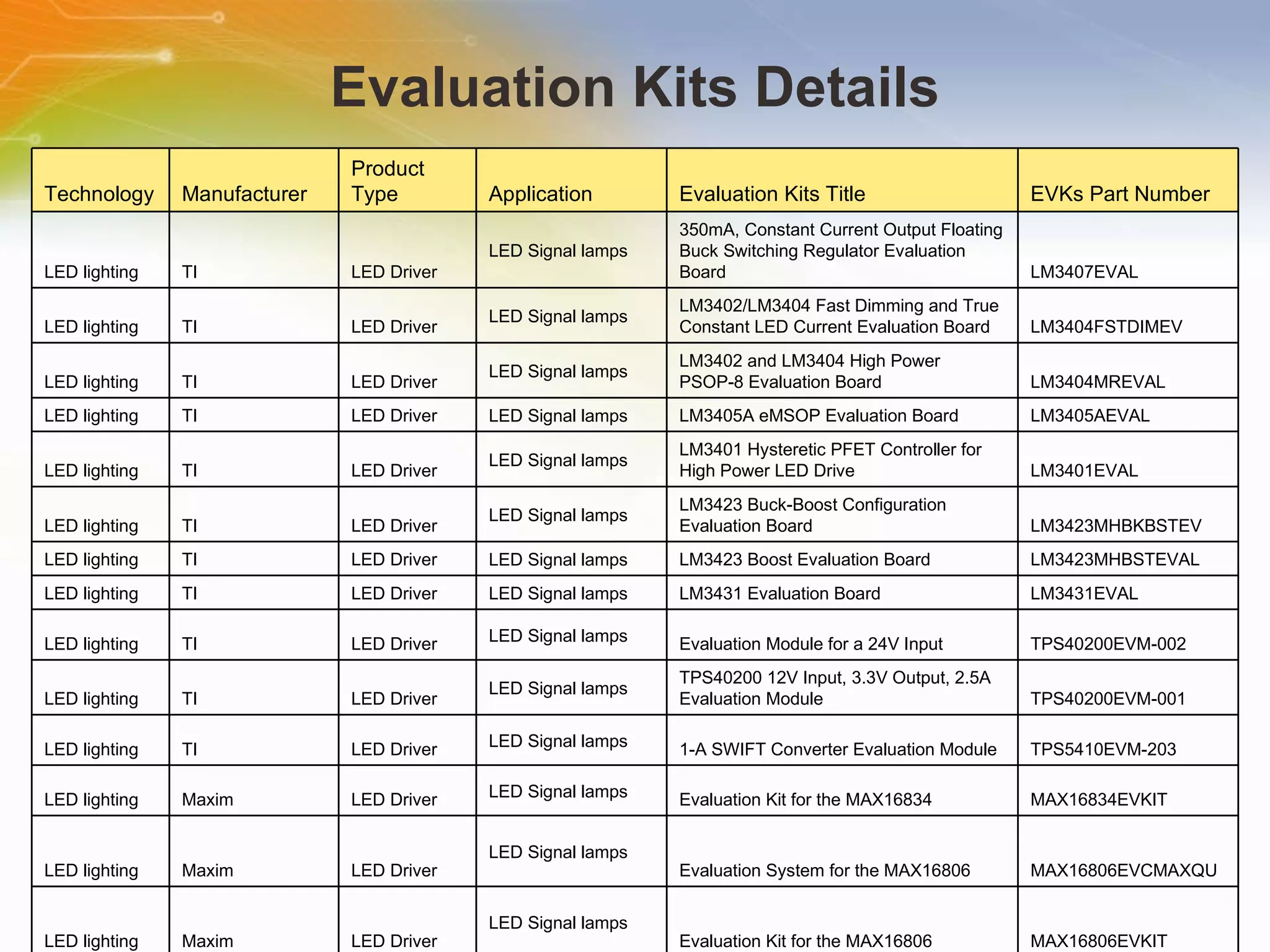
The document provides information on LED solutions for automotive lighting, including an overview of analog and digital LED driver circuits, PWM dimming techniques, buck-boost LED driver design examples using Maxim integrated circuits, and selection guides for MCUs, CAN transceivers, voltage regulators, and peripheral components suitable for automotive LED applications. Evaluation kits are also listed from manufacturers like Texas Instruments and Maxim for testing LED driver circuits.