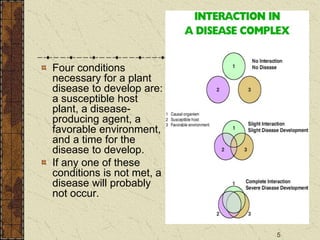
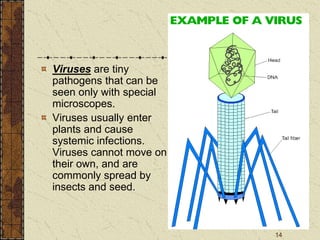
Four conditions are necessary for a plant disease to develop: a susceptible host plant, a disease-producing agent, a favorable environment, and time for the disease to develop. Plant diseases are classified as either noninfectious or infectious. Noninfectious diseases are caused by environmental factors while infectious diseases are caused by living pathogens. Methods to control plant diseases include disease avoidance, disease tolerance, and cultural controls like crop rotation, tillage, and weed control. Successful disease management strategies consider both reducing current crop losses and future plantings through integrating control methods and understanding disease development.