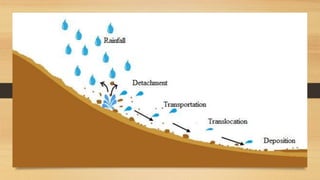
The document discusses erosion, specifically water and wind erosion, detailing the processes by which soil is moved and the types of erosion like splash, sheet, rill, and gully erosion, while emphasizing the need for effective control measures. It also covers deforestation, highlighting its causes, particularly agricultural expansion and urbanization, and the negative impacts on ecosystems, biodiversity, and climate. Potential solutions to combat deforestation are provided, encouraging individual actions like tree planting and supporting sustainable products.