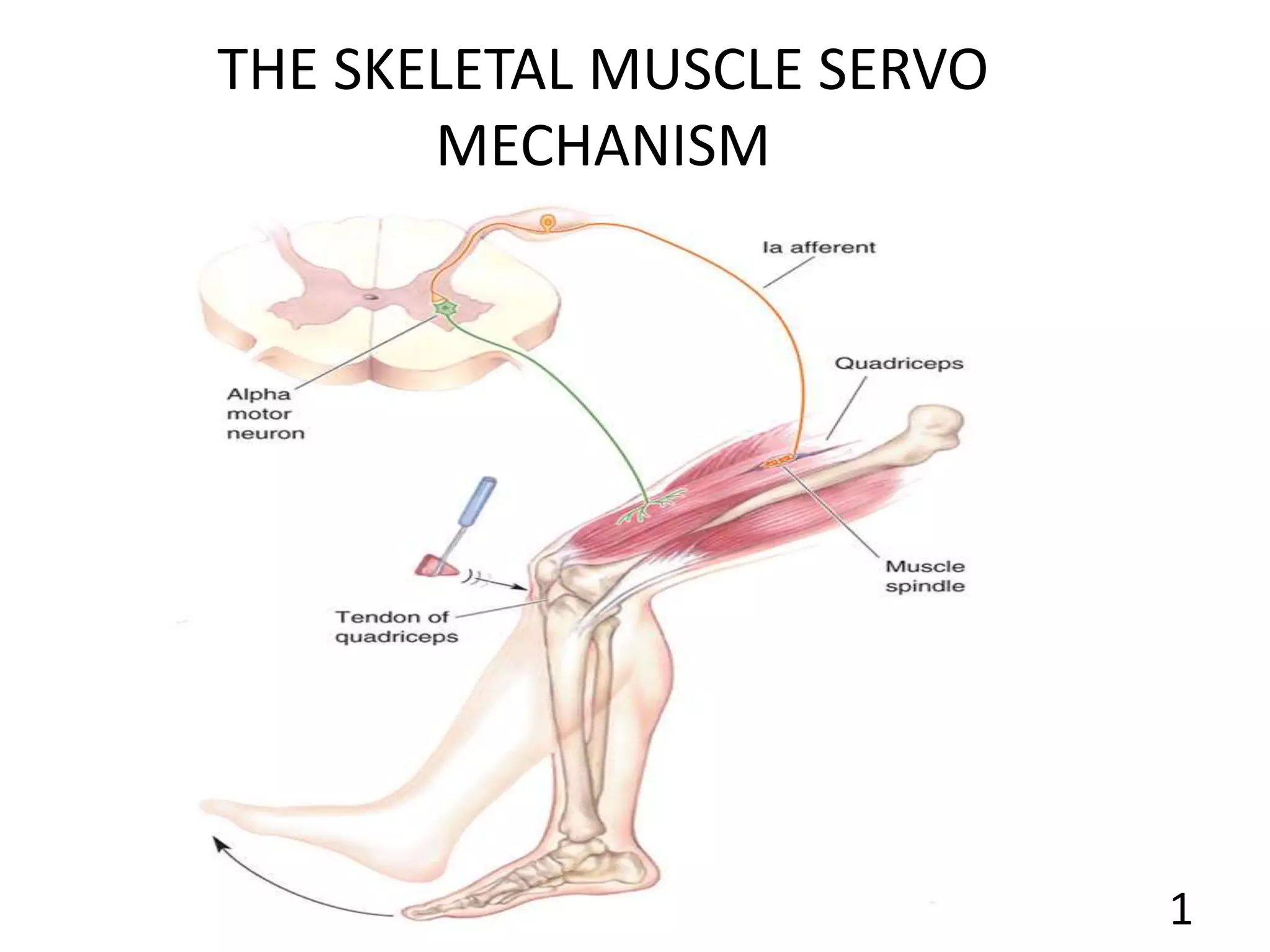
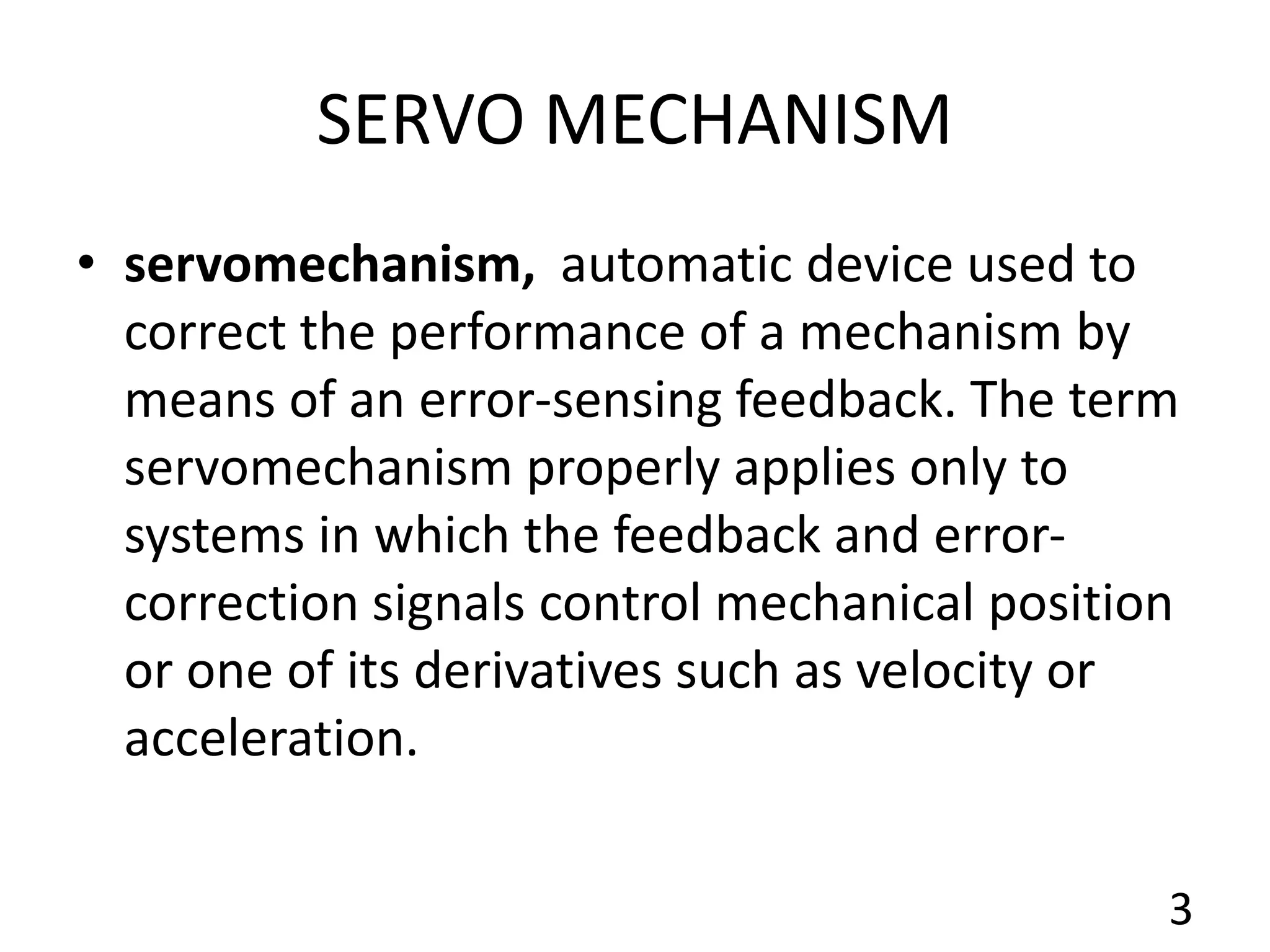
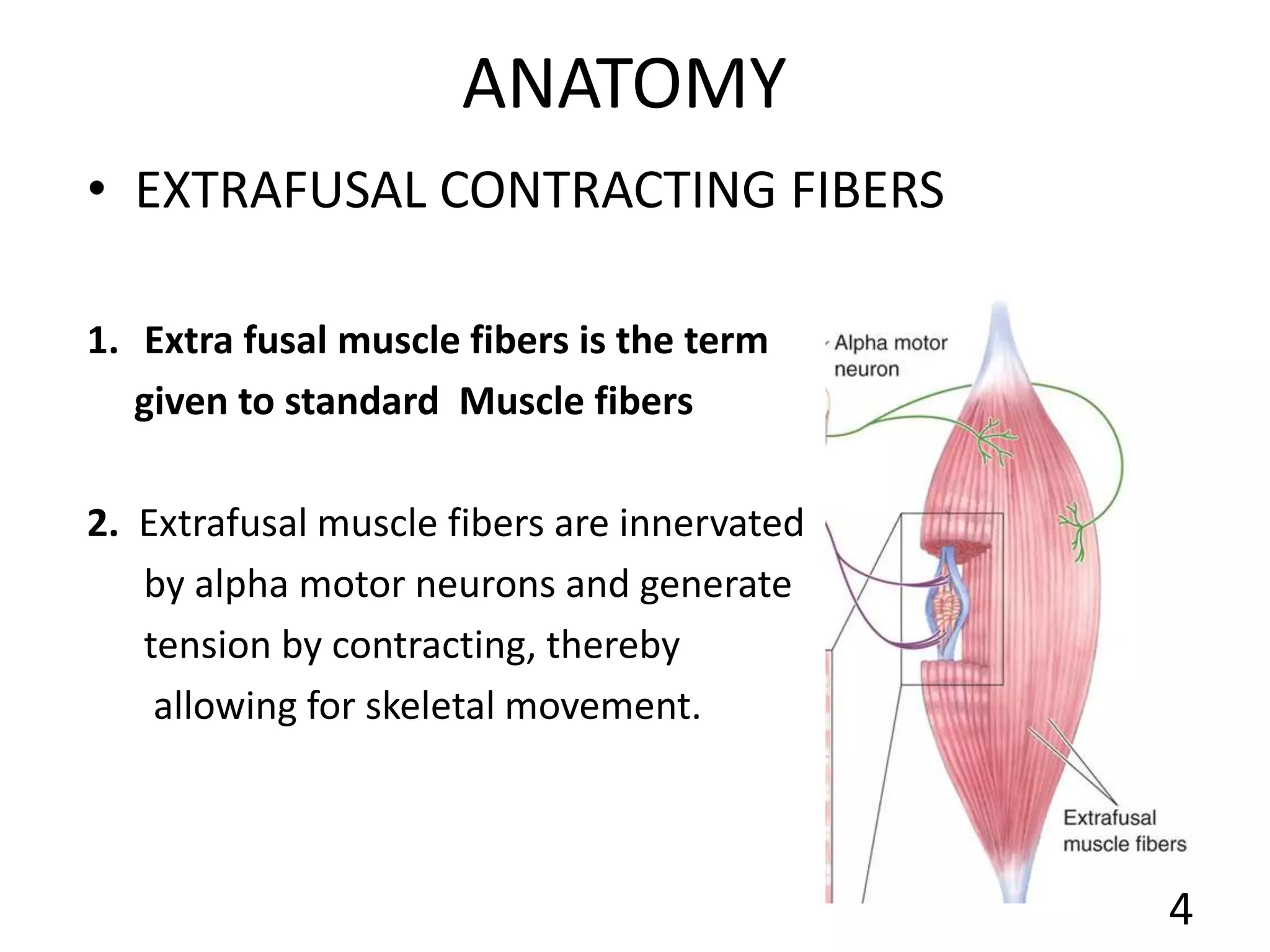
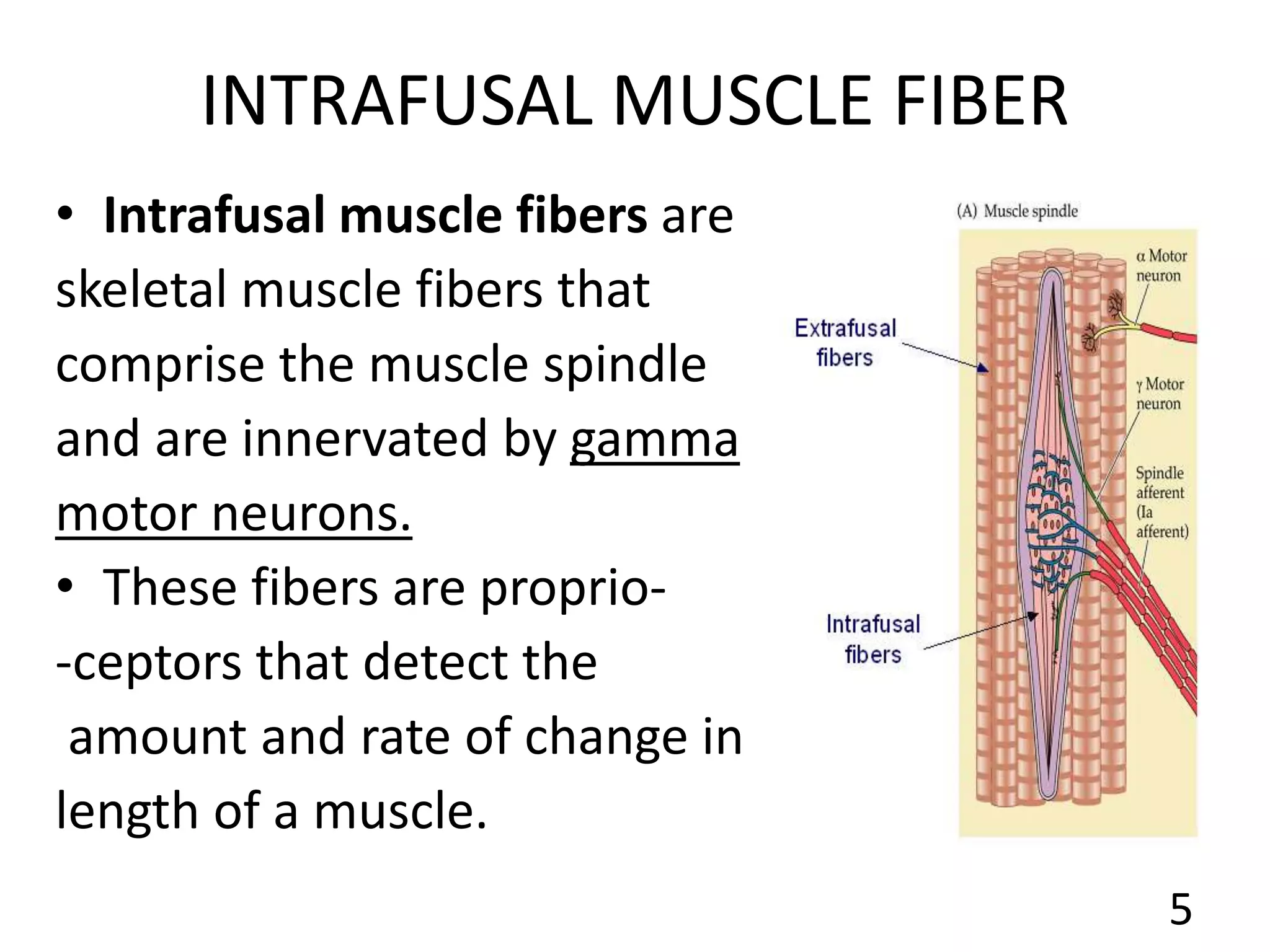
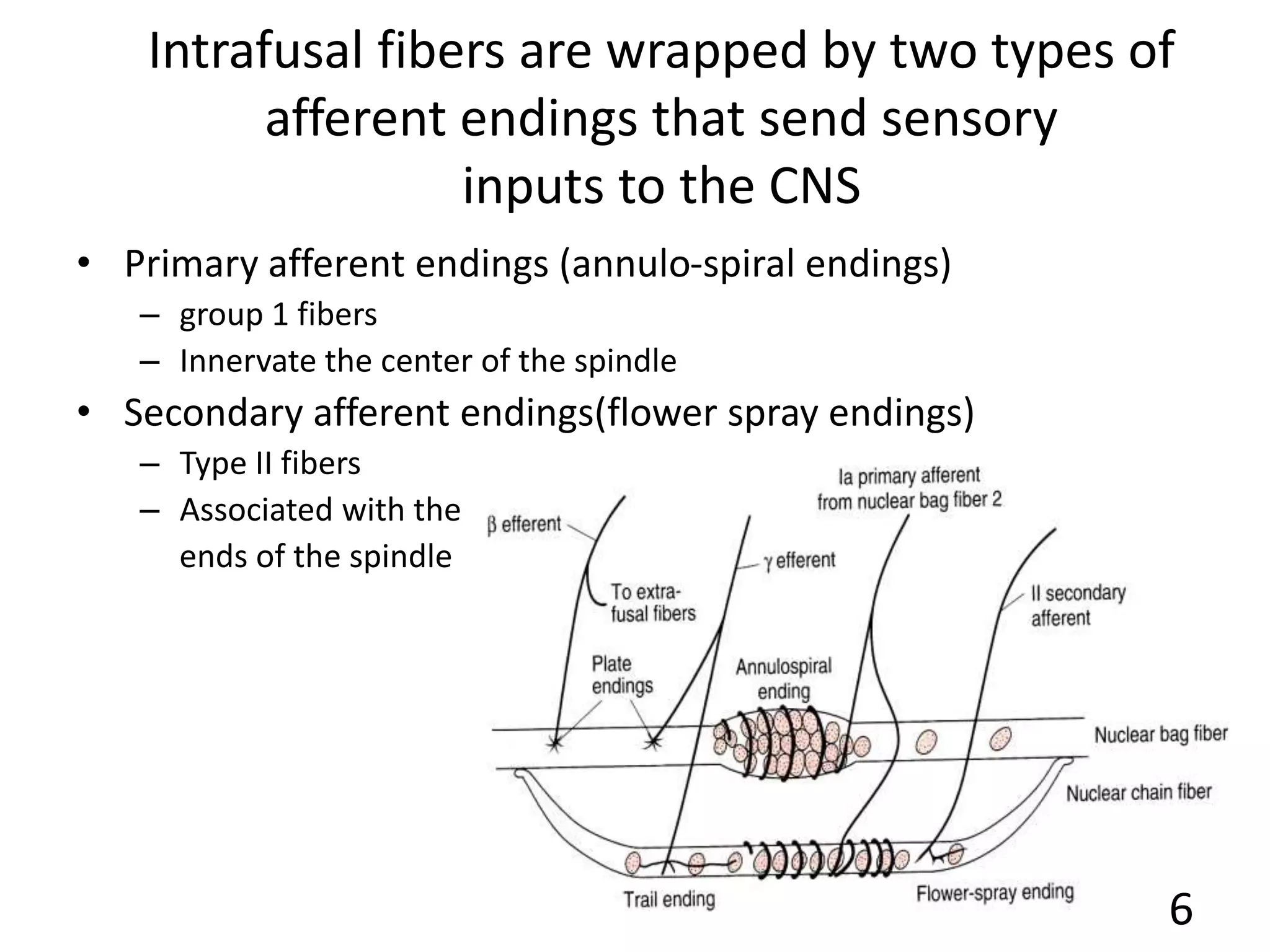
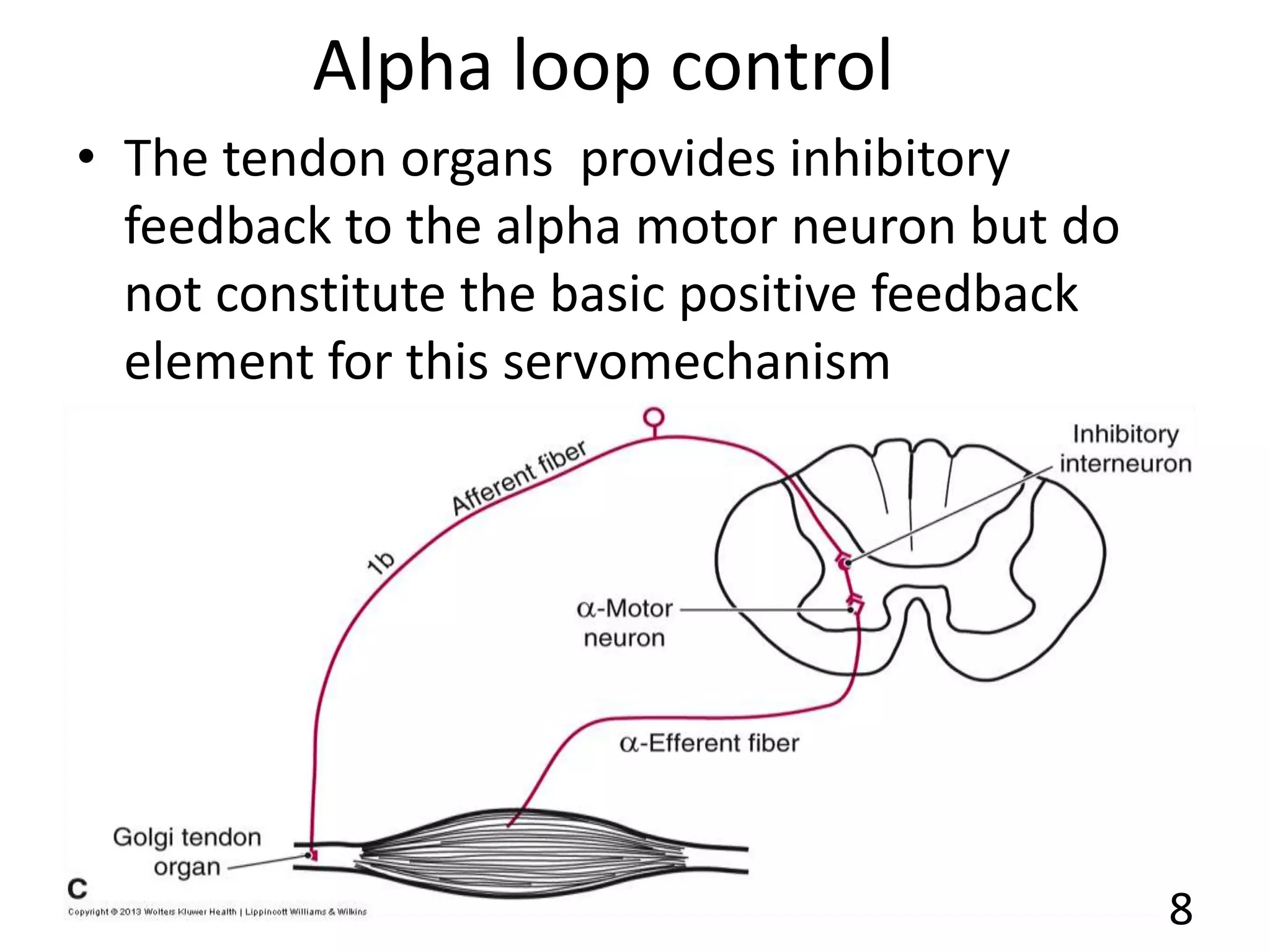
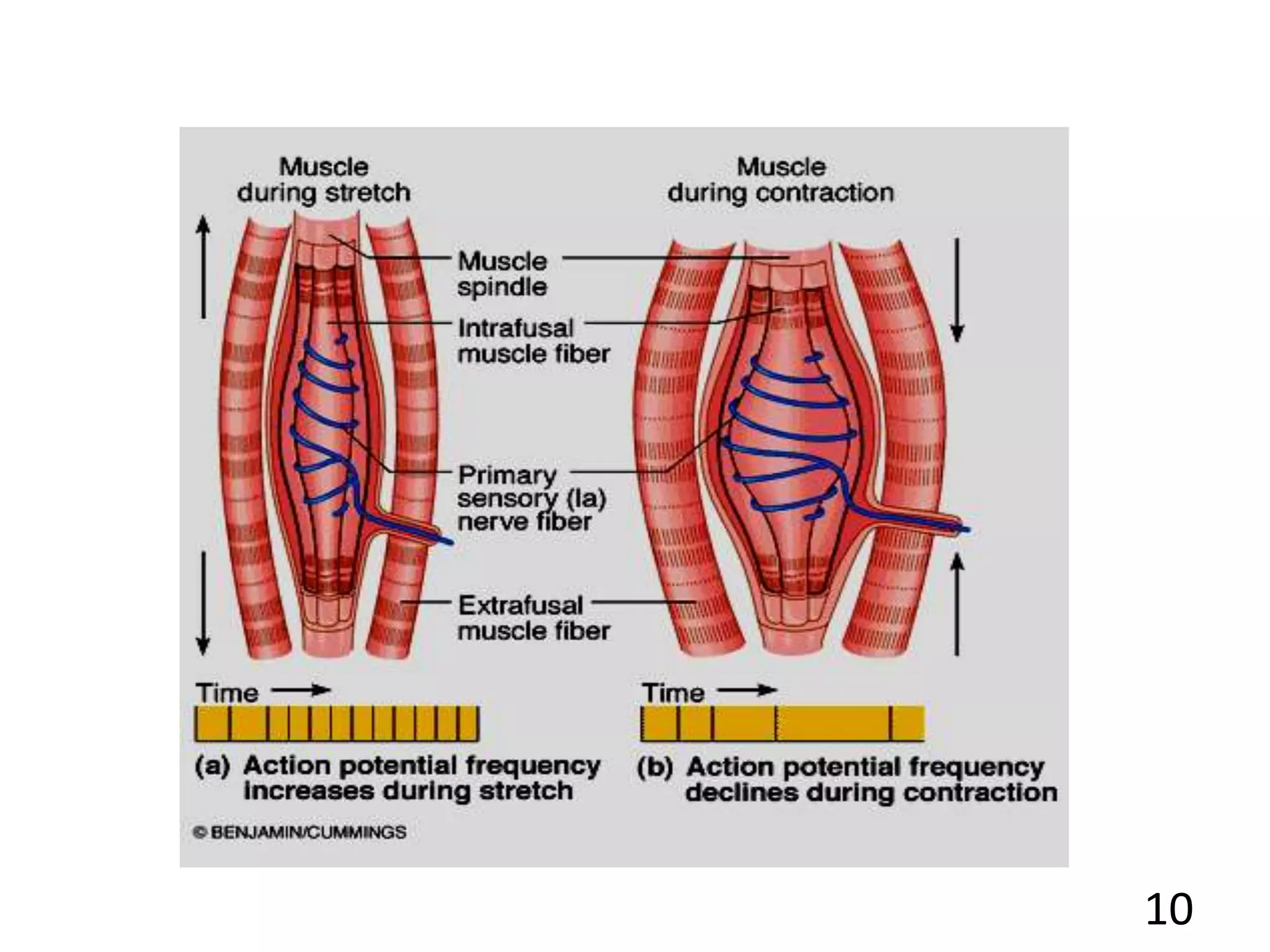
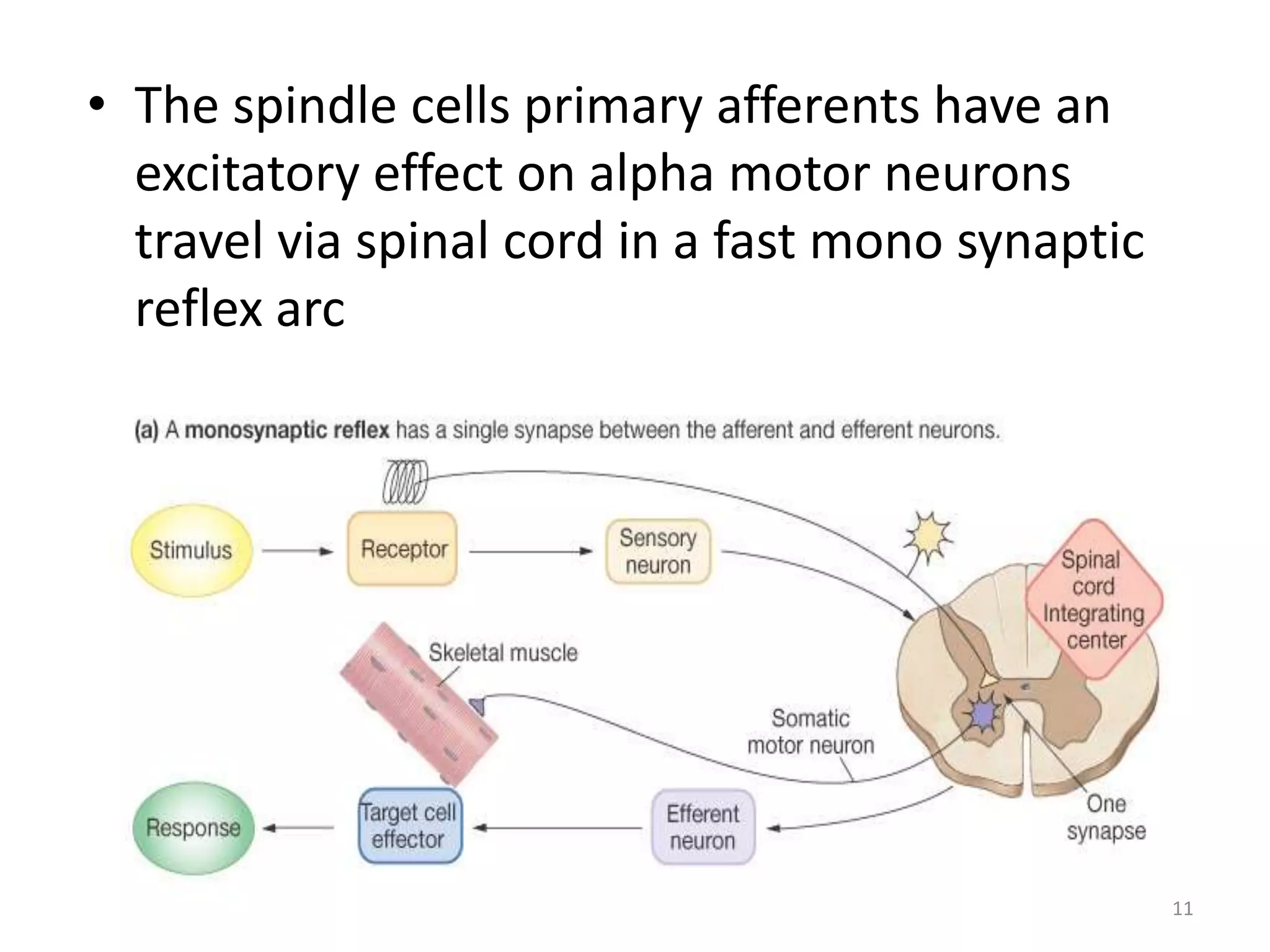
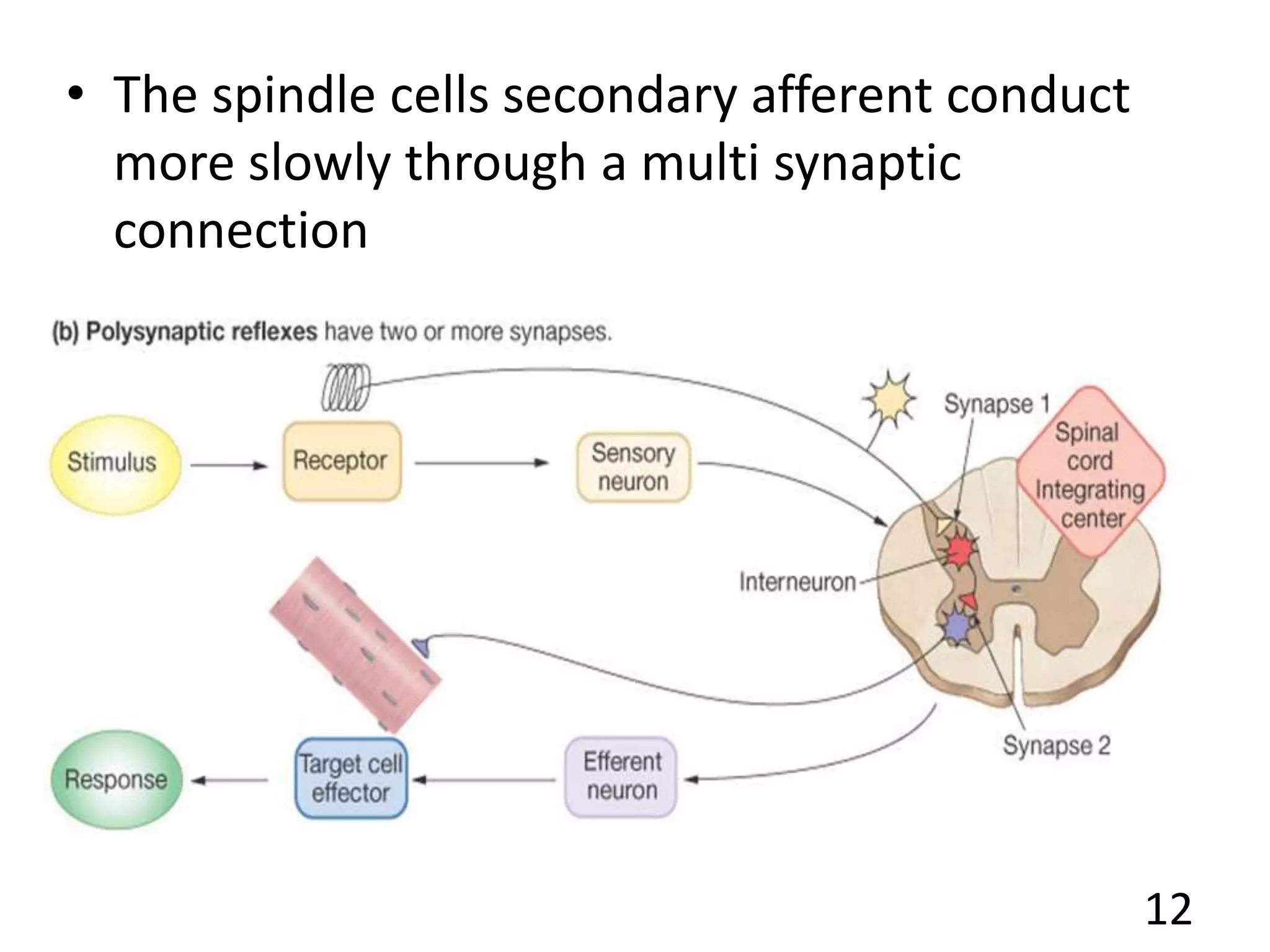
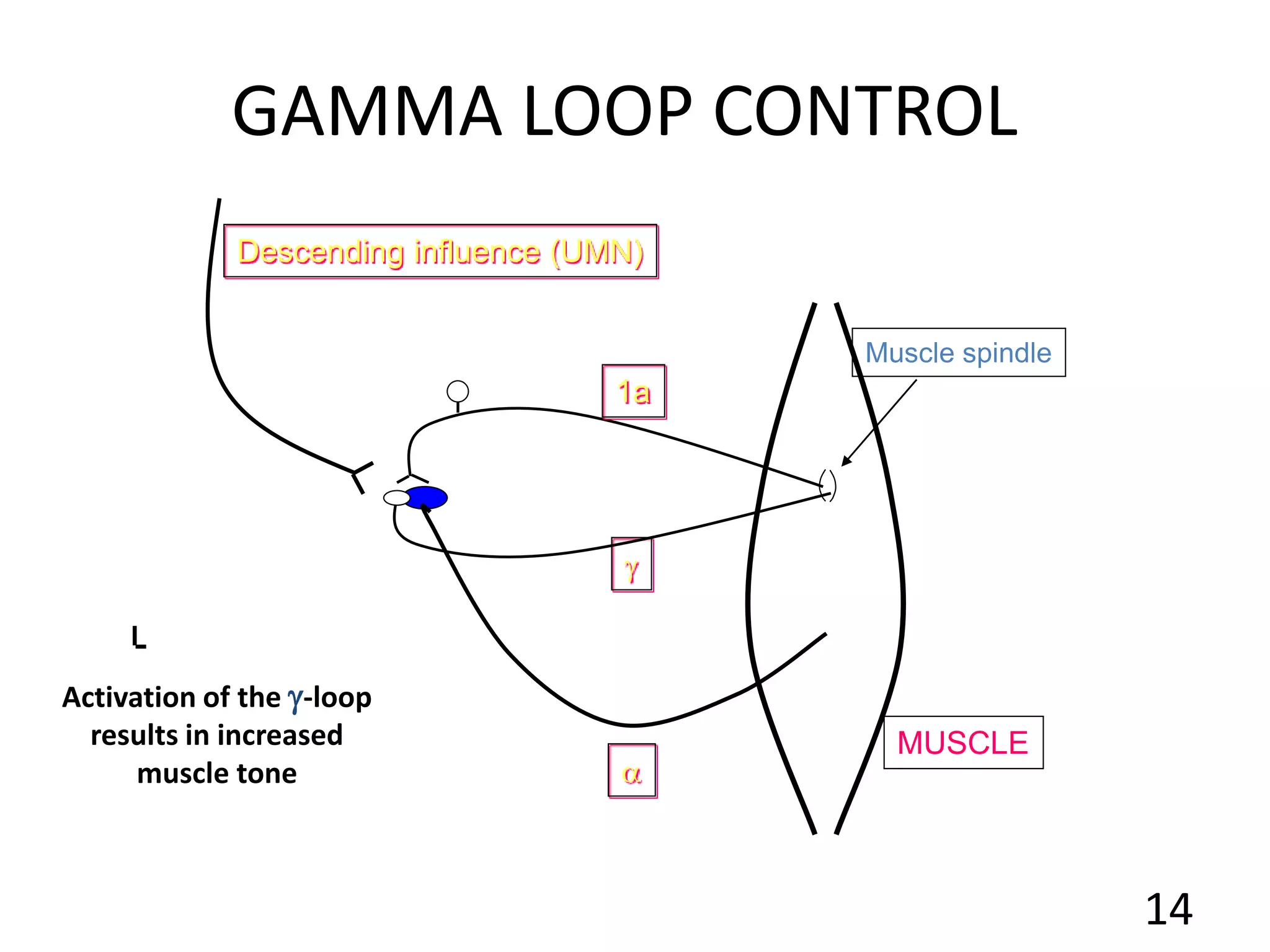
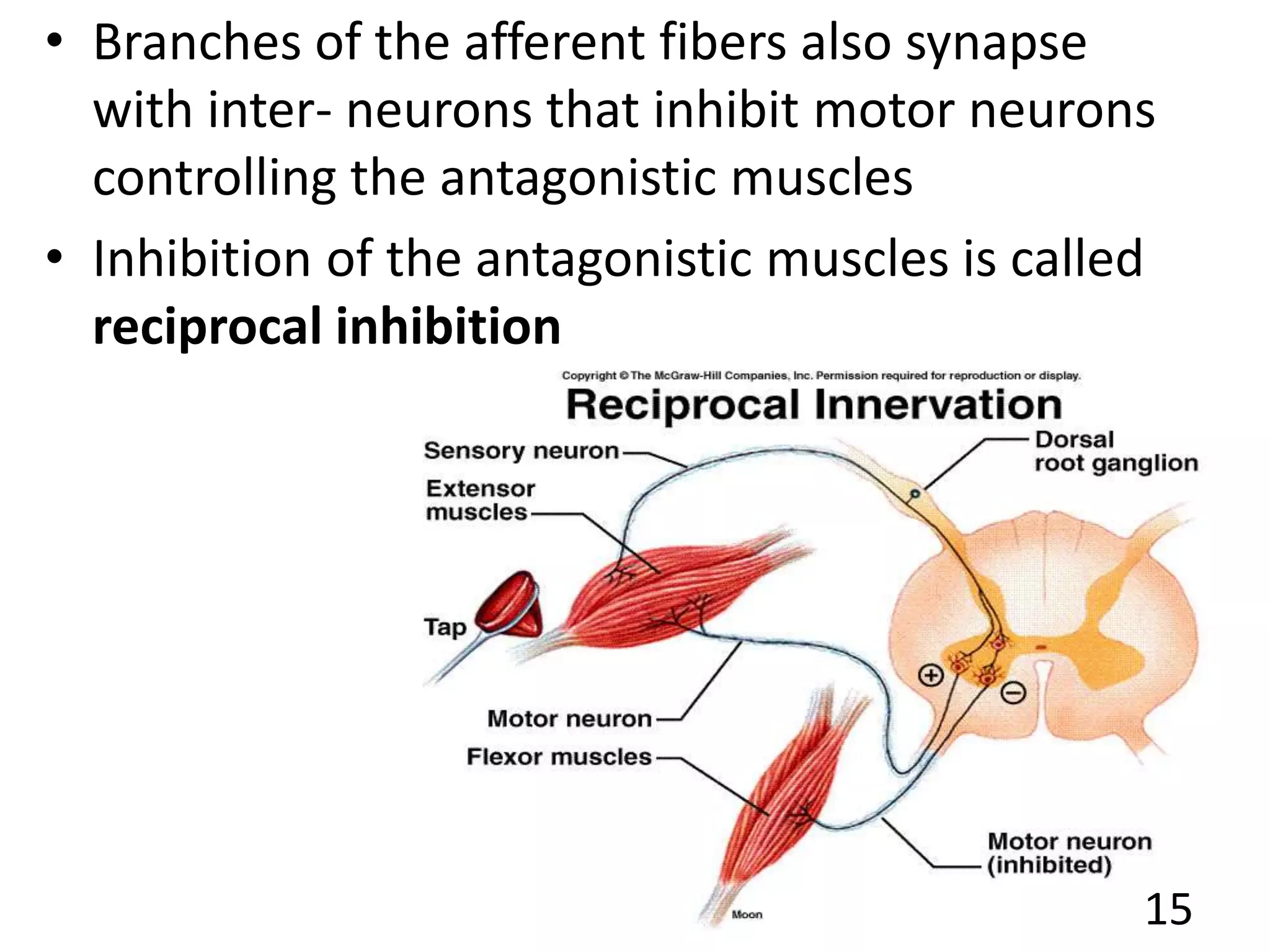
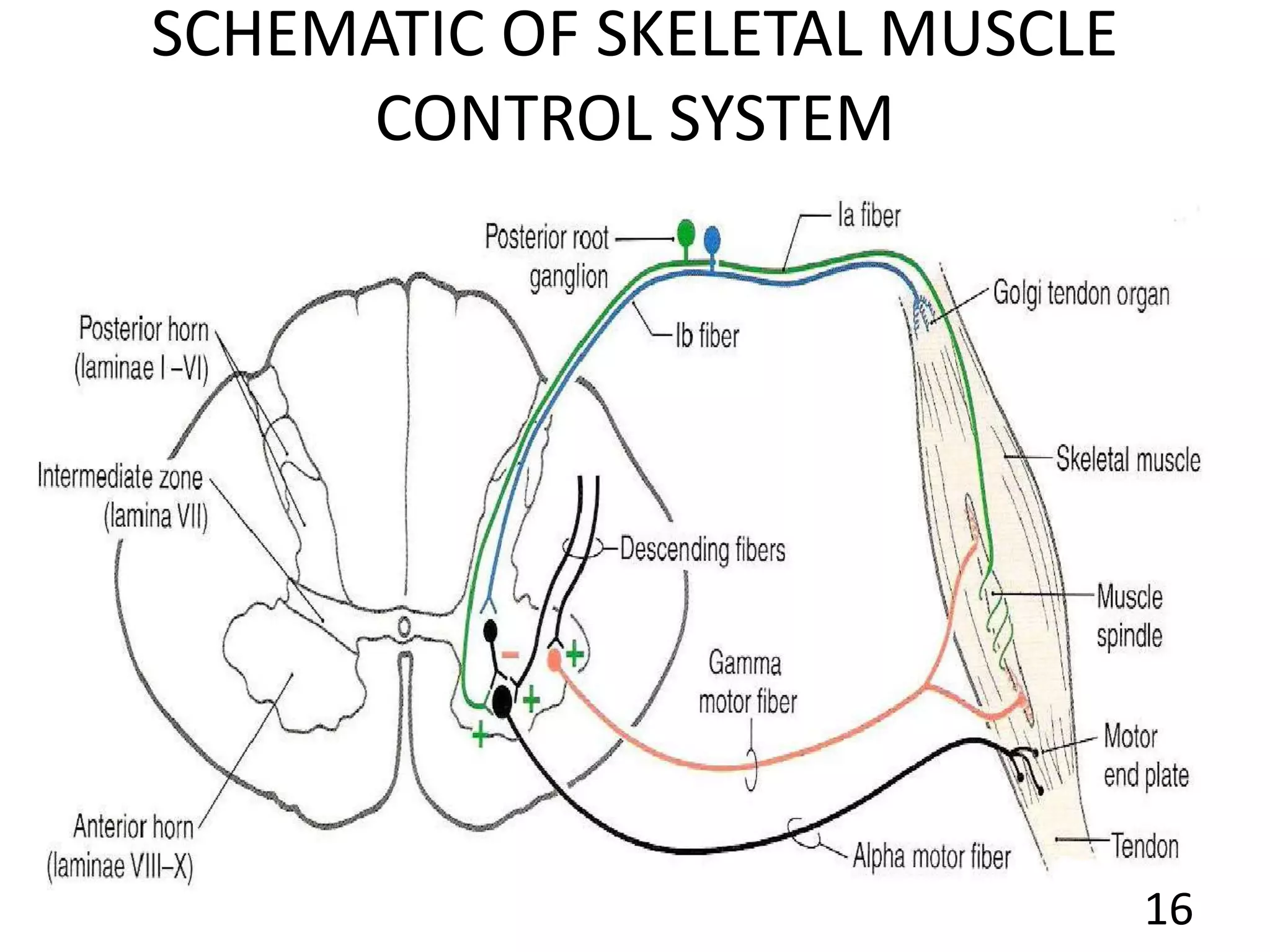
This document describes the skeletal muscle servo mechanism, which uses feedback loops to control muscle contraction and movement. It discusses the anatomy of extrafusal and intrafusal muscle fibers, with the latter comprising muscle spindles innervated by gamma motor neurons. Muscle spindles contain primary and secondary afferent endings that detect muscle length and rate of change. The alpha and gamma loops provide feedback to regulate motor neuron activity and maintain proper muscle tone and movement. The gamma loop activates intrafusal fibers, signaling changes in muscle length to the CNS via muscle spindle afferents.