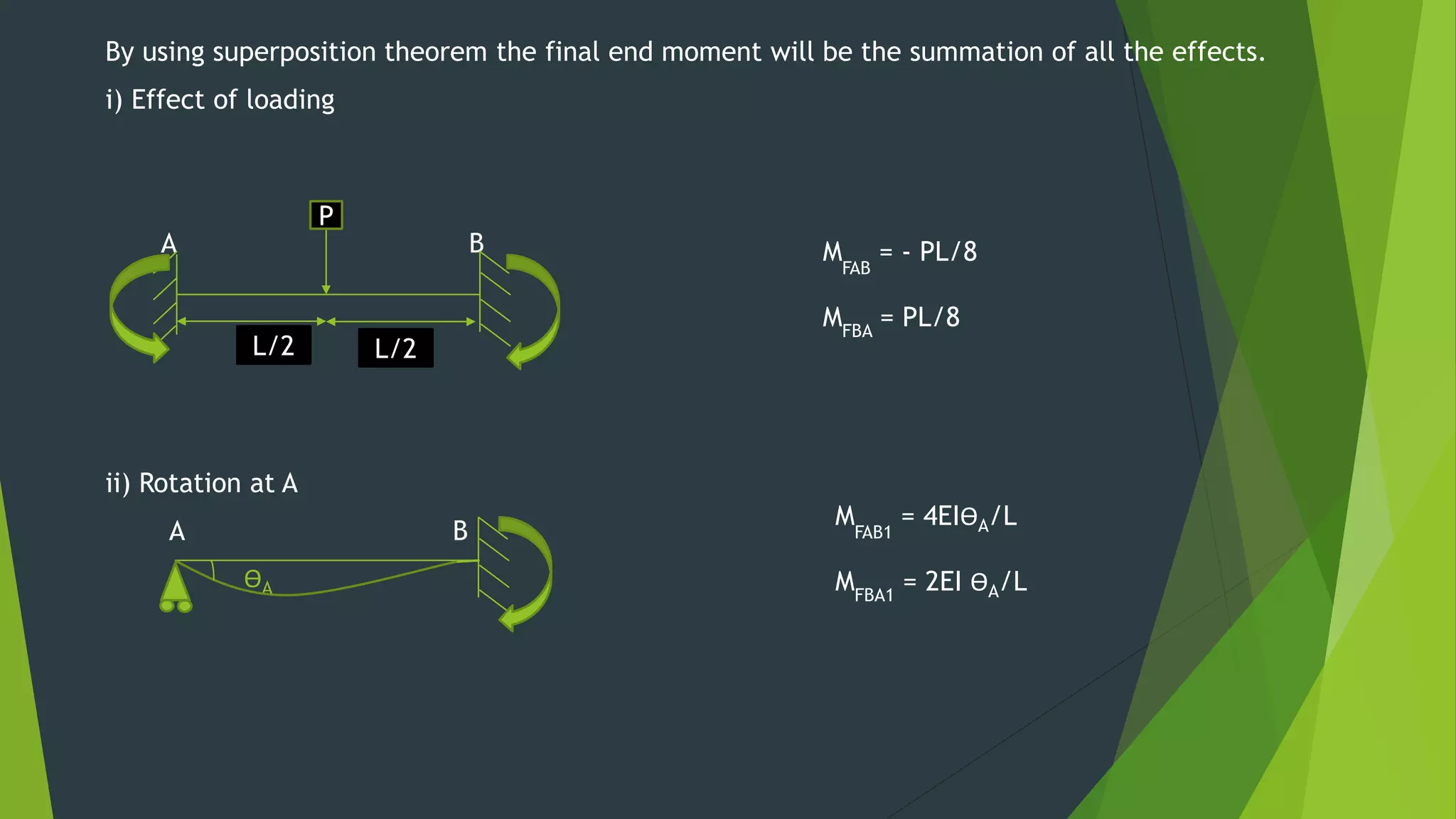
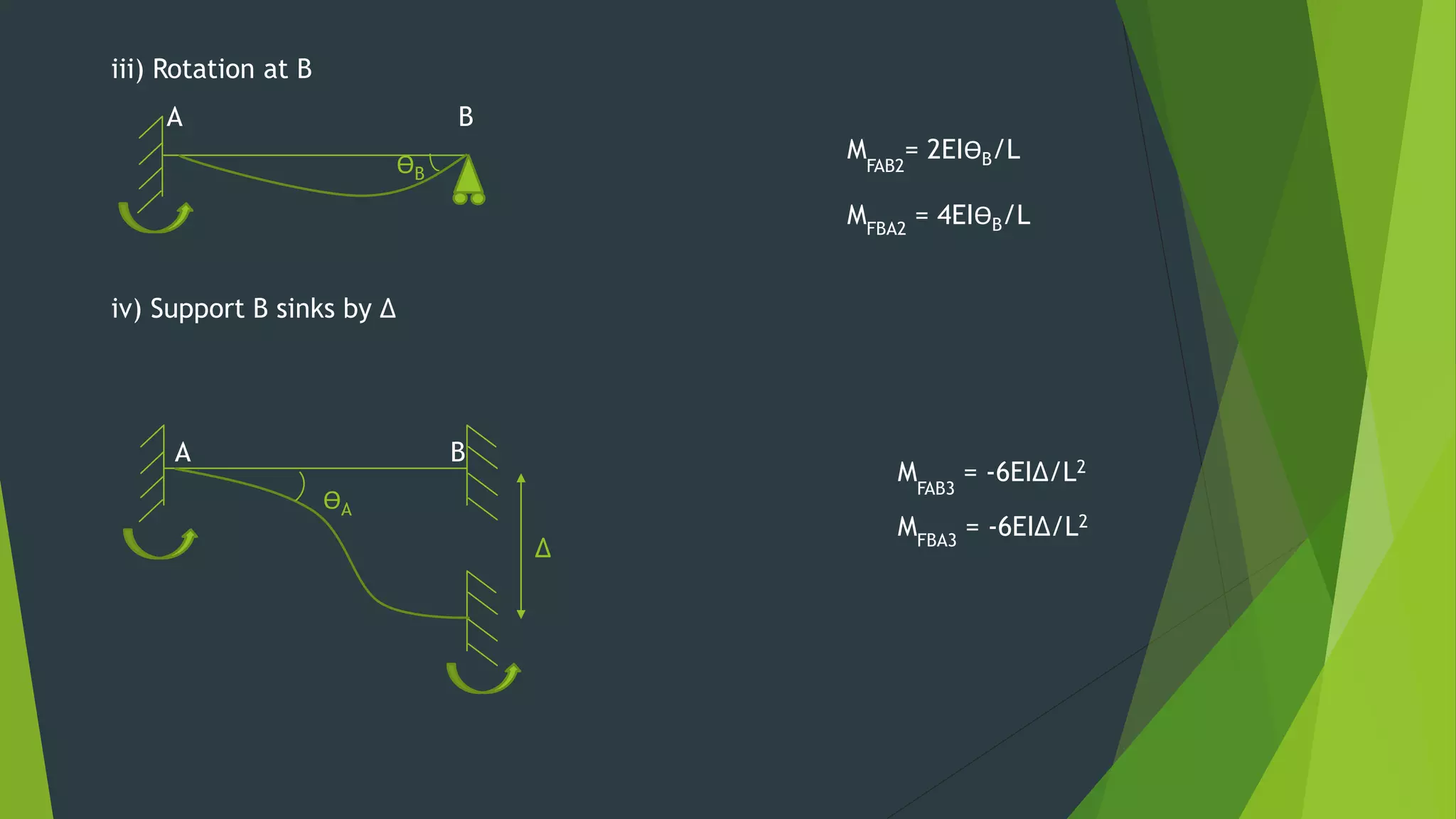
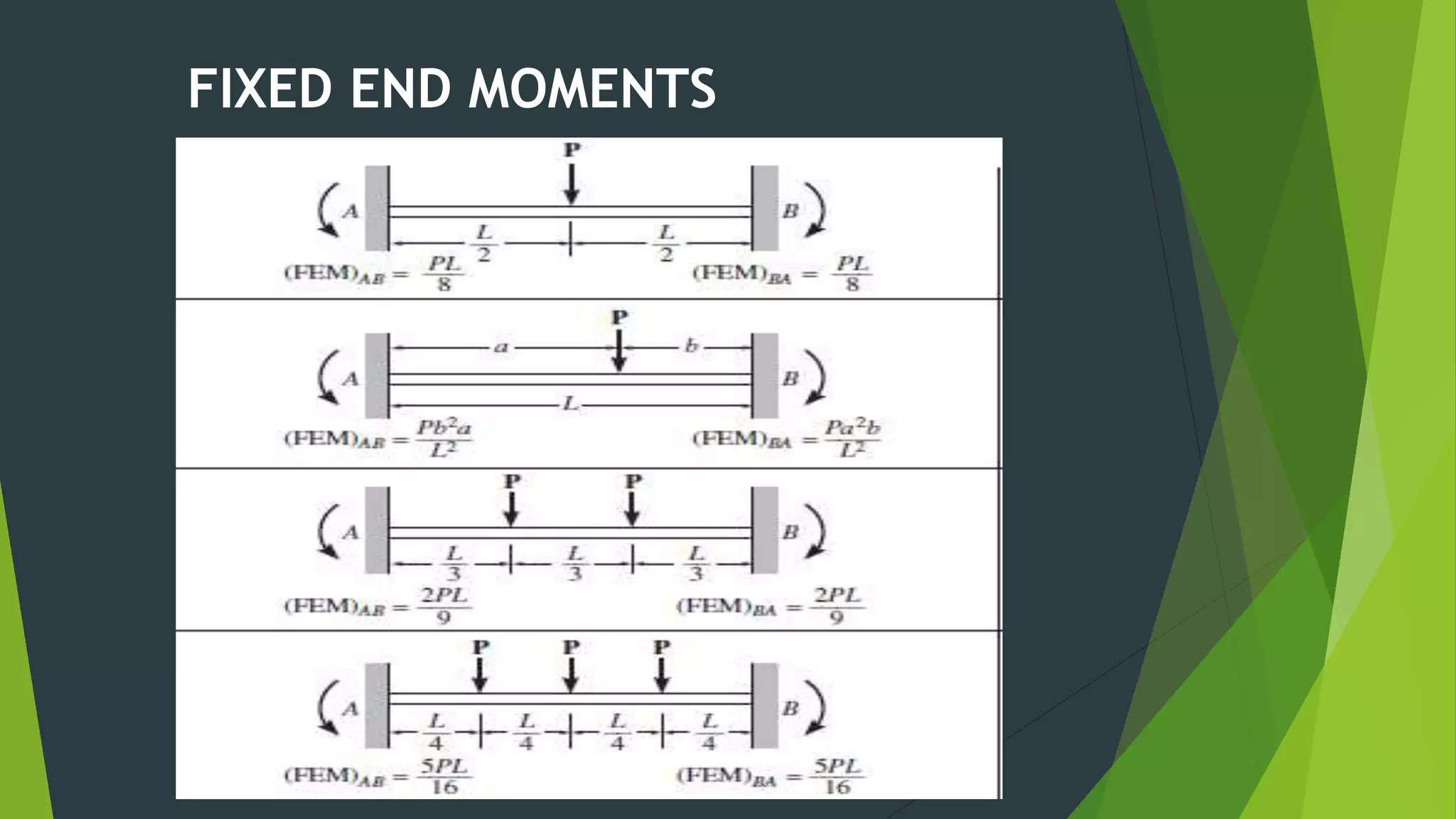
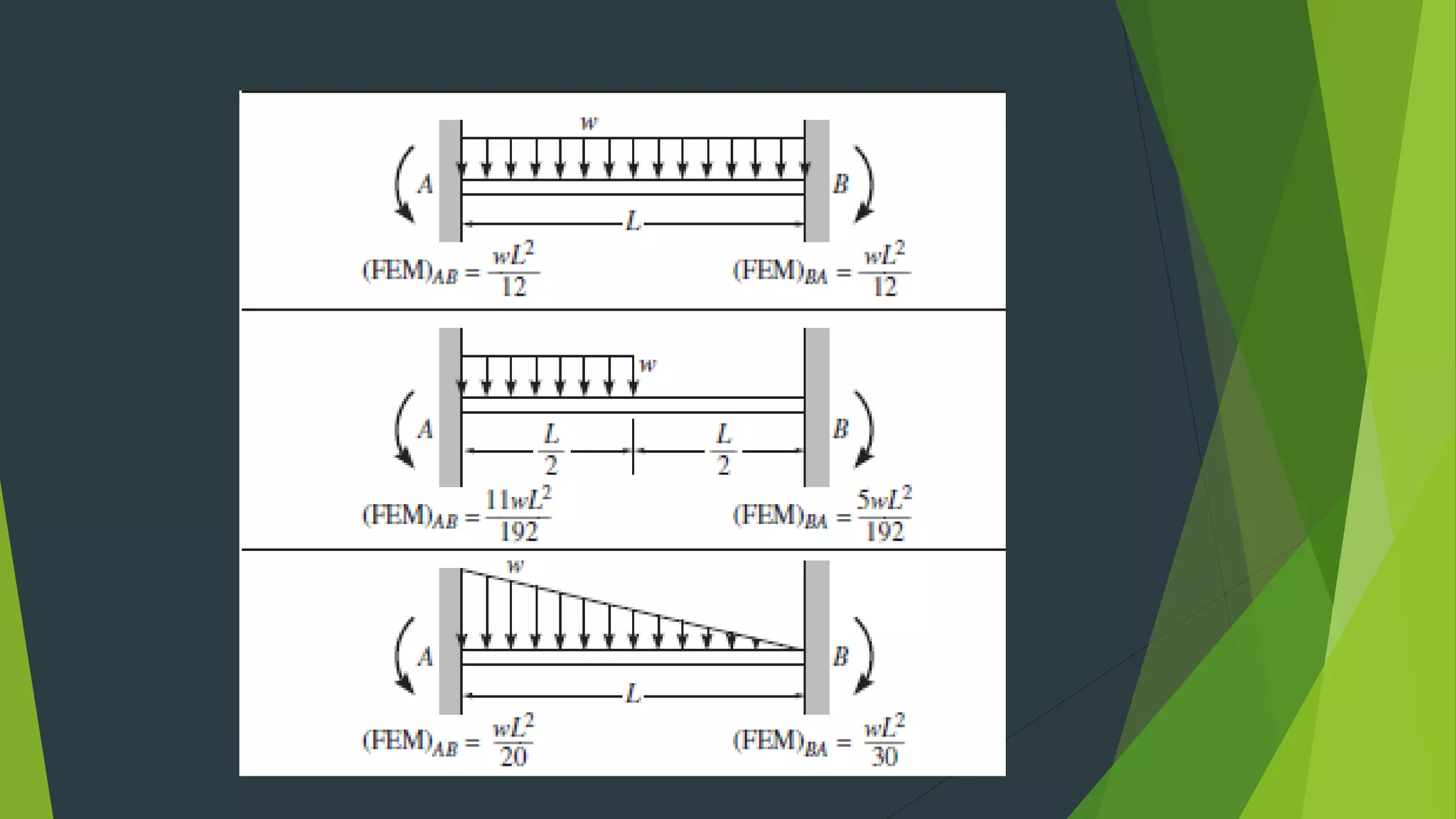
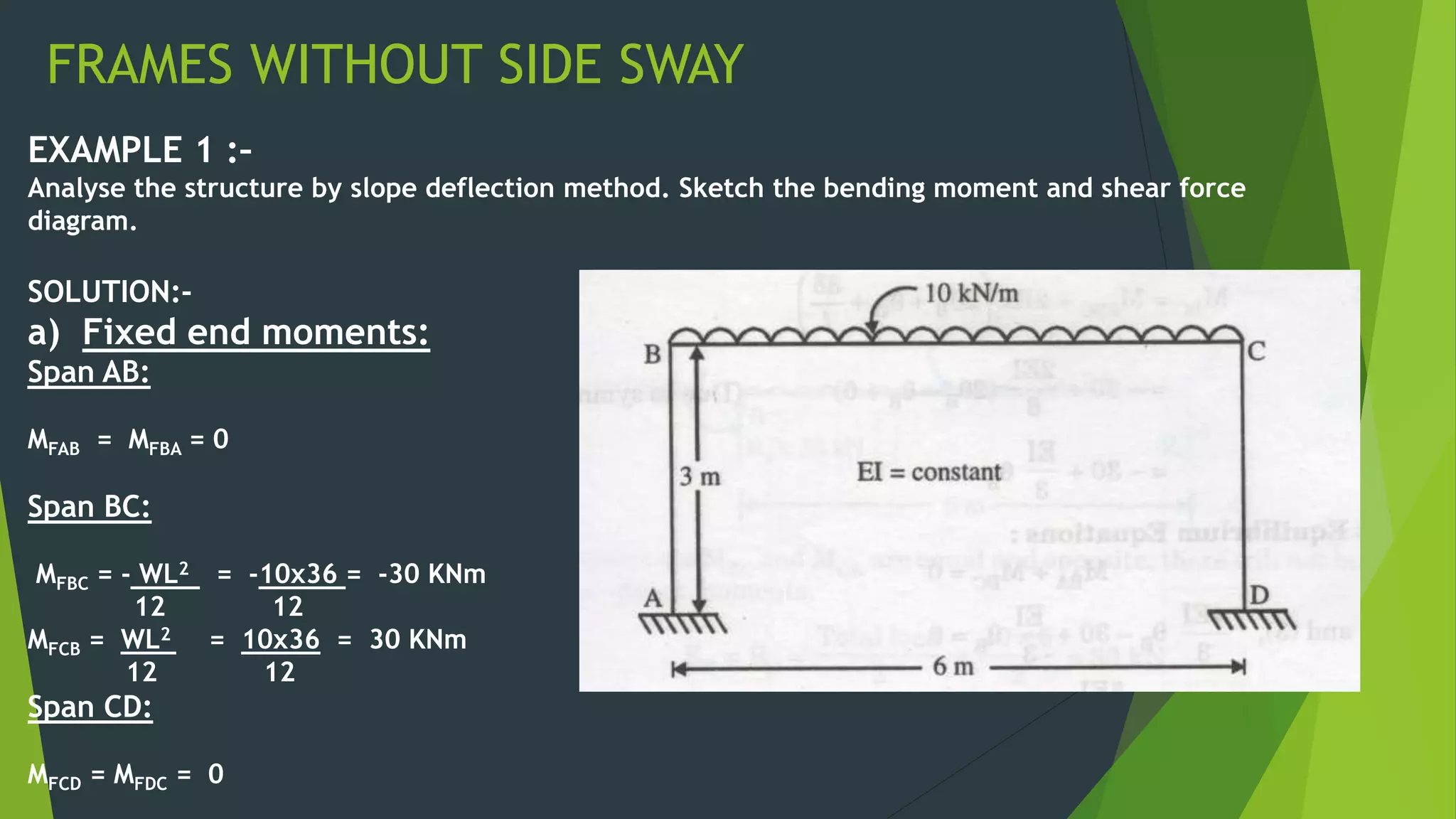
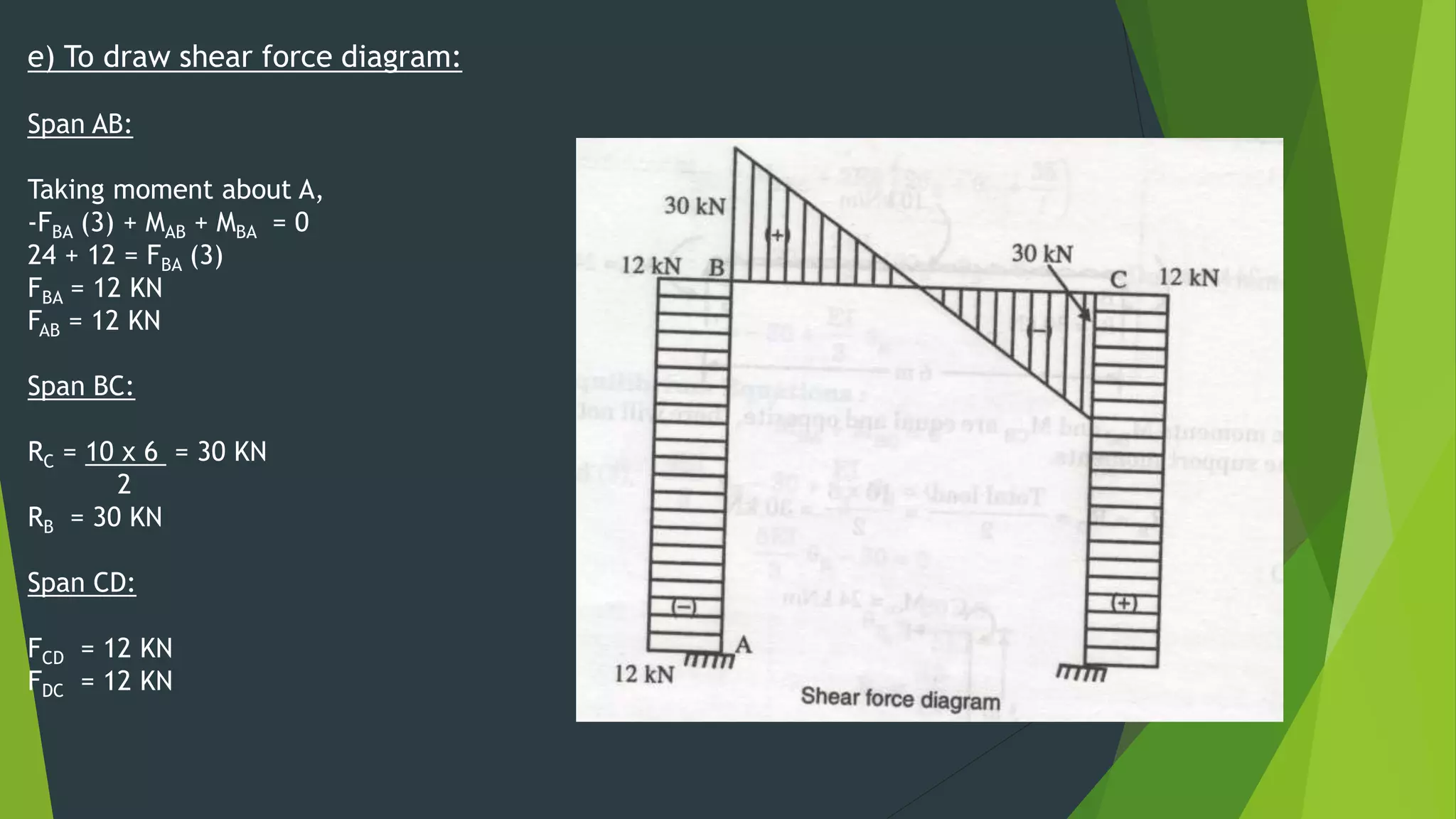
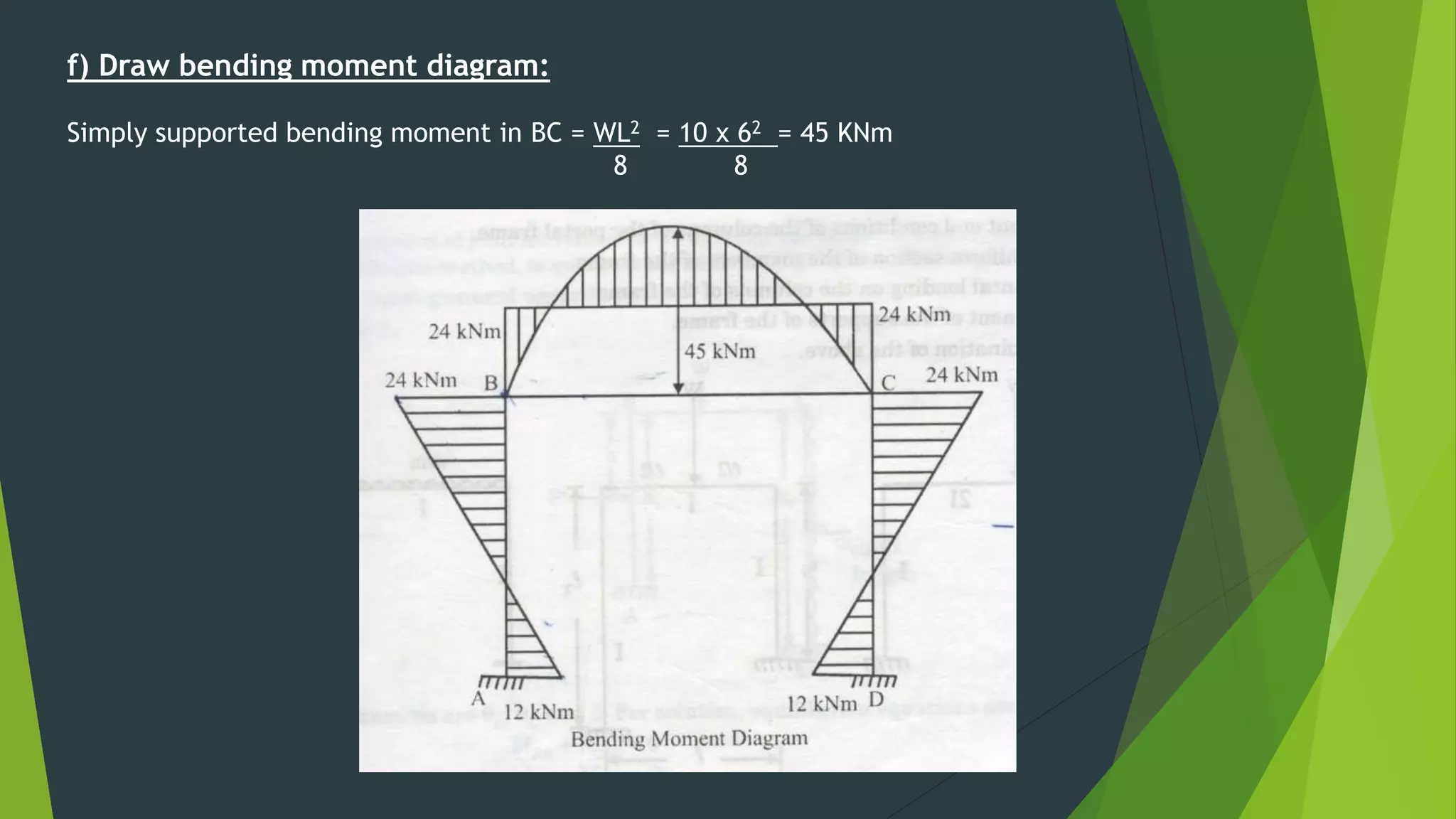
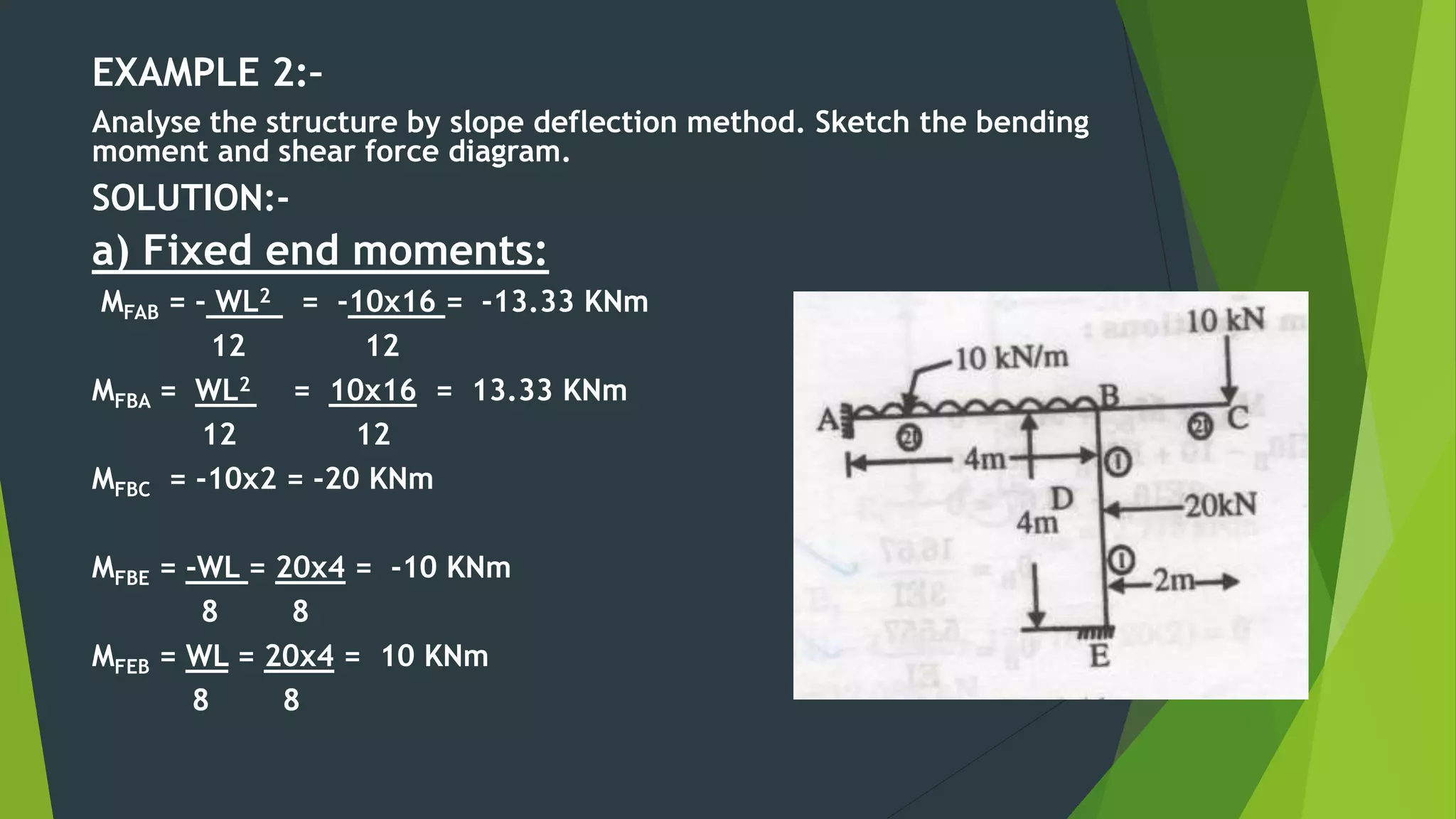
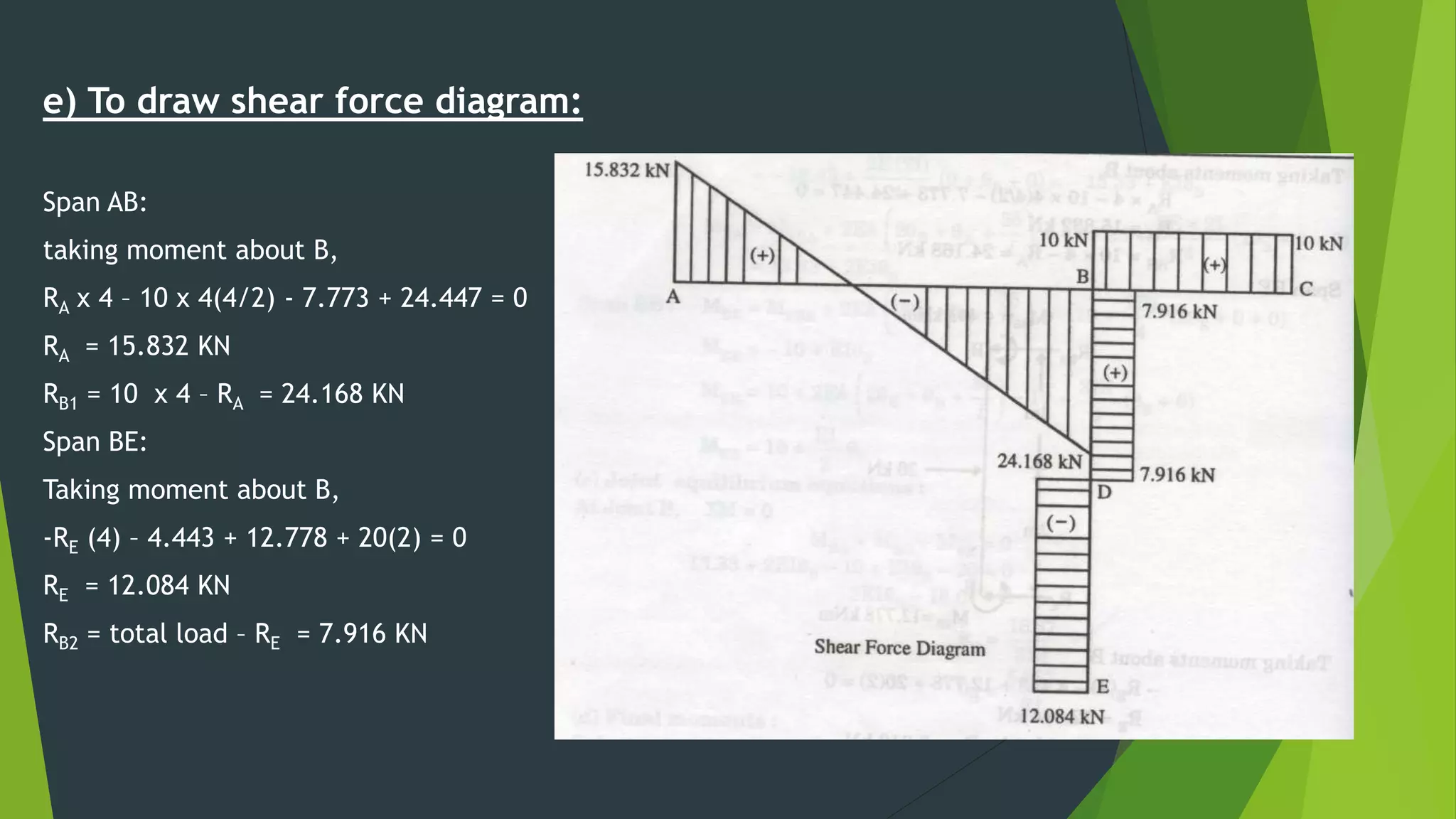
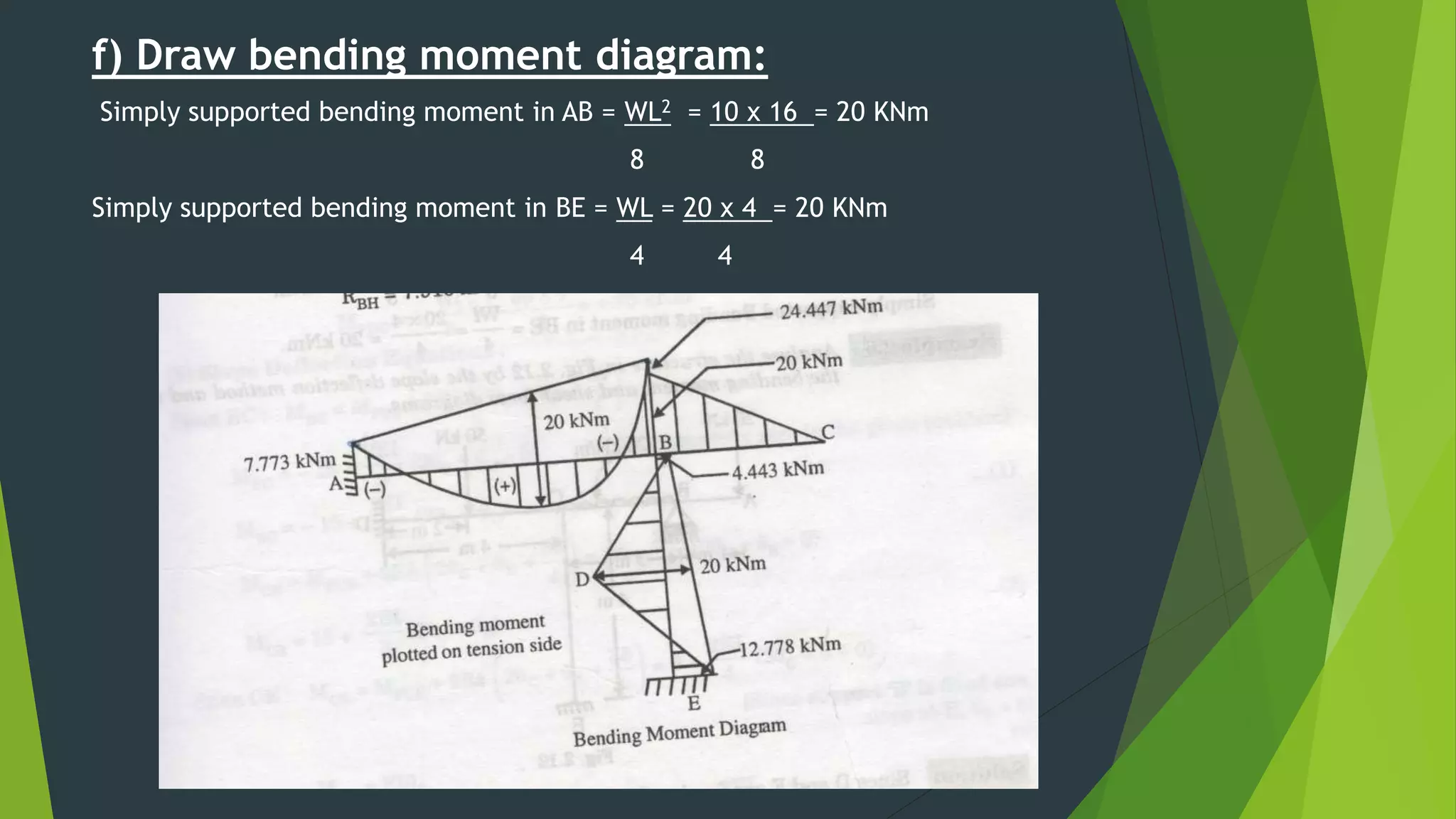
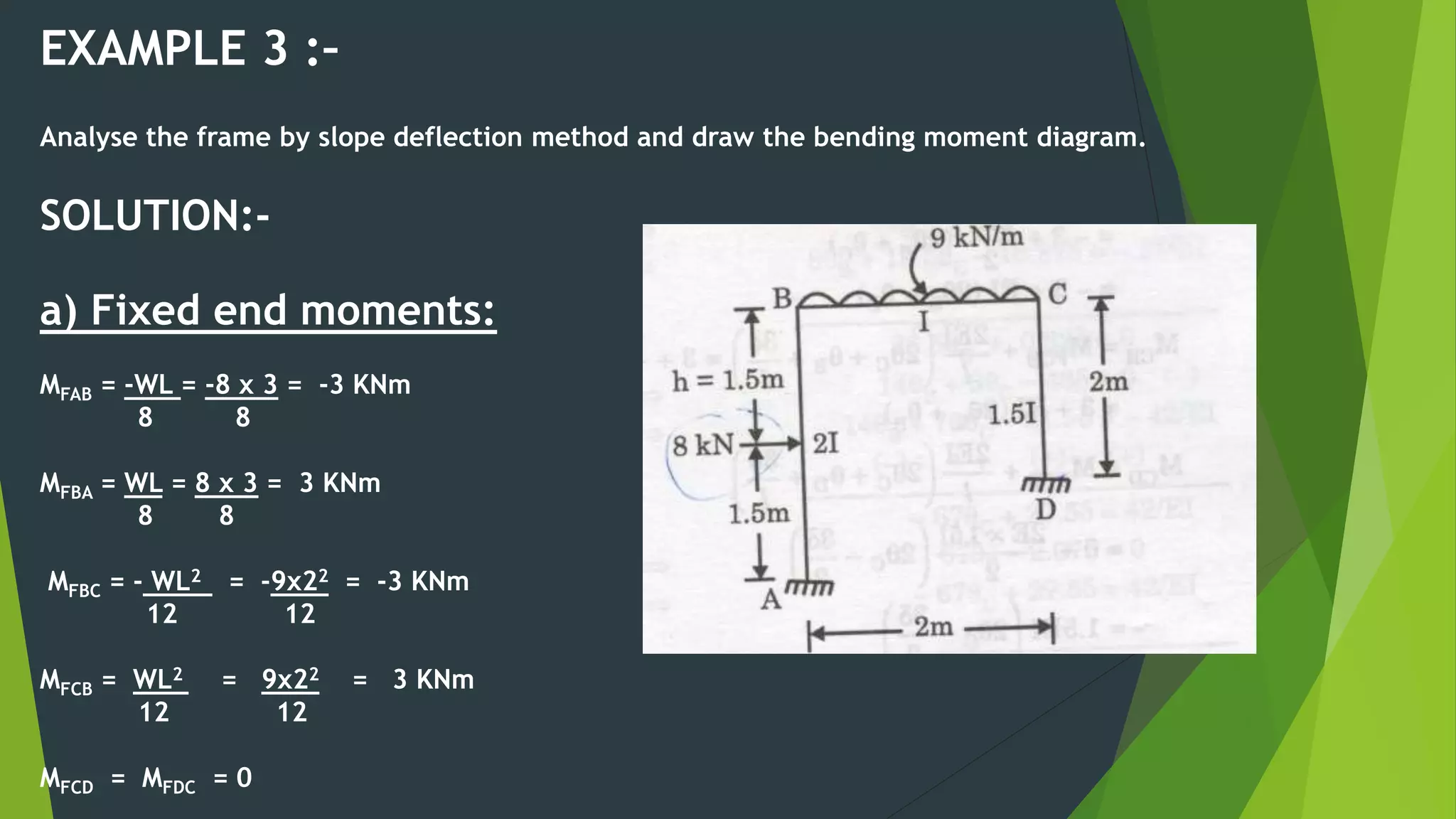
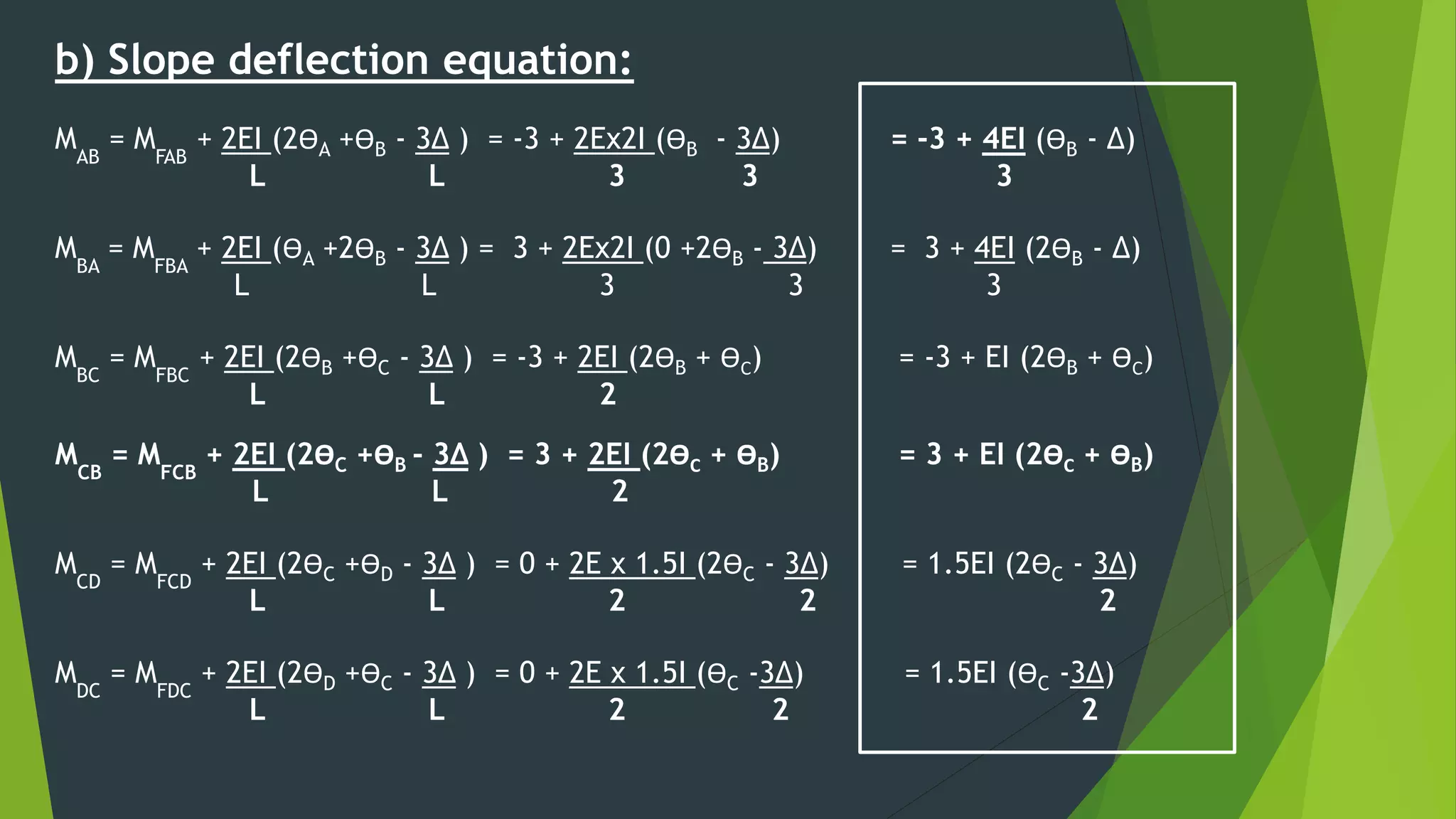
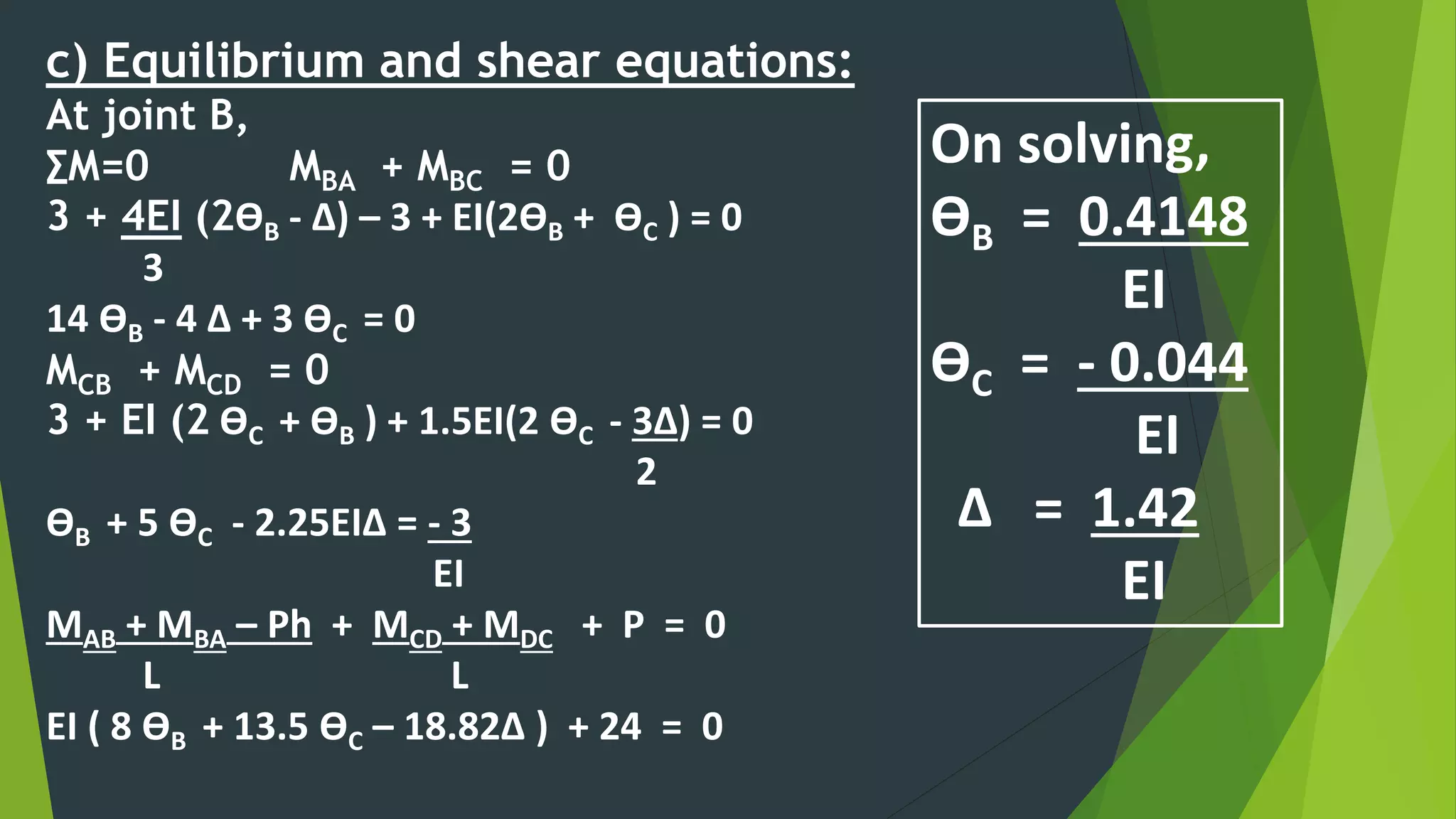
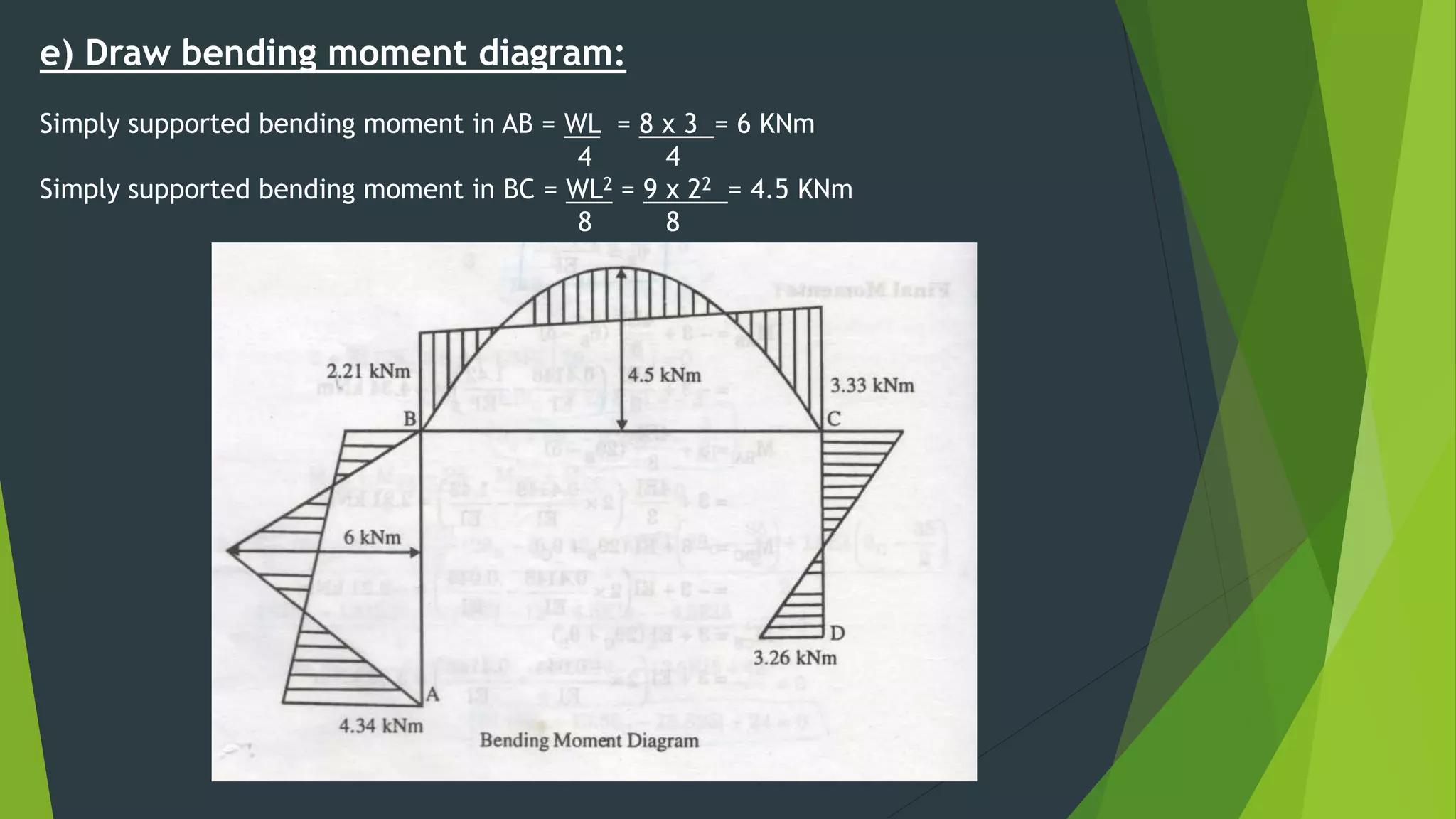
This document presents the slope deflection method for analyzing statically indeterminate beams and frames. It discusses the assumptions of the method, which include rigid joints and neglecting distortions from axial and shear stresses. Examples are provided to demonstrate solving for unknown joint rotations and displacements using equilibrium equations, then determining final end moments and drawing shear and bending moment diagrams. Portal frames are discussed, including how side sway can be accounted for in the analysis.