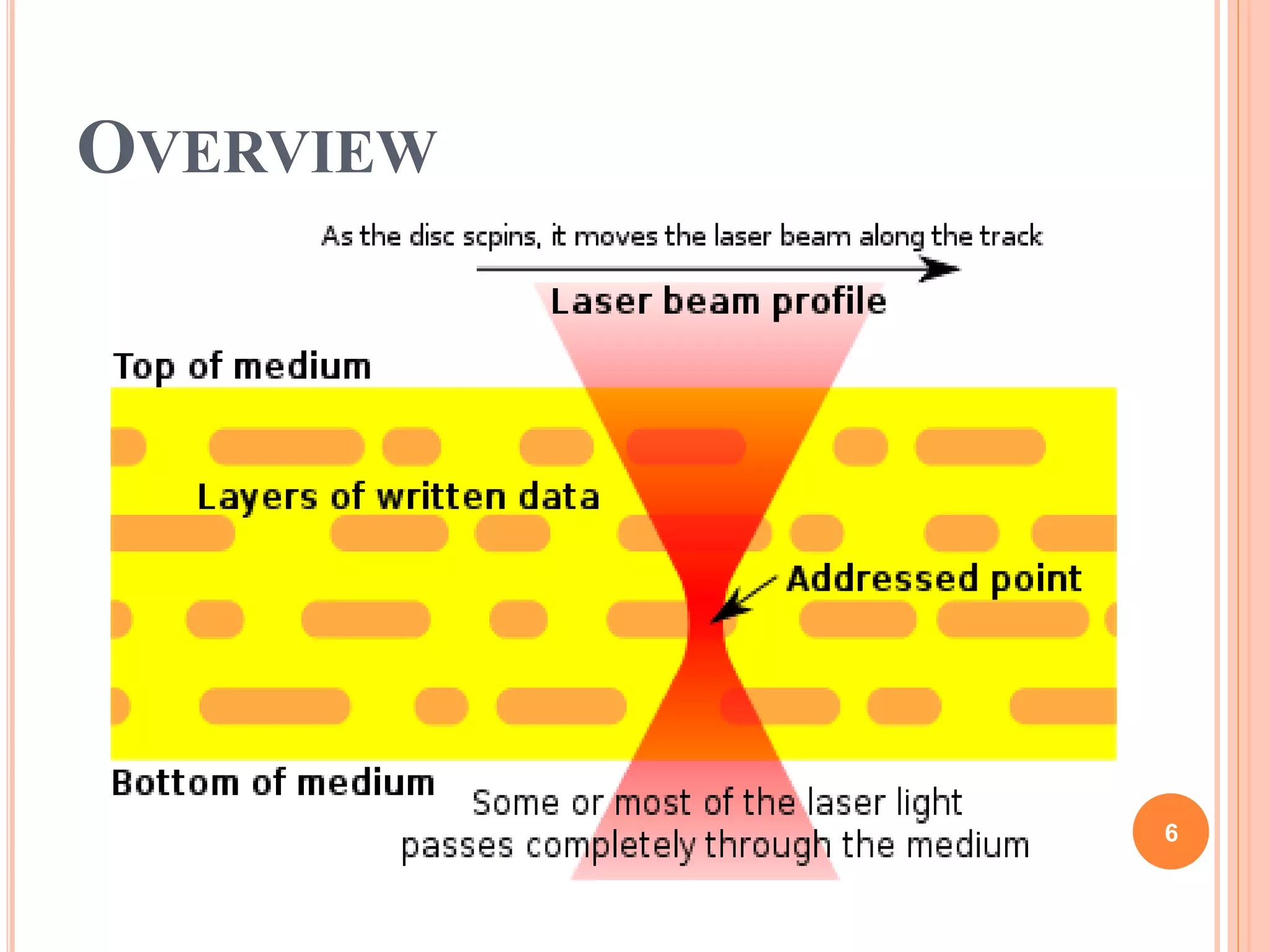
The document discusses 3D optical data storage, which potentially allows for high-capacity data recording on DVD-sized disks. It covers the history, writing and reading processes, media and drive design, development challenges, applications, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of this technology. Despite no commercial products yet available, several companies are actively working on bringing this innovation to market.