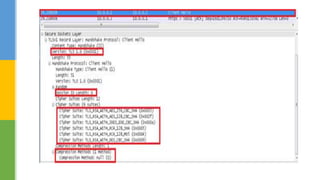
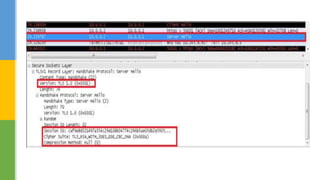
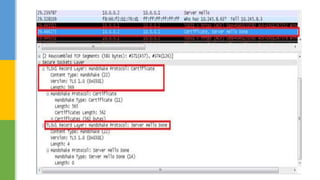
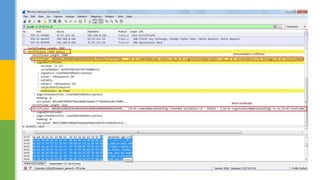
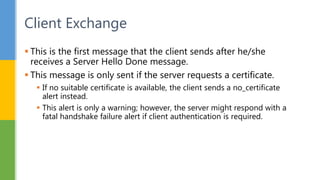
SSL (Secure Socket Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are cryptographic protocols that ensure secure communication over networks by providing features like integrity, confidentiality, and authentication. The document outlines the SSL/TLS handshake process, including client-server parameter exchange and certificate verification, alongside certificate validation methods like CRL and OCSP. It emphasizes the importance of these protocols for secure web browsing, email, and other applications, detailing the steps involved in establishing a secure connection.