Embed presentation
Downloaded 101 times





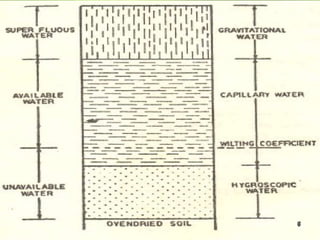

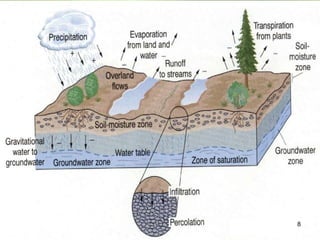







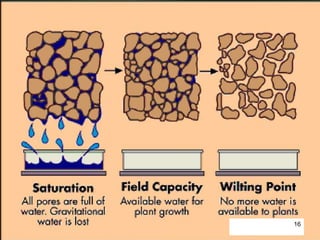

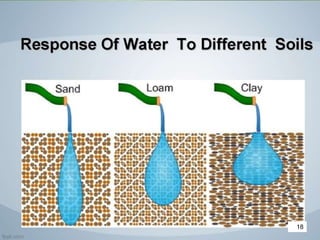

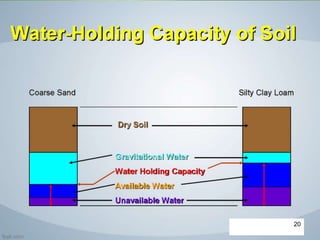

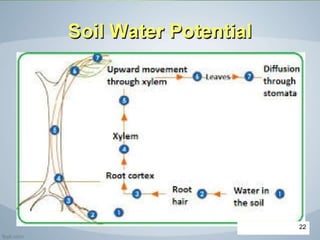
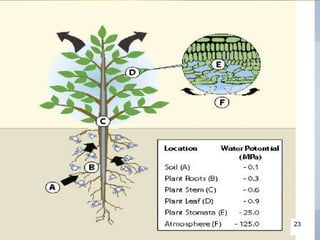






The document discusses soil water, including its classification, movement through soil, availability to plants, and factors that affect availability. It introduces key concepts like infiltration, percolation, pore space, and how soil acts as a sponge to take up and retain water, with pore space allowing for storage and movement of water. The document also covers indicators of plant water stress, development of water deficiency in plants, and concluding with factors that influence water availability.




























