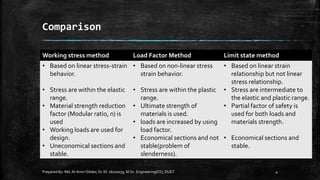
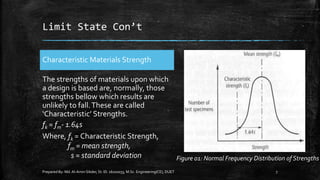
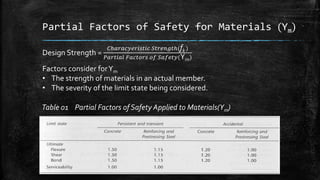
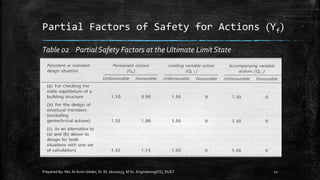
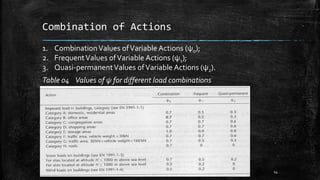
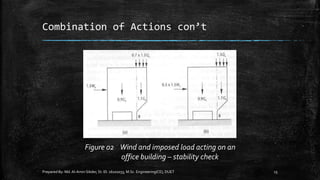
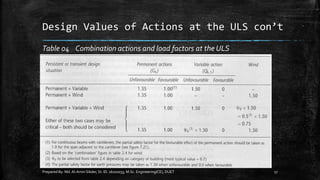
The document provides an introduction to limit state design in civil engineering, outlining its importance in ensuring structures are safe under worst loadings and function effectively during regular conditions. It describes various design methods, including permissible stress, load factor, and limit state methods, while detailing the characteristic strengths of materials and the significance of partial safety factors. Additionally, it discusses the two main types of limit states—ultimate limit state (ULS) and serviceability limit state (SLS)—and their implications for structural design.