This document discusses different types of soil structures:
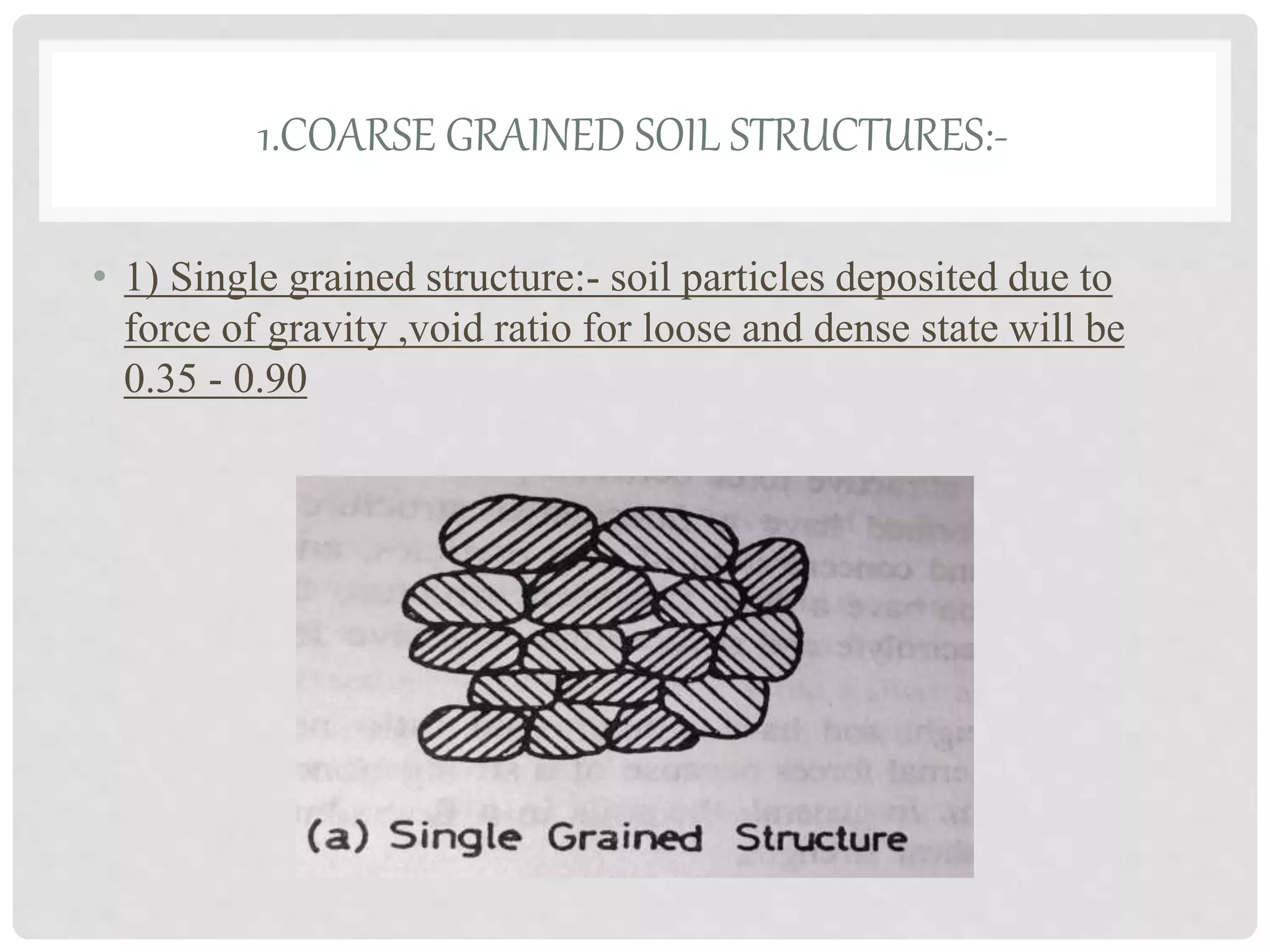
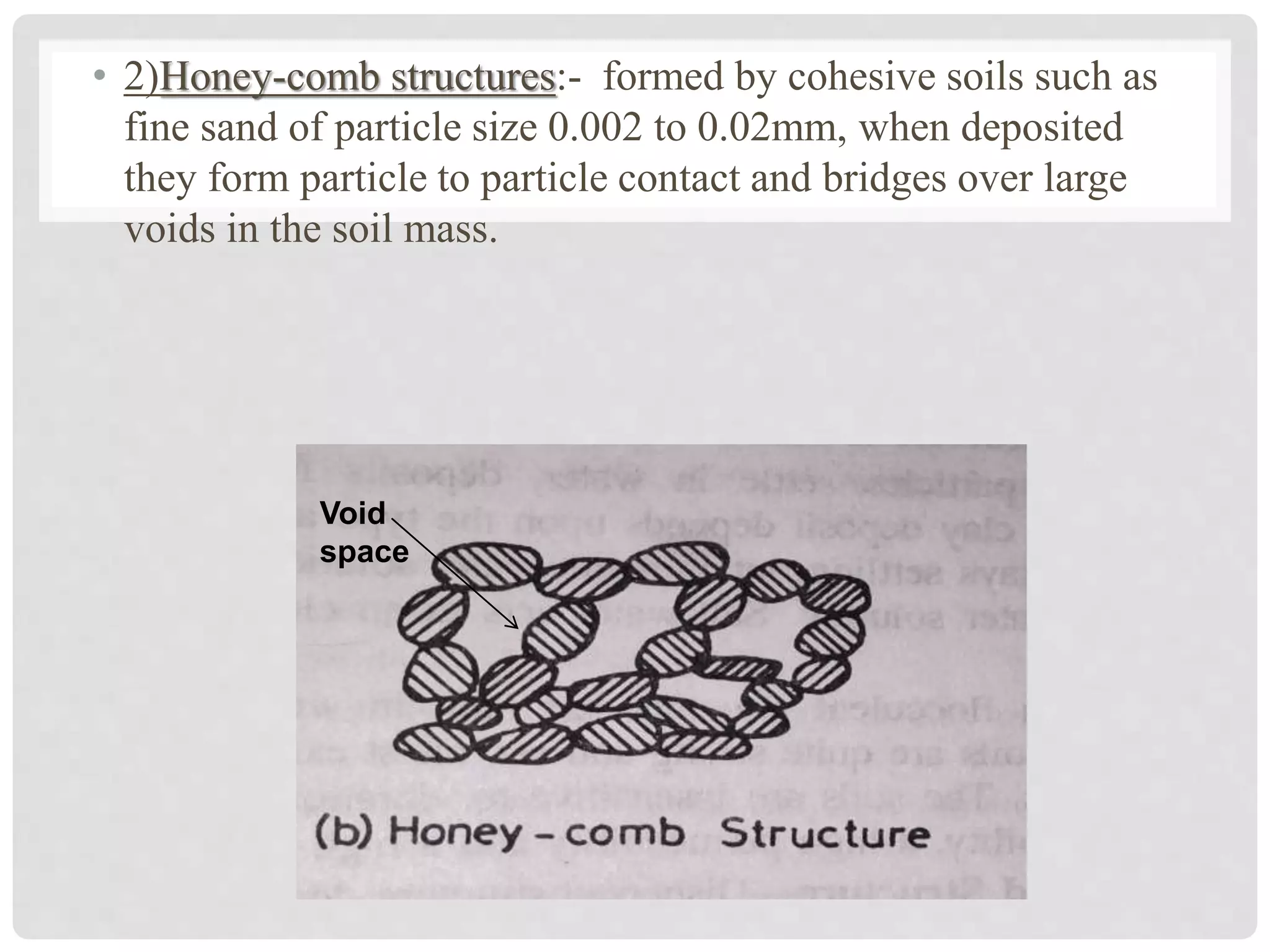
1. Coarse-grained soil structures include single grained structures where particles are deposited by gravity and honeycomb structures formed by fine sand particles.
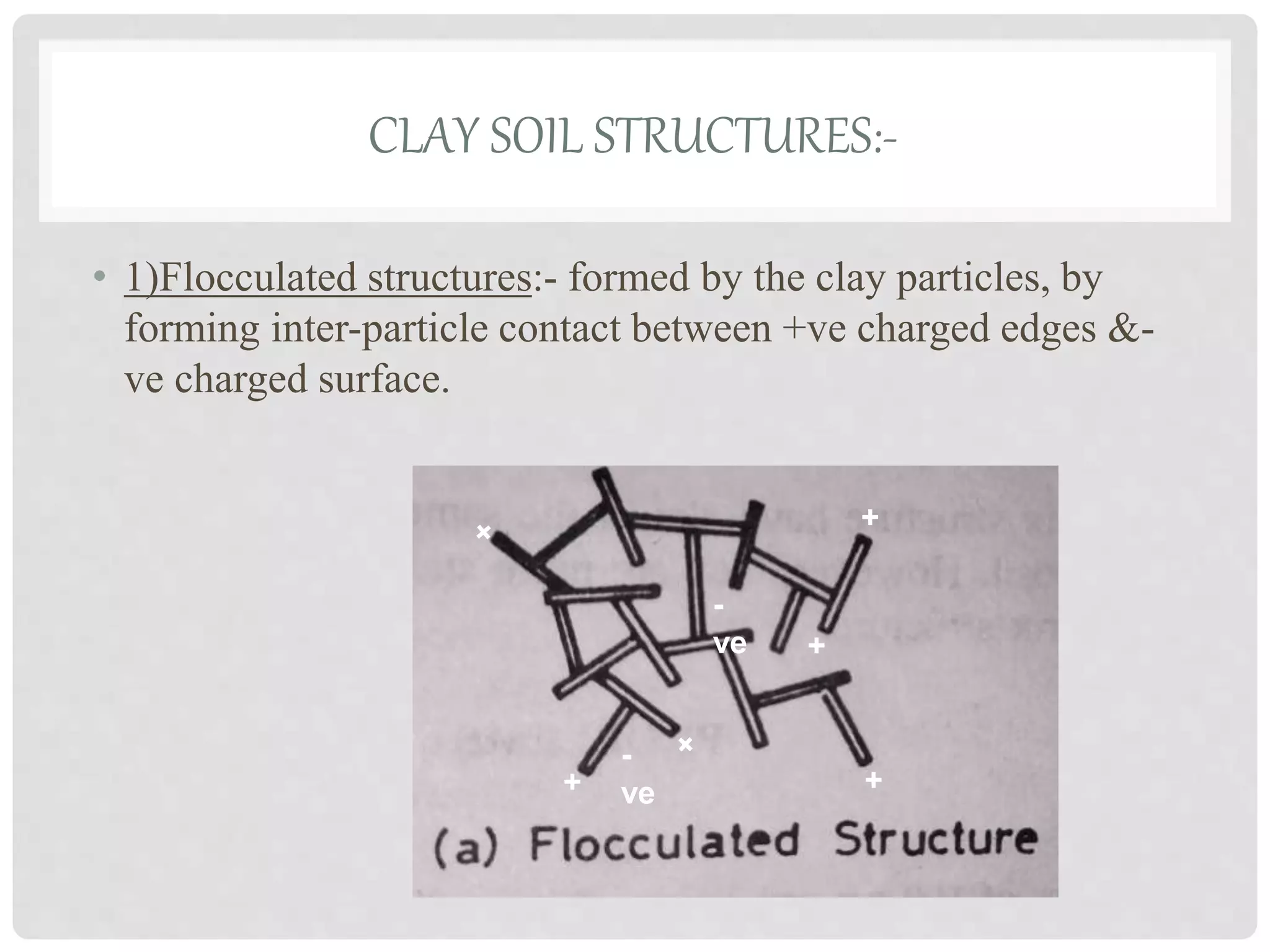
2. Clay soil structures include flocculated structures formed by clay particle contact and dispersed structures formed by remolding.
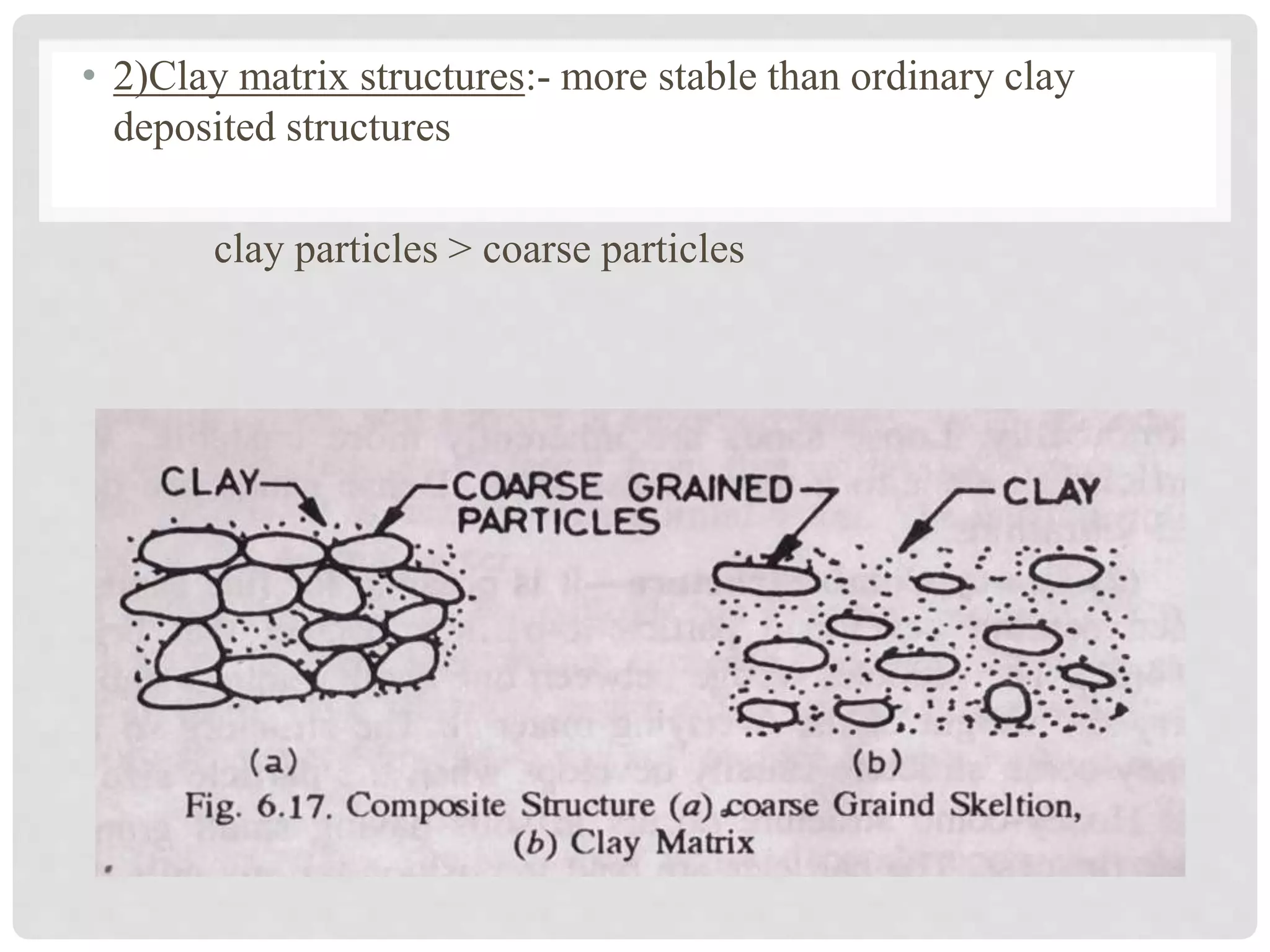
3. Mixed soil structures include coarse-grained skeleton structures with bulky particles and clay matrix structures with more clay than coarse particles.