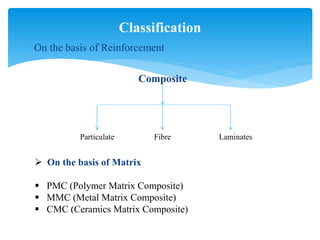
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on ceramic matrix composites (CMCs). CMCs consist of a ceramic matrix with reinforcements. They offer advantages over monolithic ceramics like higher toughness, strength, and fatigue resistance. Some key applications of CMCs mentioned are in cutting tools, aerospace components, jet engines, burners, and turbine blades, as they can withstand high temperatures and offer corrosion resistance. The document discusses properties, advantages, disadvantages and applications of CMCs.