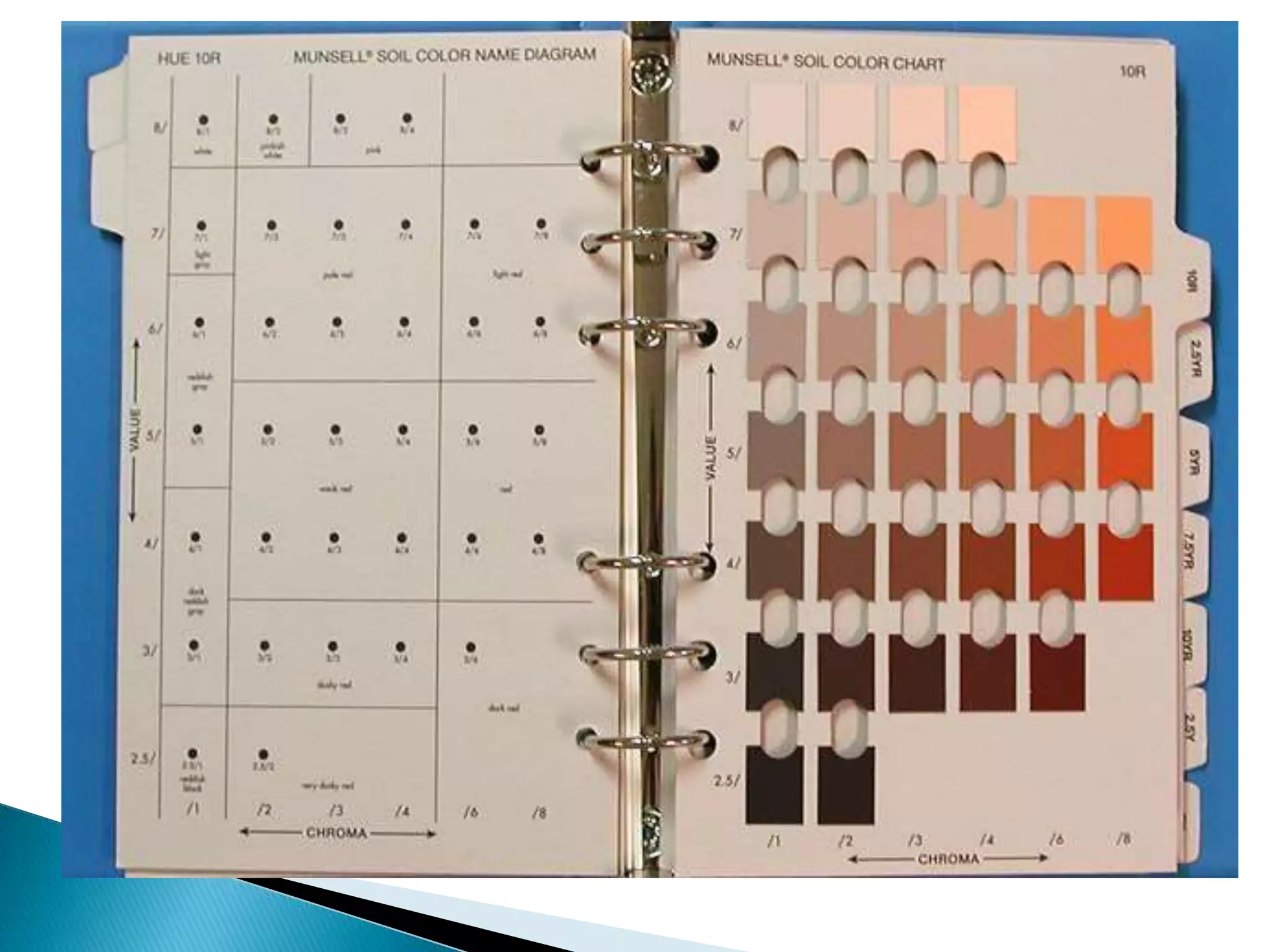
The document discusses the physical properties of soil, including its formation from weathering rocks, composition of solid, liquid, and gas phases, texture determined by sand, silt and clay content, structure defined by arrangement of particles, density, porosity, temperature, and classification of soil water. Key topics covered are the three phases of soil, factors influencing soil color, common soil structures like platy and granular, and definition of terms like bulk density, field capacity, and permanent wilting point.