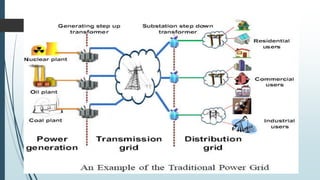
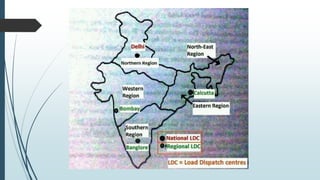
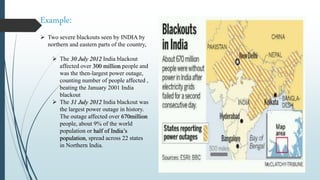
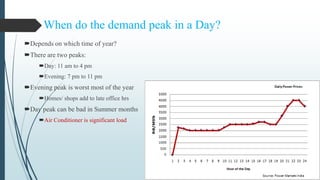
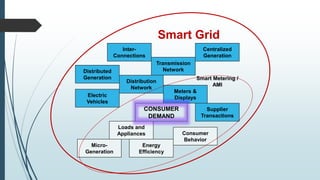
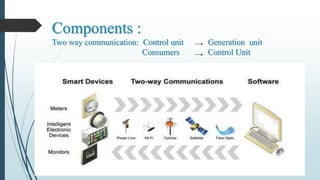
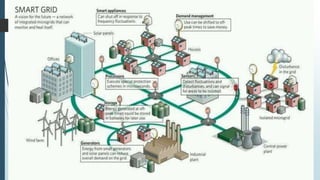
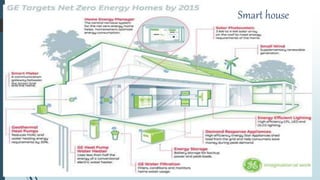
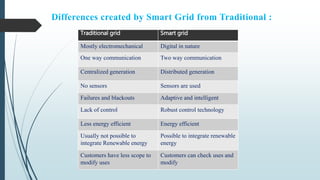
This document provides an overview of traditional electricity grids and introduces smart grid systems. It discusses problems with traditional grids like blackouts and inefficiencies. The smart grid aims to address these through advanced infrastructure, metering, monitoring, management and communication technologies. This allows for two-way communication between energy producers and consumers, integrated renewable energy, automated maintenance and self-healing of outages. The document outlines India's plans to adopt smart grid technologies and analyzes barriers to implementation like high costs and security risks. Overall, smart grids are expected to improve energy efficiency, reliability and consumers' ability to manage their energy usage.