The document summarizes a seminar presentation on HVDC (high voltage direct current) transmission. Some key points:
- HVDC transmission has advantages over HVAC like lower transmission losses over long distances. The first HVDC link was between Gotland and mainland Sweden in 1954.
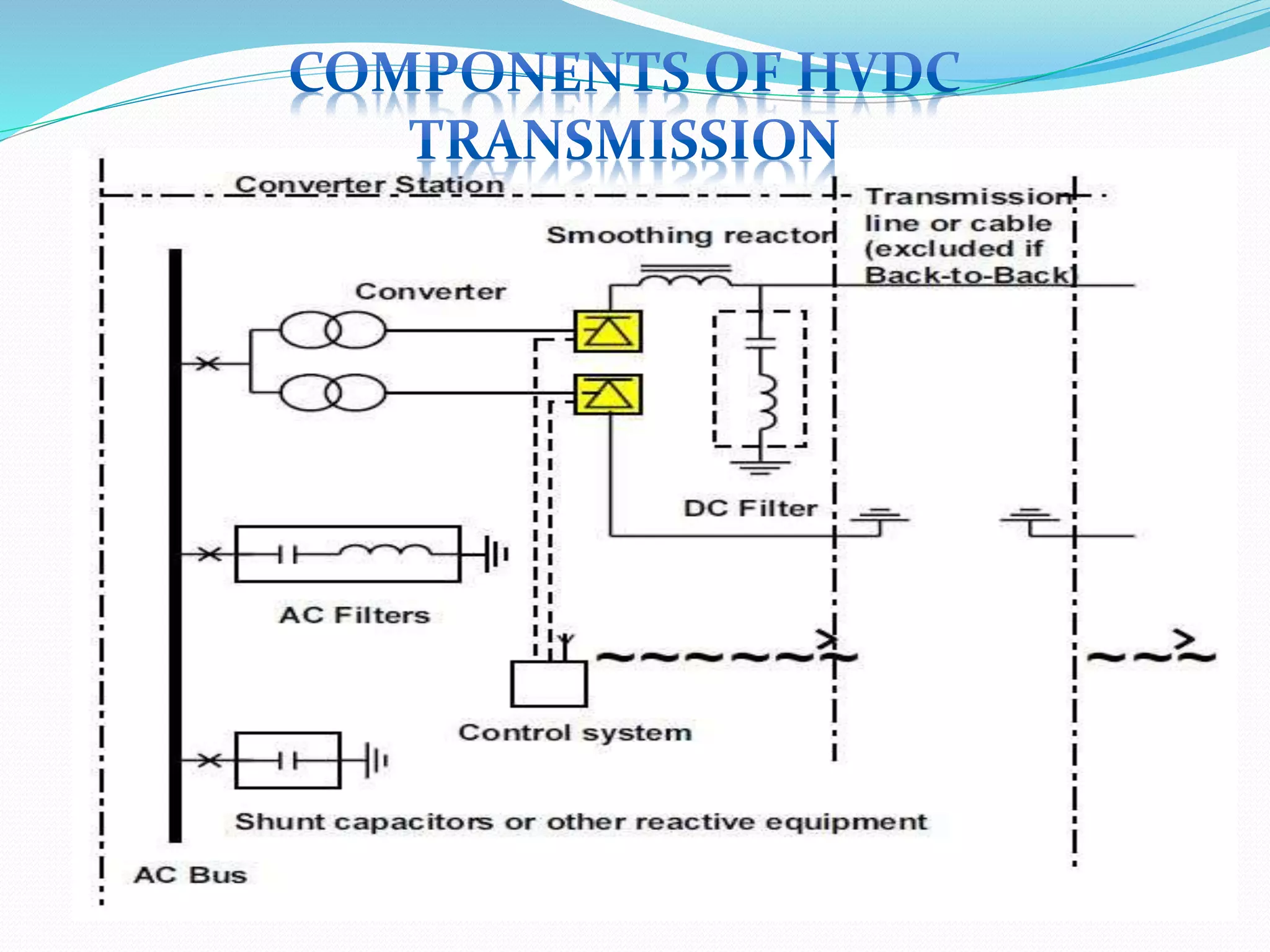
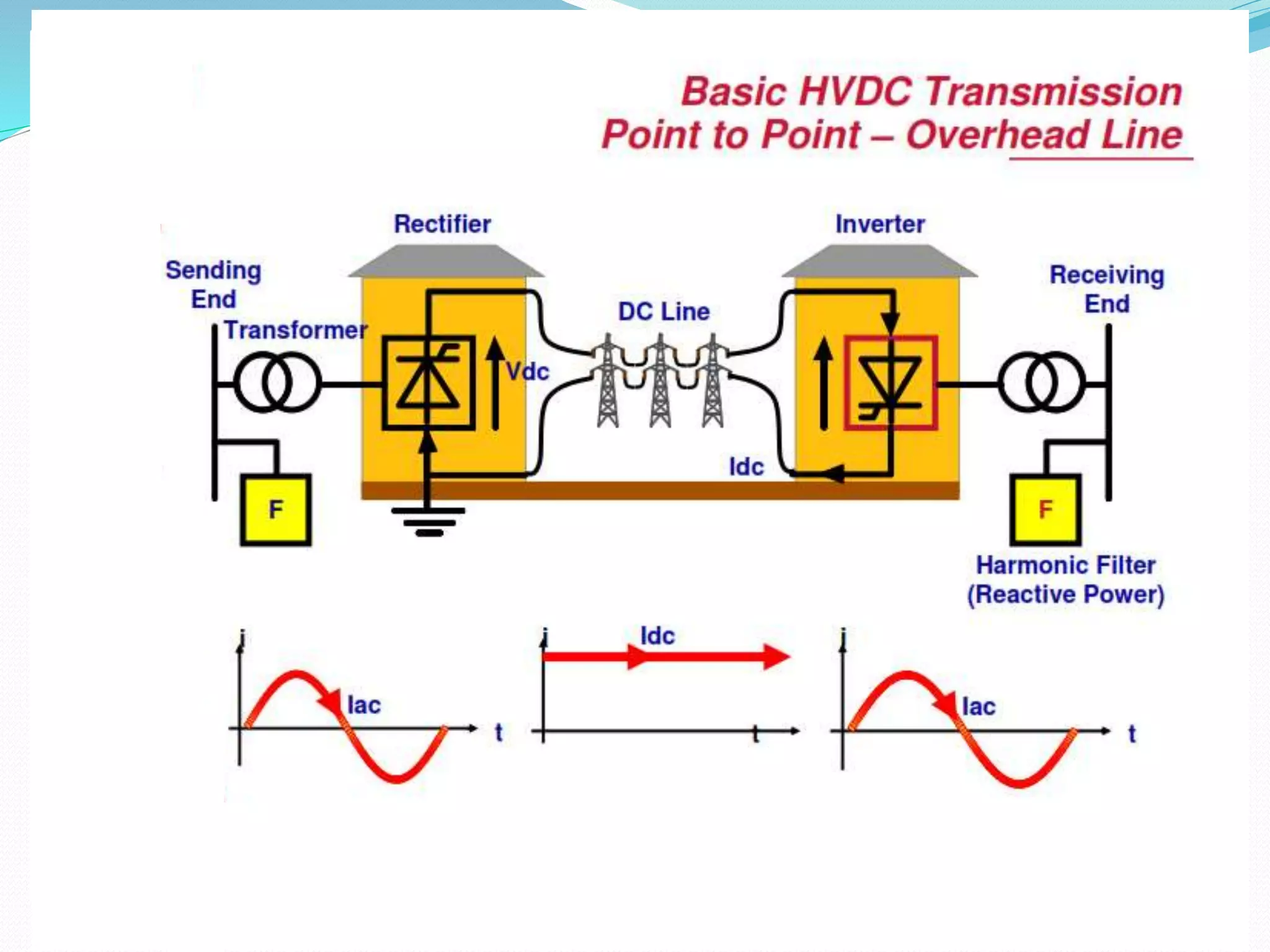
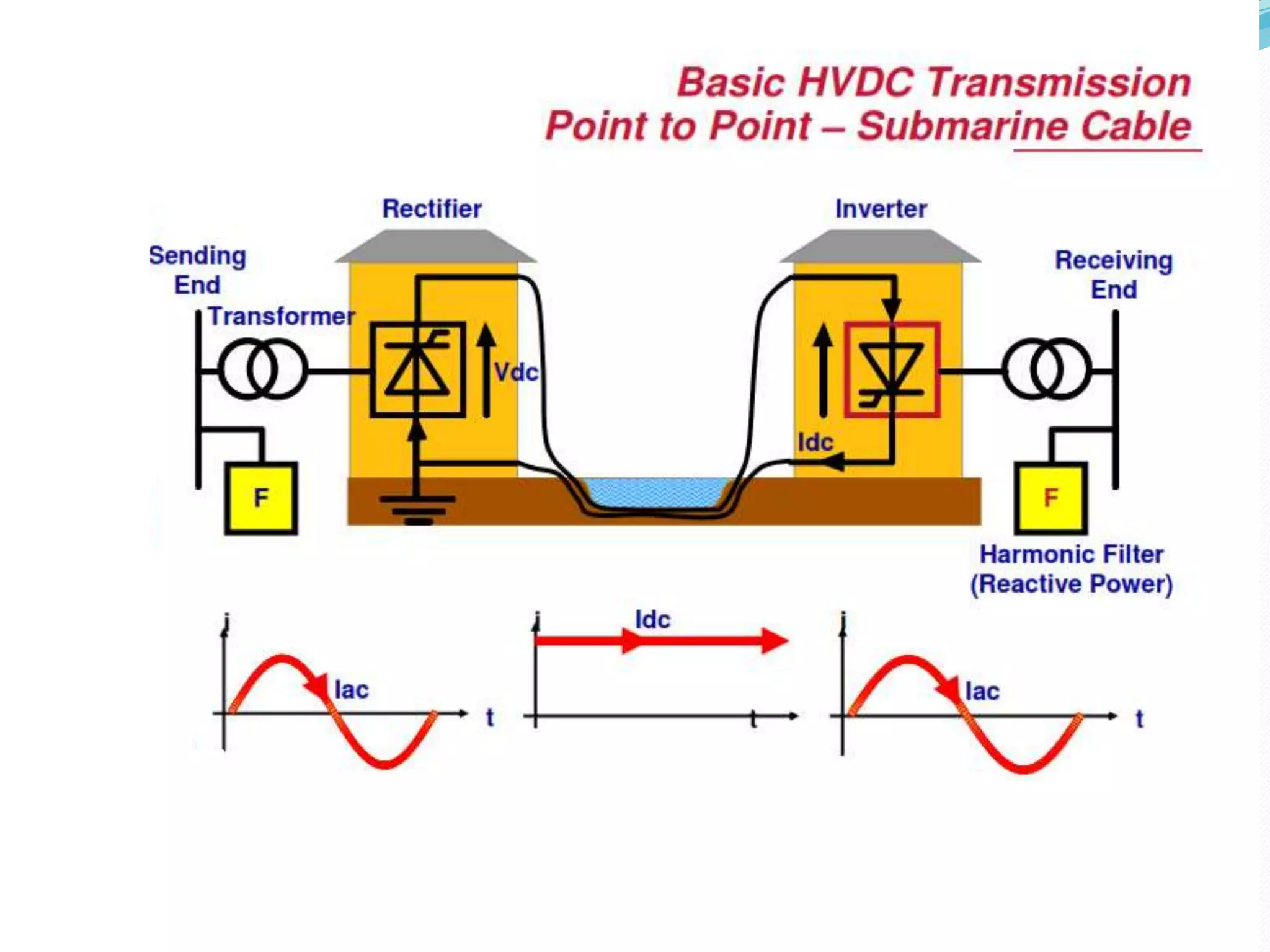
- HVDC uses direct current instead of alternating current to transmit electricity over long distances. It requires only two conductors instead of three. Losses are also lower compared to HVAC.
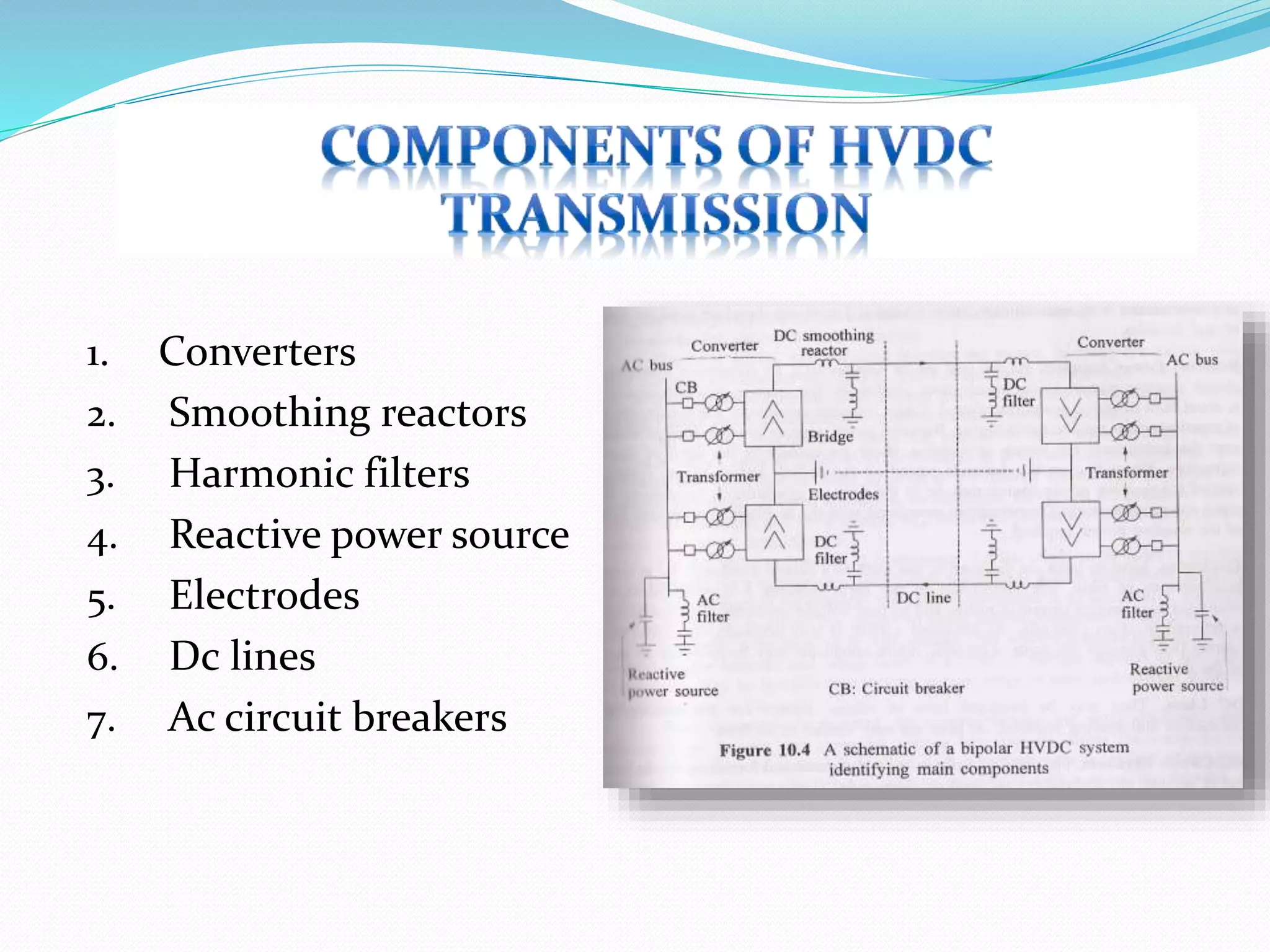
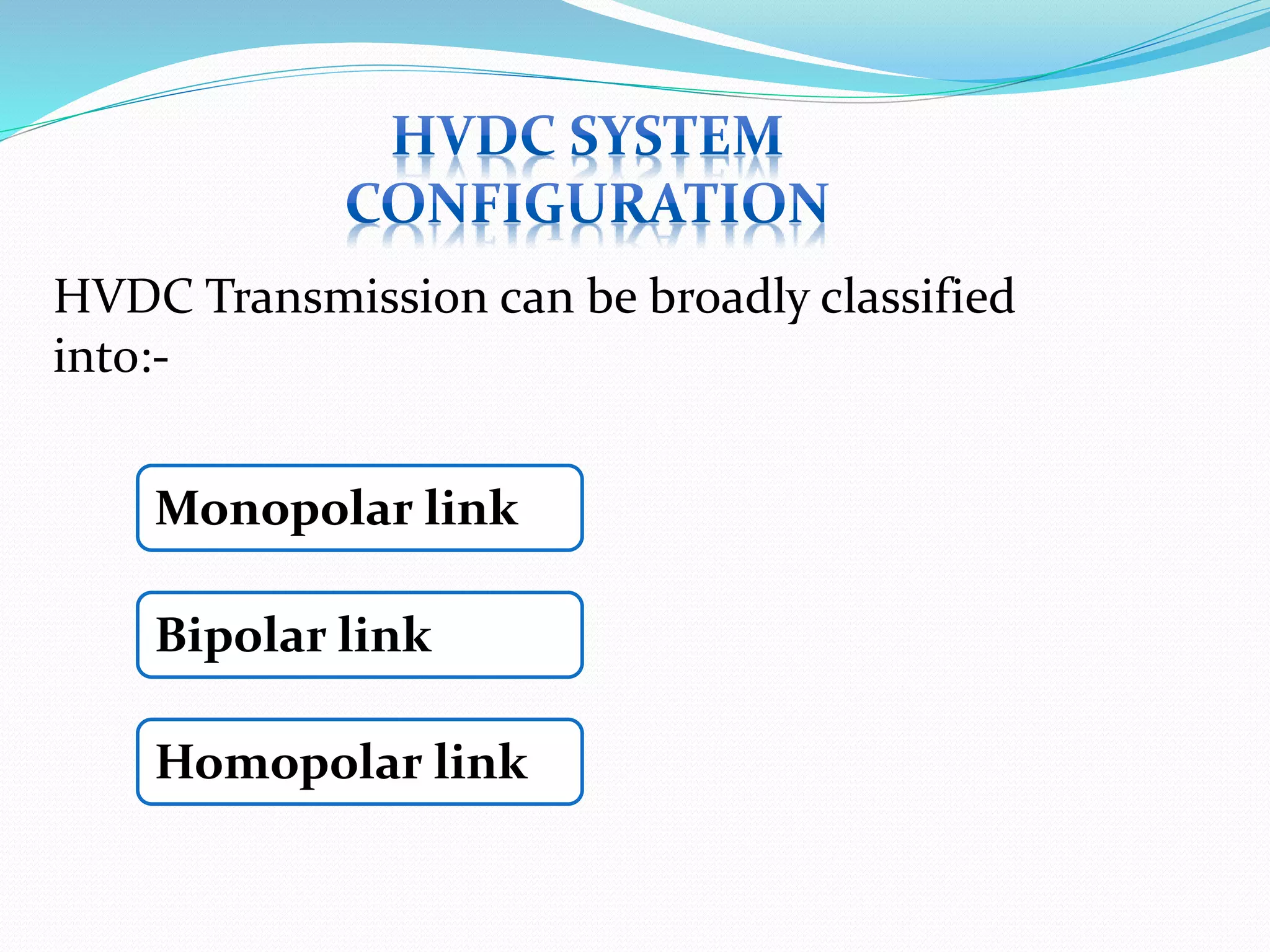
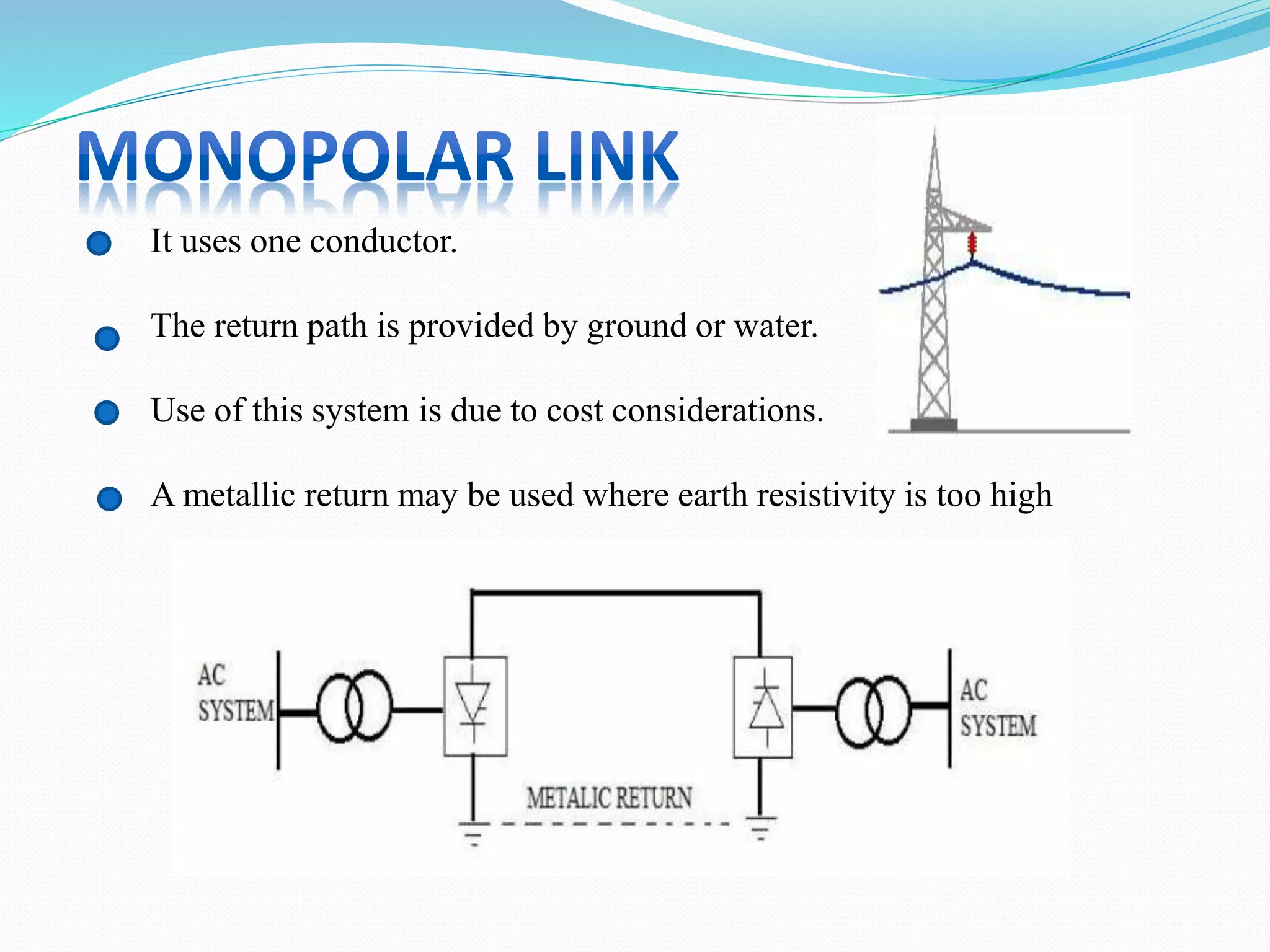
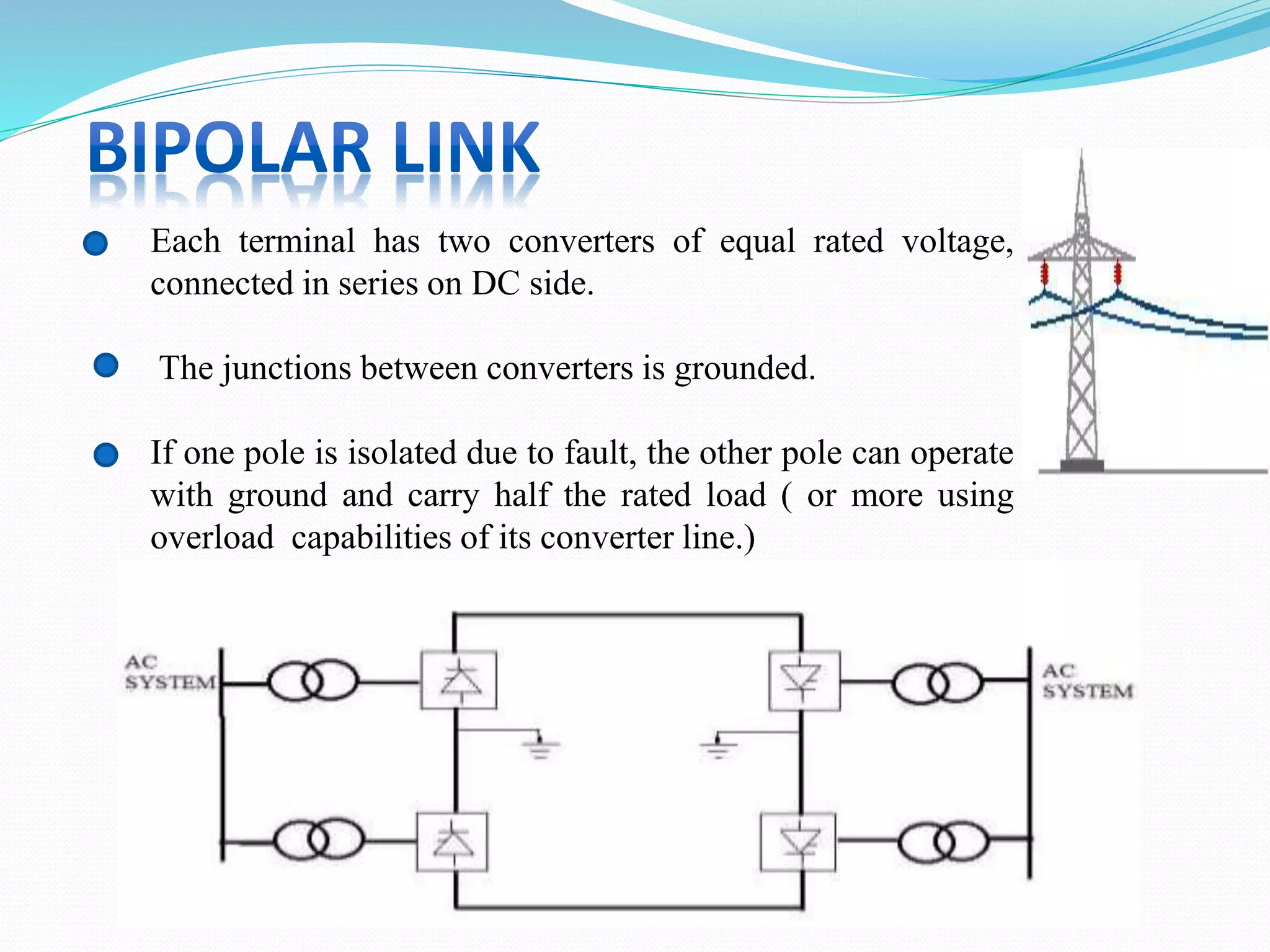
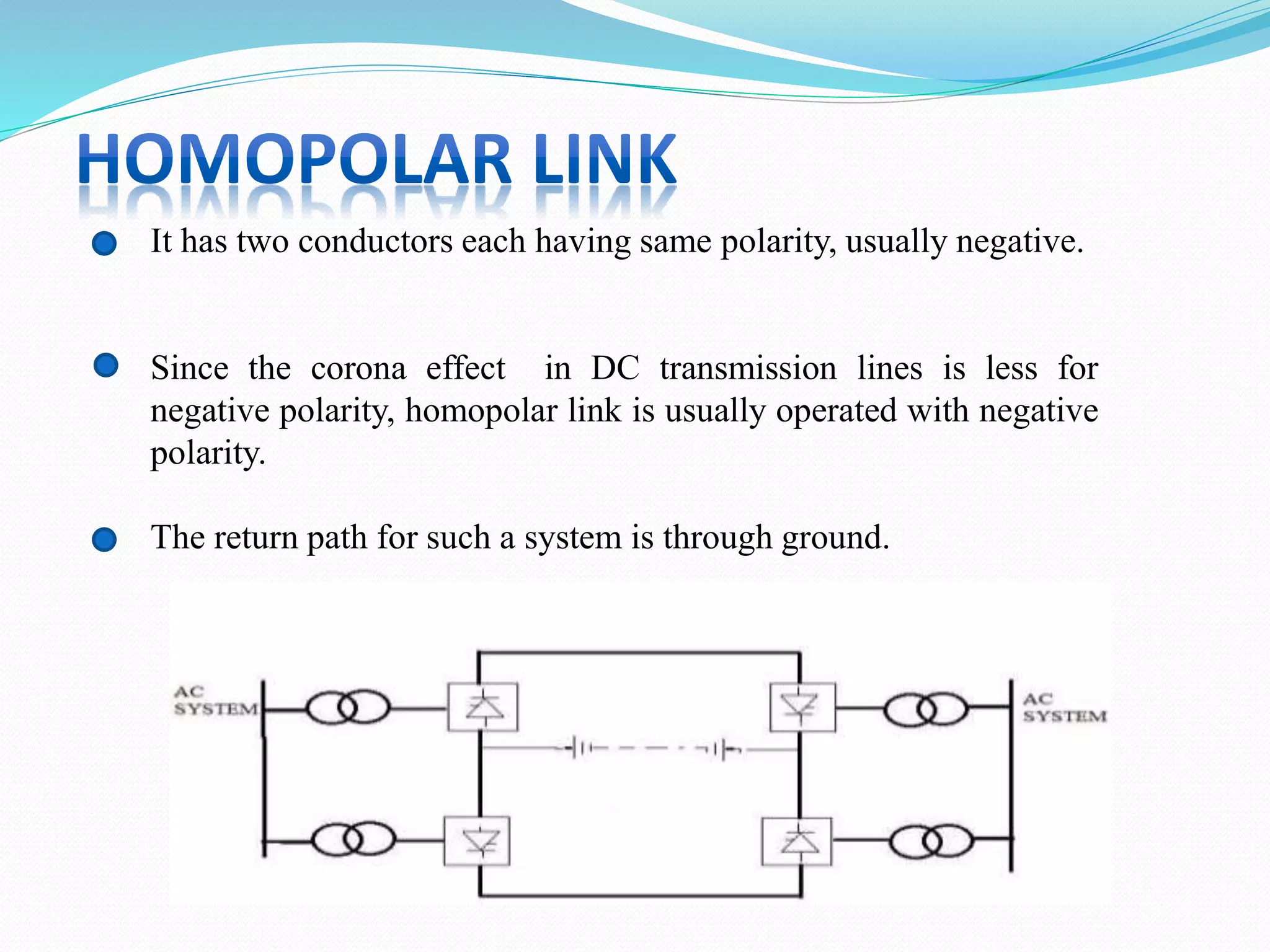
- HVDC transmission can be classified as homopolar, monopolar or bipolar depending on the conductor configuration. Early HVDC projects in India included the Rihand-Delhi and Chandrapur-Padghe lines which helped transmit