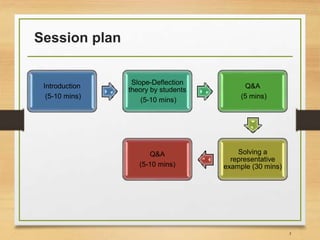
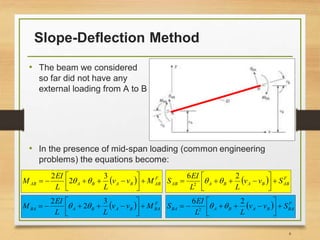
This document provides an example of solving a structural analysis problem using the slope-deflection method. It includes:
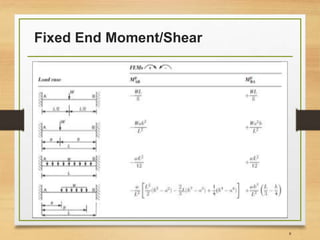
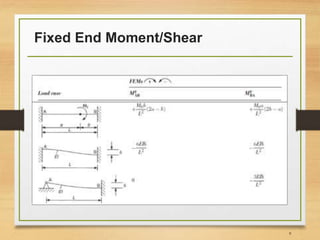
1) Introducing the slope-deflection equations for a beam with mid-span loading.
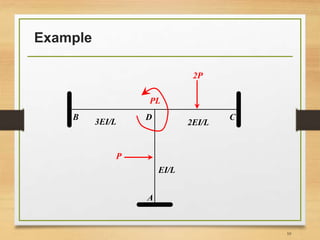
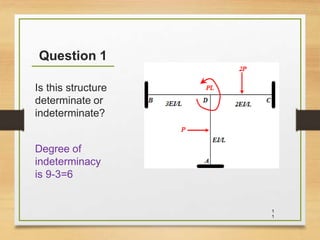
2) Presenting a sample frame structure problem and determining it is indeterminate.
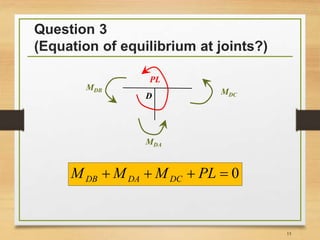
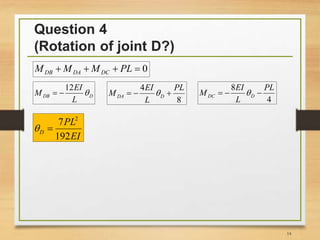
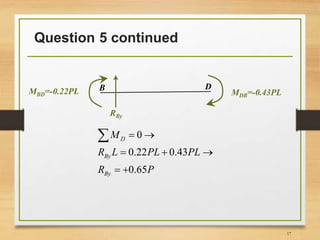
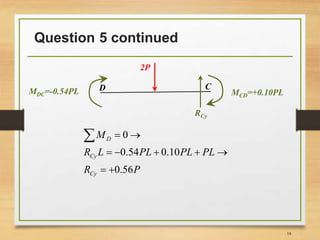
3) Writing the slope-deflection equations and equilibrium equations to solve for member end forces and joint rotations.
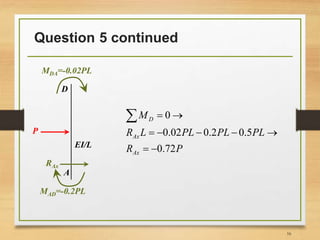
4) Calculating support reactions based on the member end forces.
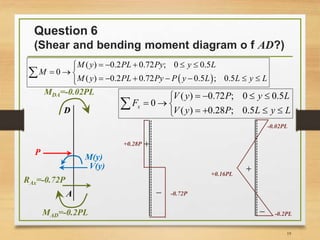
5) Drawing the shear and bending moment diagrams.