This document discusses soaps and detergents used for laundering and dry cleaning. It provides information on:
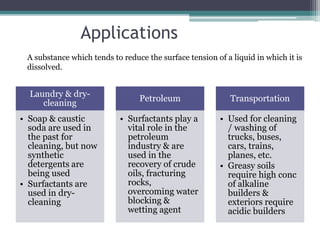
- Laundering uses water to dissolve soils through agitation and higher temperatures. Dry cleaning uses solvents instead of water for delicate fabrics.
- Common dry cleaning solvents include Stoddard, perchloroethylene, and valclene A.
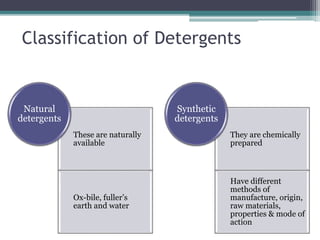
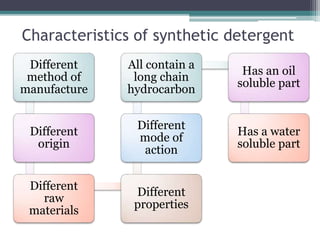
- Detergents contain surfactants and other additives to help remove soils from fabrics. They have a hydrophobic and hydrophilic end that attract soils and suspend them in wash water.
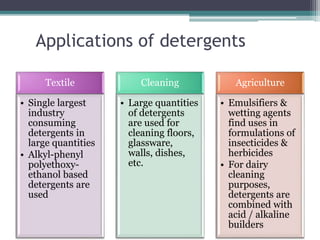
- Detergents are widely used for cleaning textiles, dishes, surfaces and in agriculture and petroleum industries. They are available in powder,