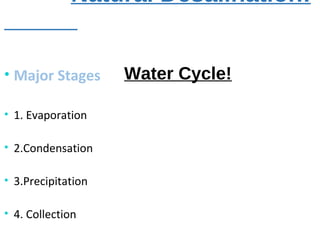
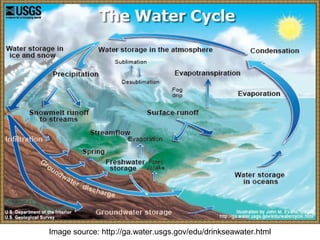
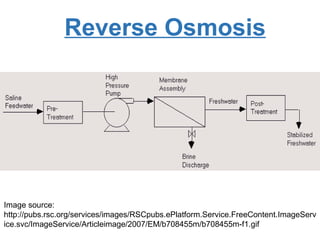
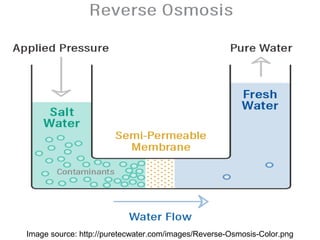
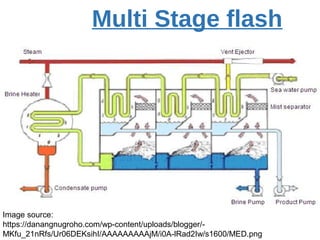
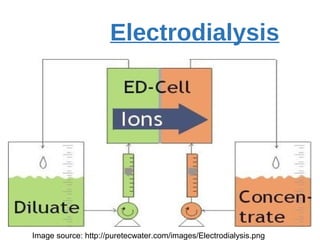
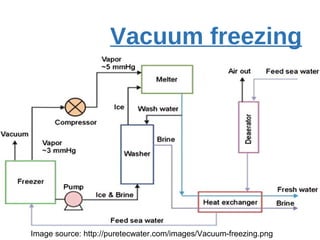
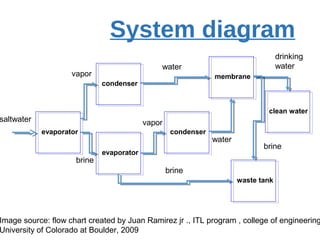
The presentation discusses desalination, a process used to convert seawater into potable water, highlighting methods such as reverse osmosis, multistage flash, electrodialysis, and vacuum freezing. While desalination addresses water scarcity, especially in dry regions, it is noted to be expensive, with some areas experiencing higher costs than gasoline. The Shoaiba desalination plant is mentioned as the world's largest, producing 450,000 m3/day at a total cost of $1.06 billion.