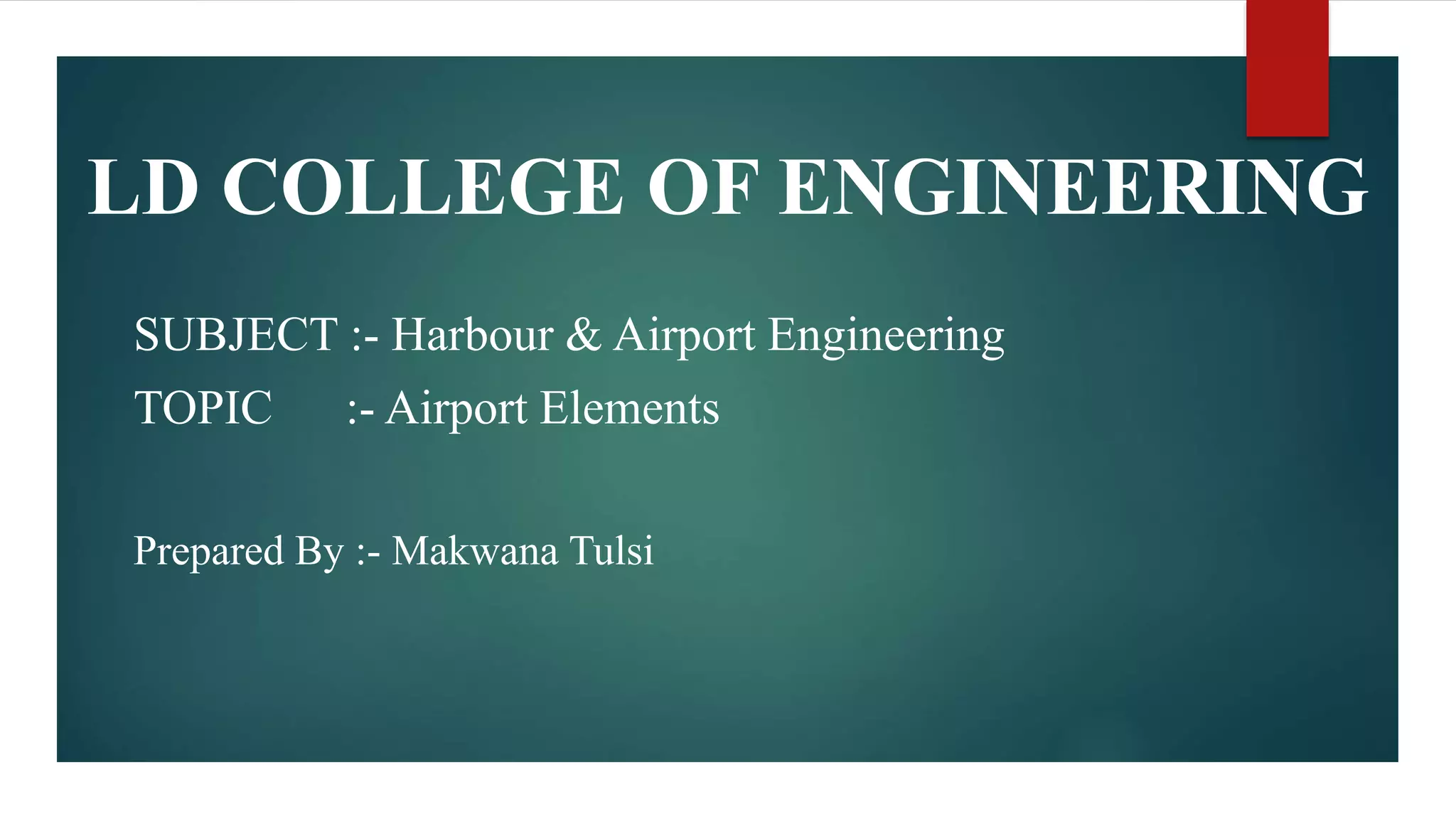
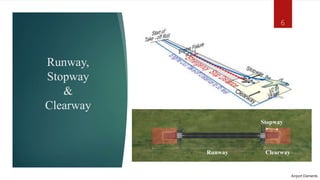
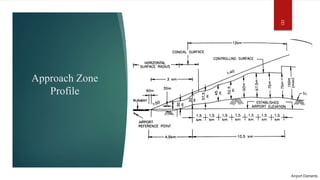
This document discusses the key elements of an airport, including runways, stopways, clearways, approach zones, land use, taxiways, aprons, terminal areas, and hangars. It provides details on each element, such as defining runways as cement landing strips for takeoffs and landings, stopways as paved areas at the end of runways for aborted takeoffs, and clearways as areas beyond runways for dealing with engine failures. It also discusses approach zone obstructions, appropriate land uses around airports and heliports, the purpose of taxiways and aprons, what makes up a terminal area, and the uses and sizes of hangars.