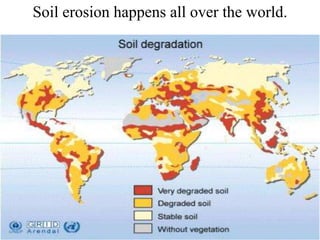
This document summarizes a seminar on soil science and soil erosion. It discusses various causes and types of soil erosion including water erosion, wind erosion, and erosion caused by animals. Water erosion is discussed in more detail, outlining different types from rain splash erosion to gully erosion. The document also addresses how human activities like deforestation, overgrazing, and bad farming practices can increase soil erosion. Finally, it provides some solutions for reducing soil erosion such as contour farming, no-till farming, reseeding plants and trees, and retaining walls.