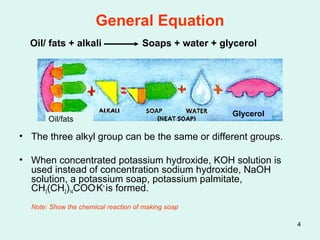
Soaps are salts of fatty acids made by saponifying fats or oils with alkalis like sodium hydroxide. They effectively clean in soft water but form scums in hard water due to insoluble precipitates. Detergents are made from petroleum sources and contain sulphonic acid groups which allow them to clean equally well in hard or soft water without scum formation. Both agents work by reducing surface tension to suspend dirt in water for removal.