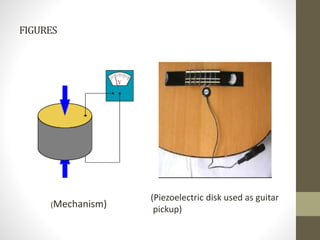
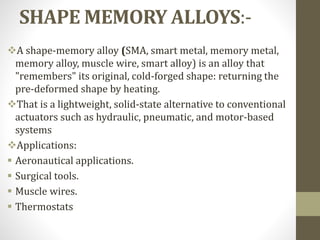
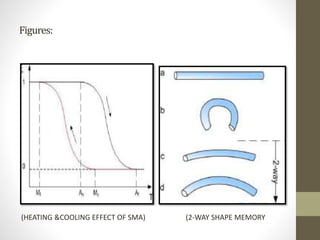
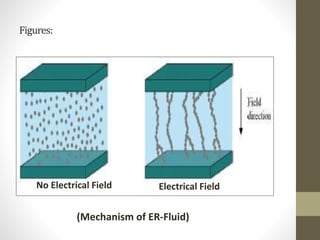
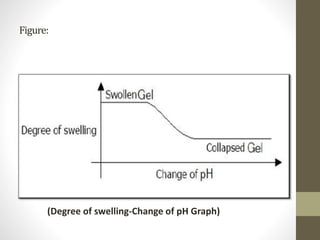
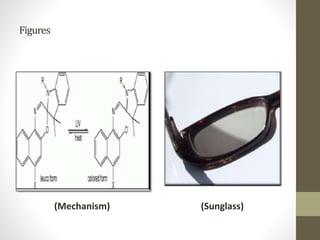
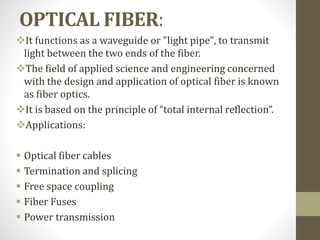
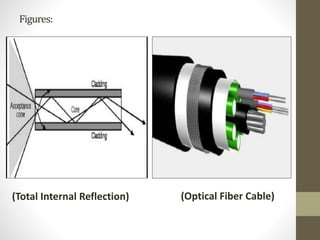
Smart materials possess intrinsic and extrinsic capabilities that allow them to rapidly respond to various stimuli, such as temperature, pressure, and magnetic fields, leading to a range of technological applications across multiple fields. They can be classified into types like piezoelectric materials, shape memory alloys, and smart gels, each with unique properties and applications, from aerospace to biomedical devices. Increasing research and development indicate that smart materials will significantly impact various industries in the future.








![(Animation of Magnetostriction)
[Magnetostrictive material (inside), magnetizing coil, and
magnetic enclosure completing the magnetic circuit (outside)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smartmaterials-201020164003/85/Smart-materials-12-320.jpg)






![REFERENCES:
Prof. Jagannath Padhy [HOD, EEE Dept.]
Asst. Prof Sidharth Sabyasachi
Lect. Smita Jana
www.google.com
www.wikipedia.com
Book-Material Science & Engineering
By Achyut Kumar Panda.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smartmaterials-201020164003/85/Smart-materials-24-320.jpg)
