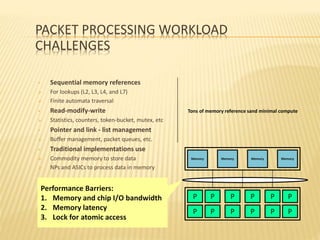
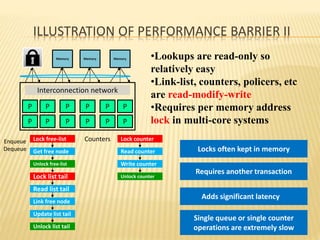
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on smart memories. It discusses the challenges of packet processing workloads due to sequential memory references and read-modify-write operations. A solution presented is smart memory, which attaches simple compute capabilities and locks directly to memory to enable local communication and keep compute close to data. The architecture of smart memory is described, using both eDRAM and DRAM. It provides advantages over traditional architectures like reduced chip I/O bandwidth and latency. In conclusion, smart memory keeps compute and locks near data to improve performance for packet processing workloads.