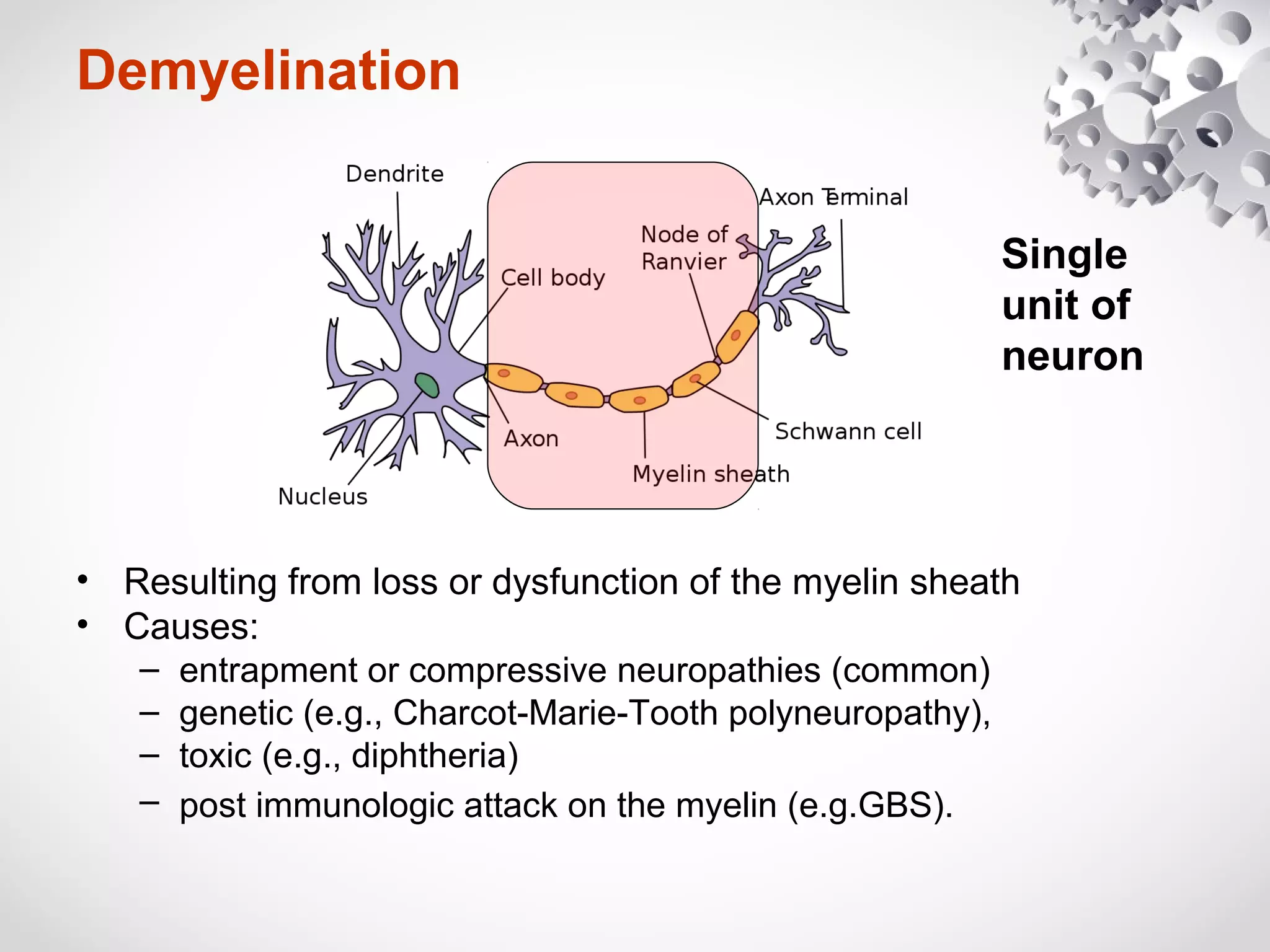
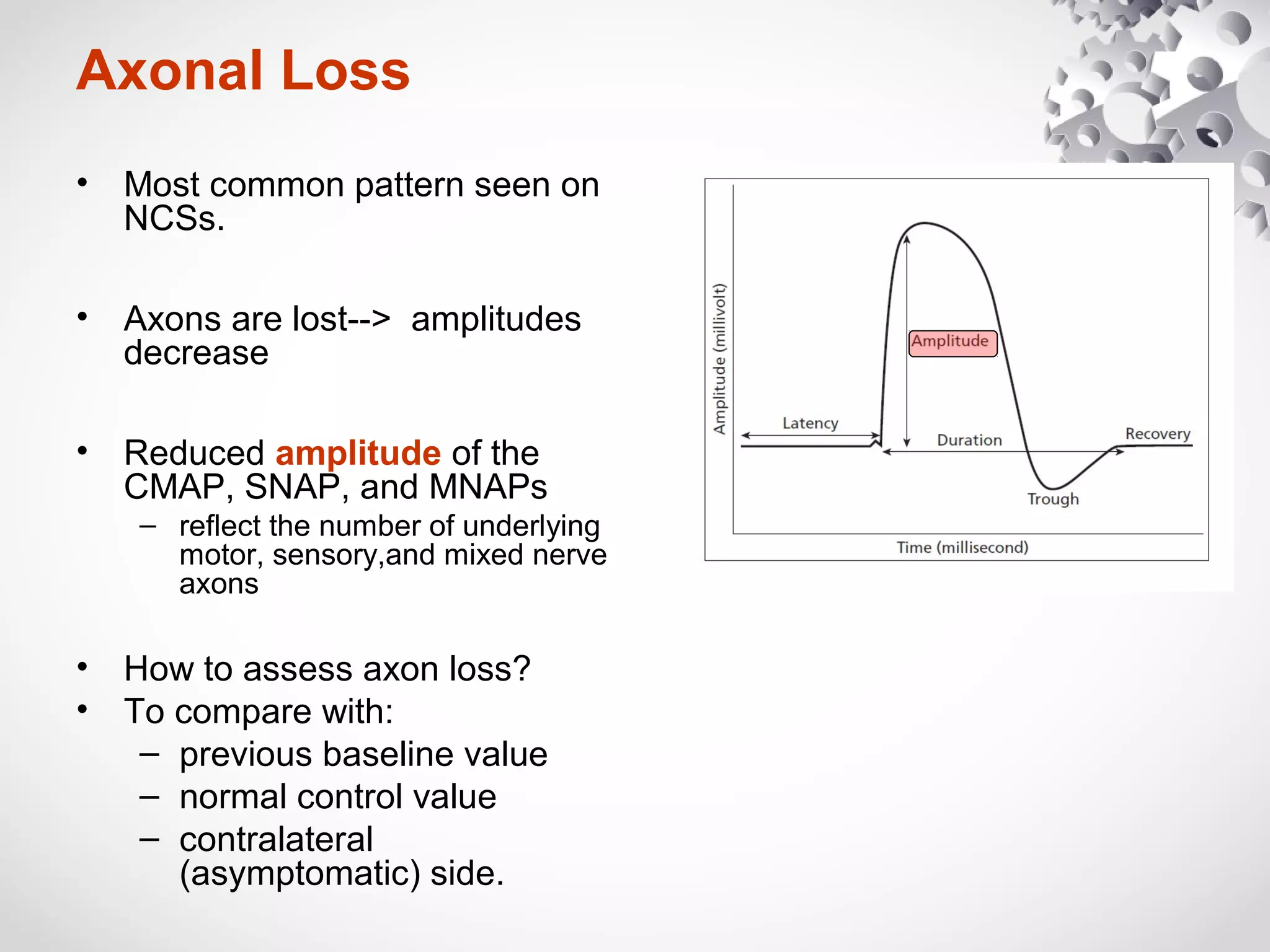
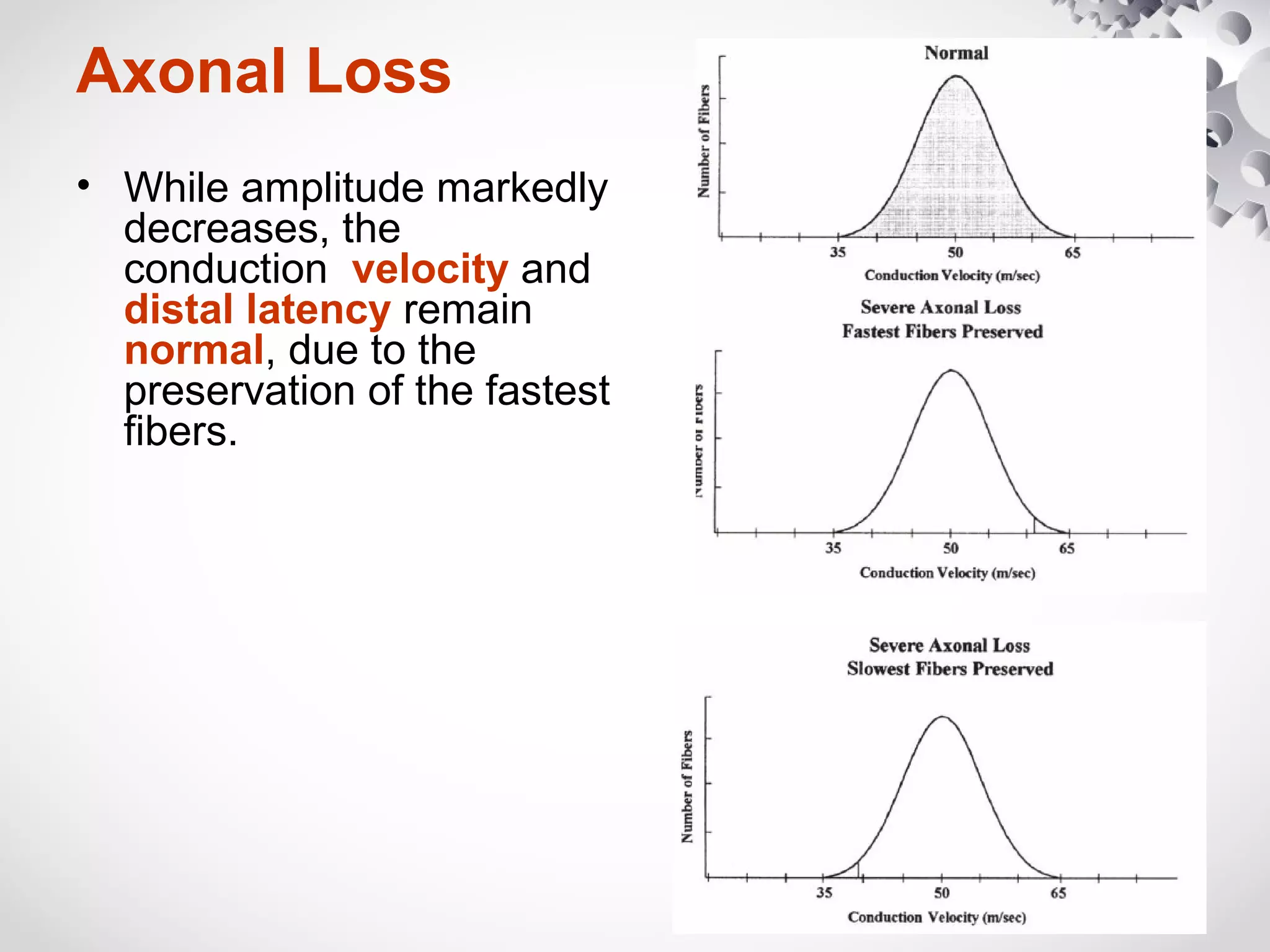
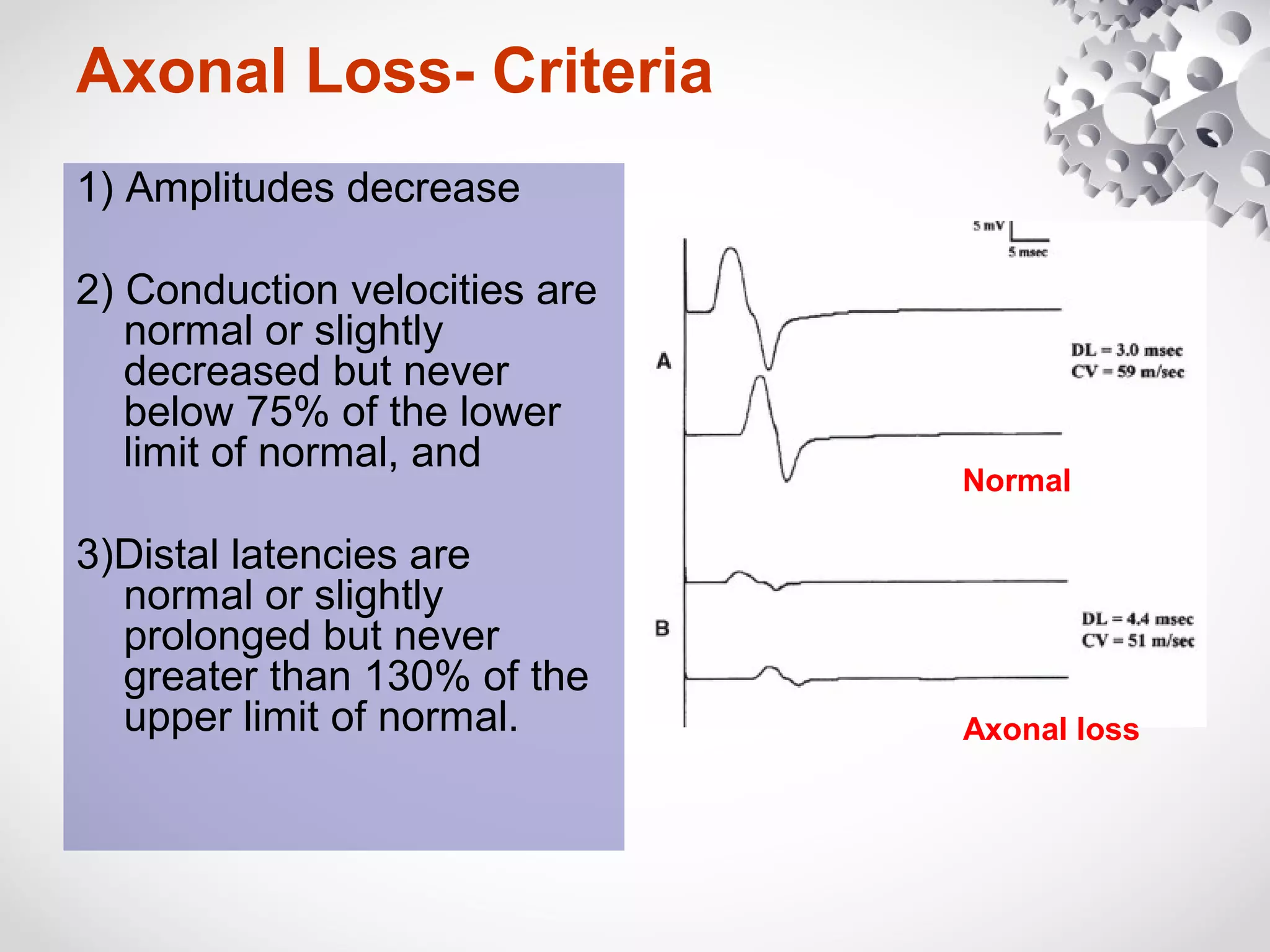
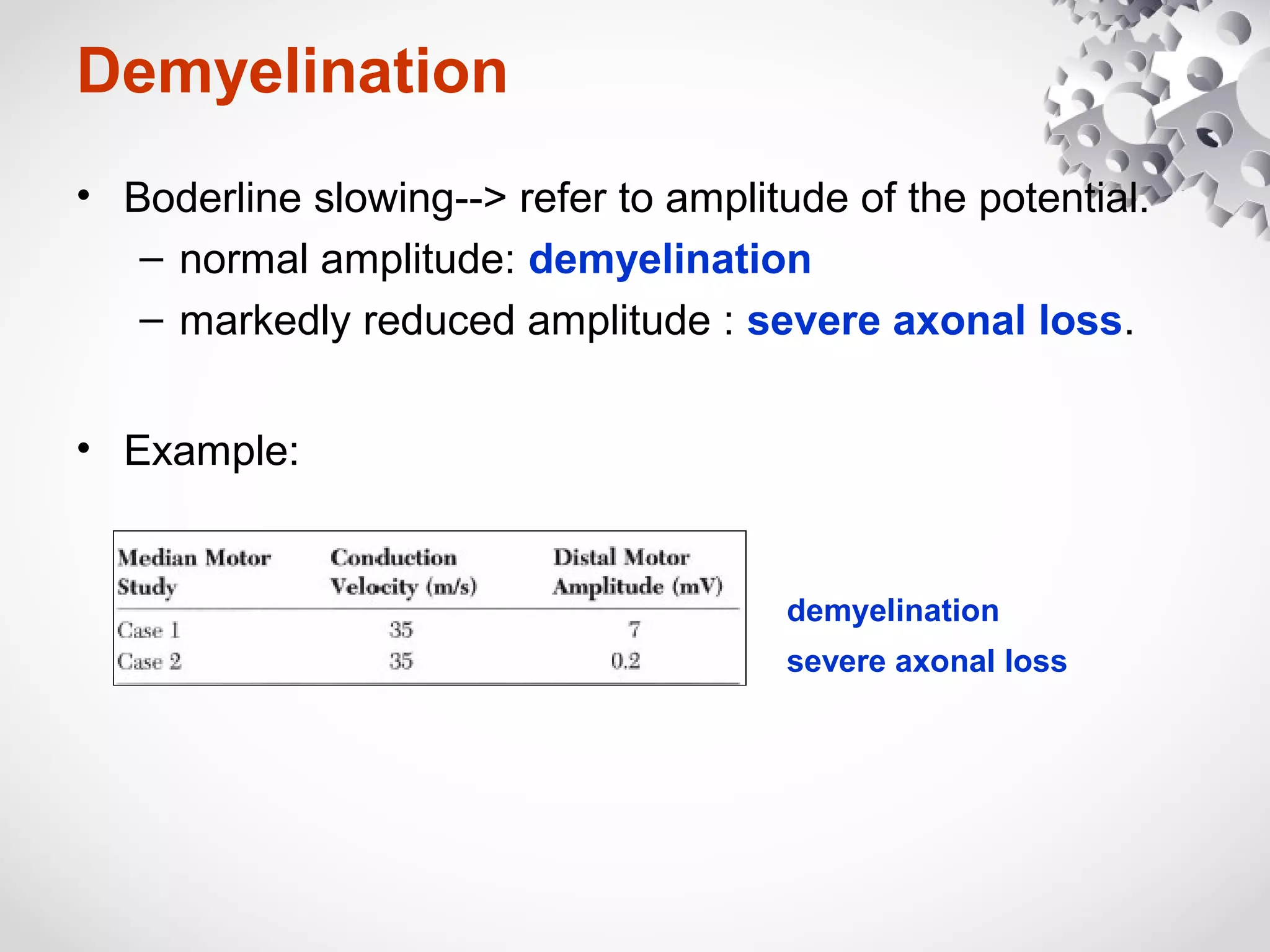
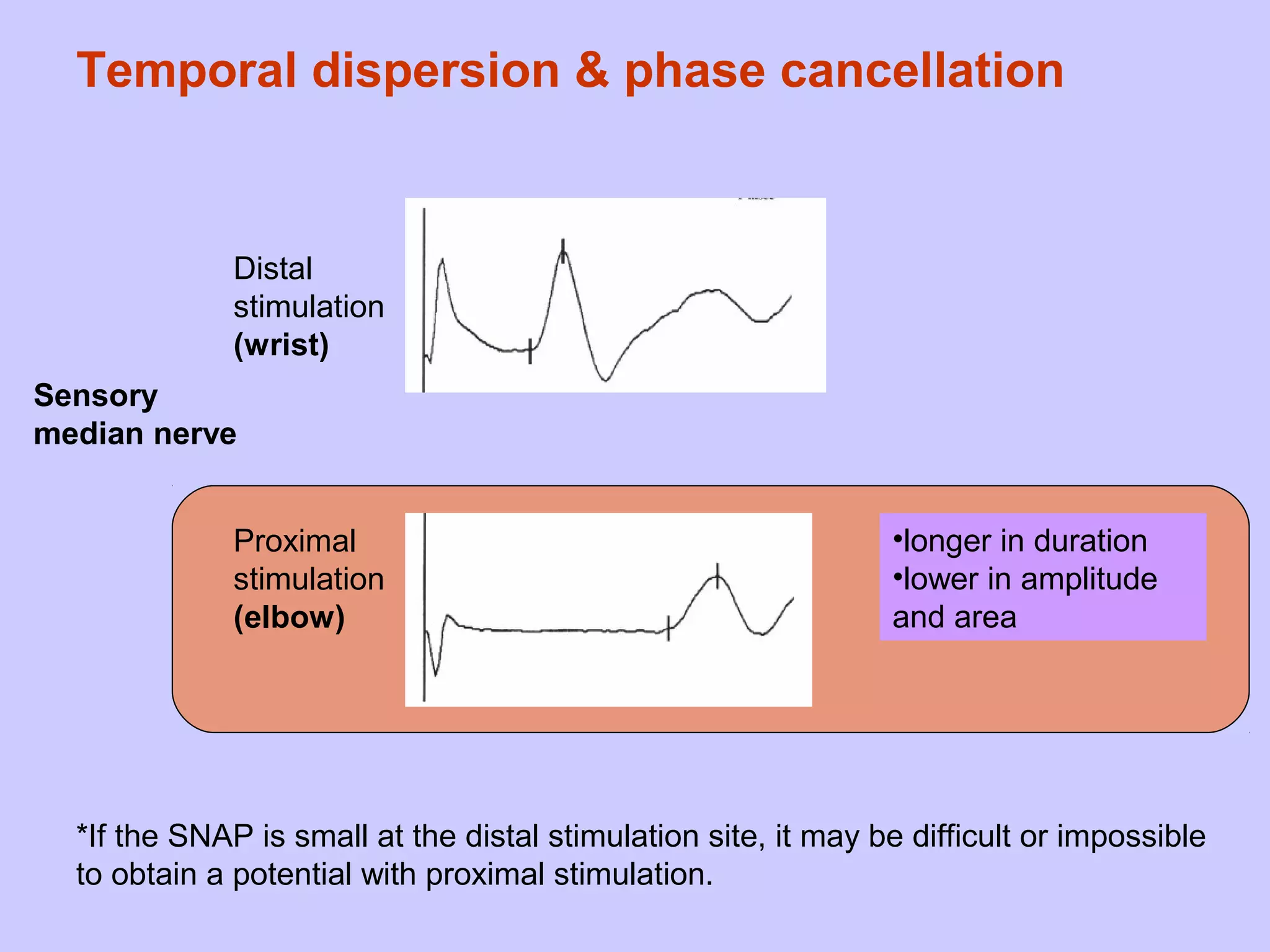
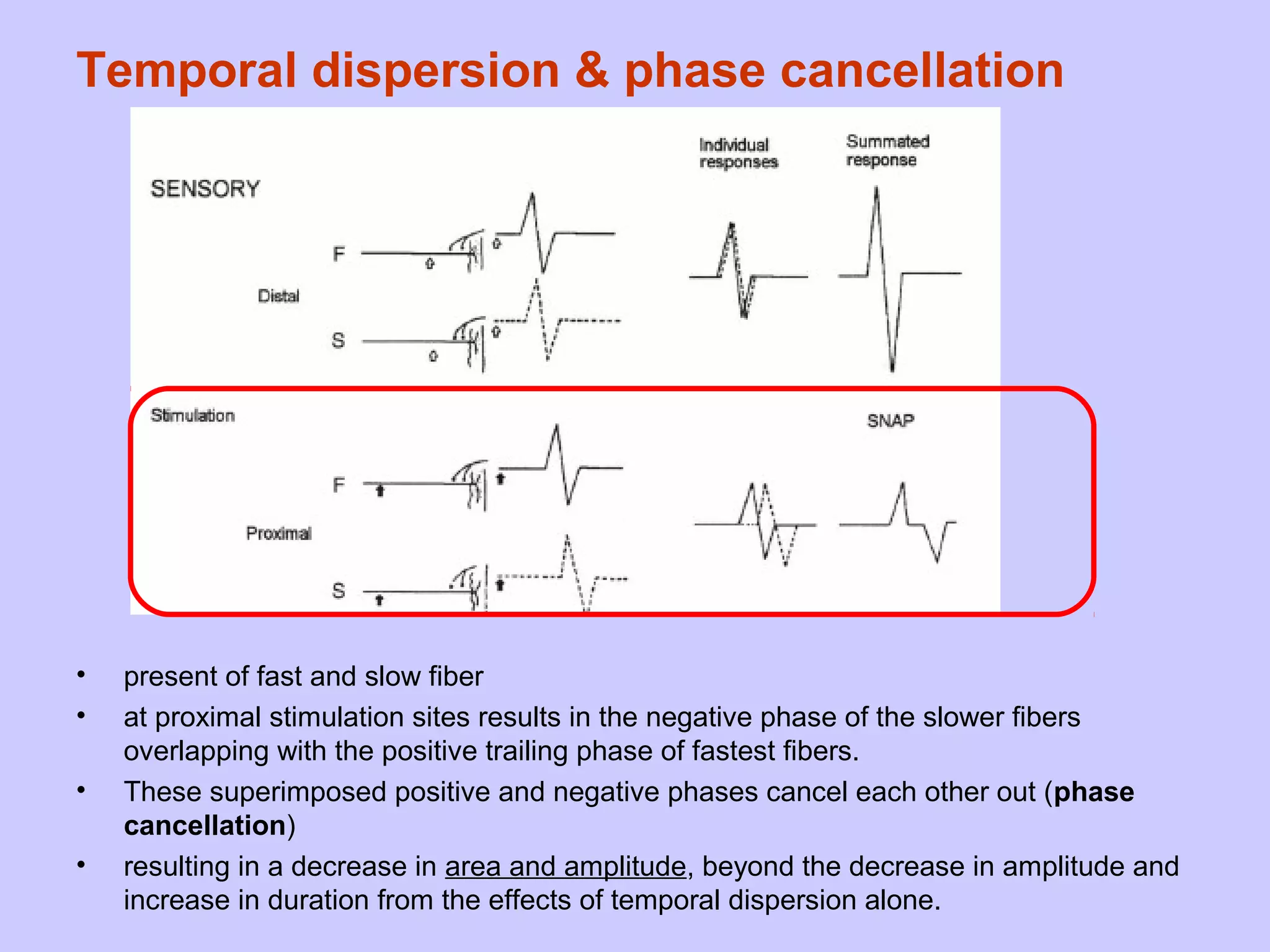
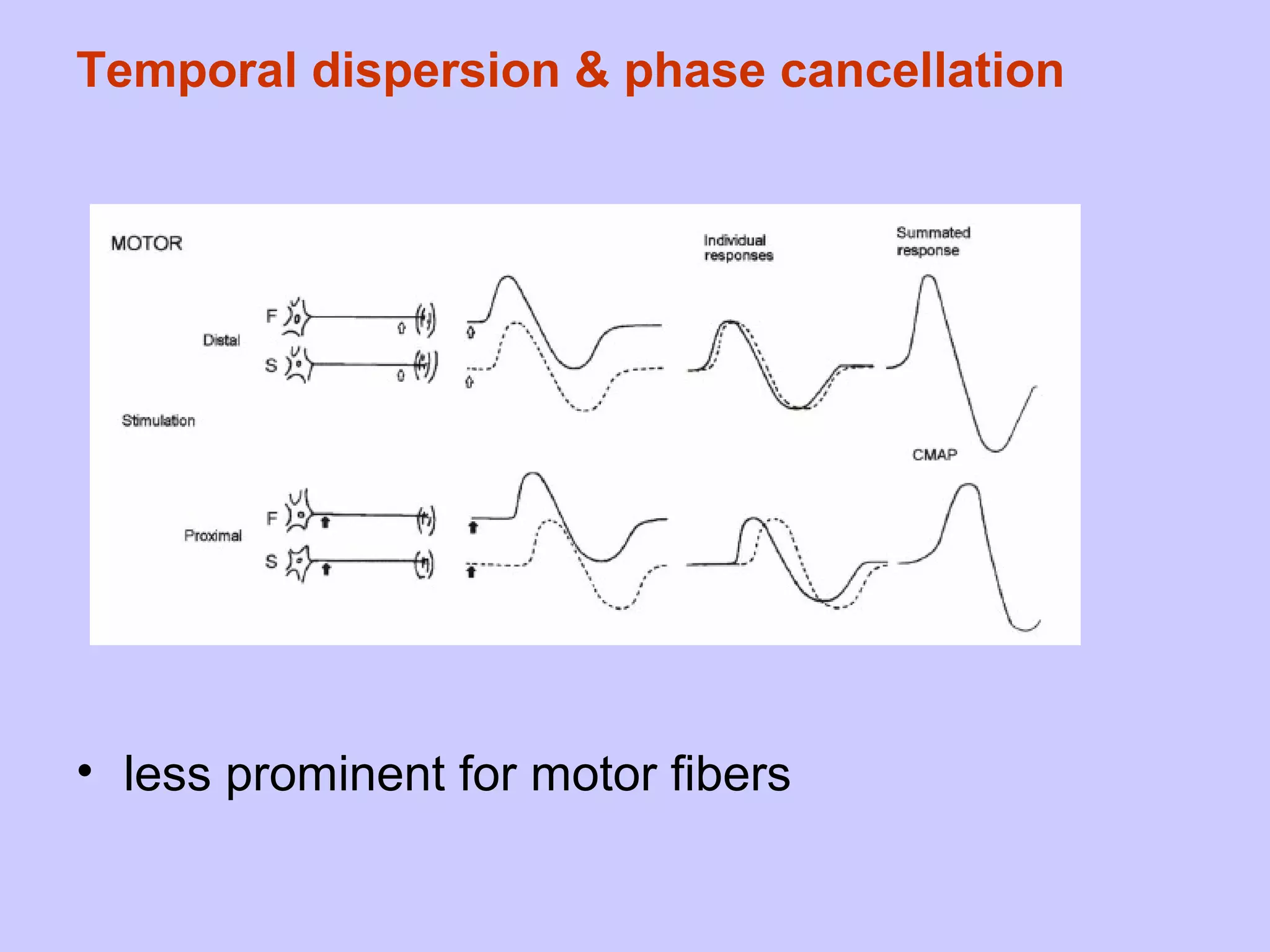
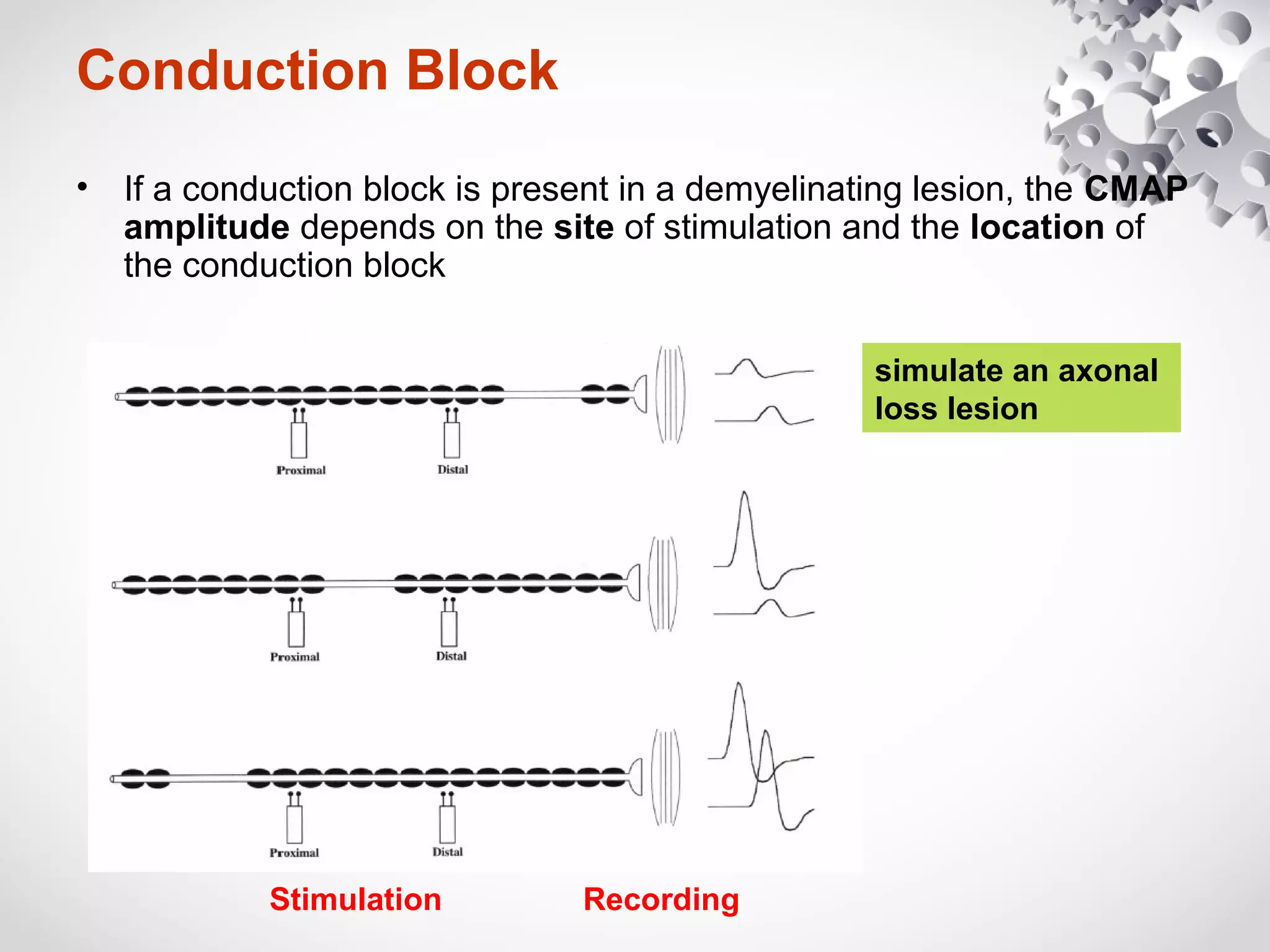
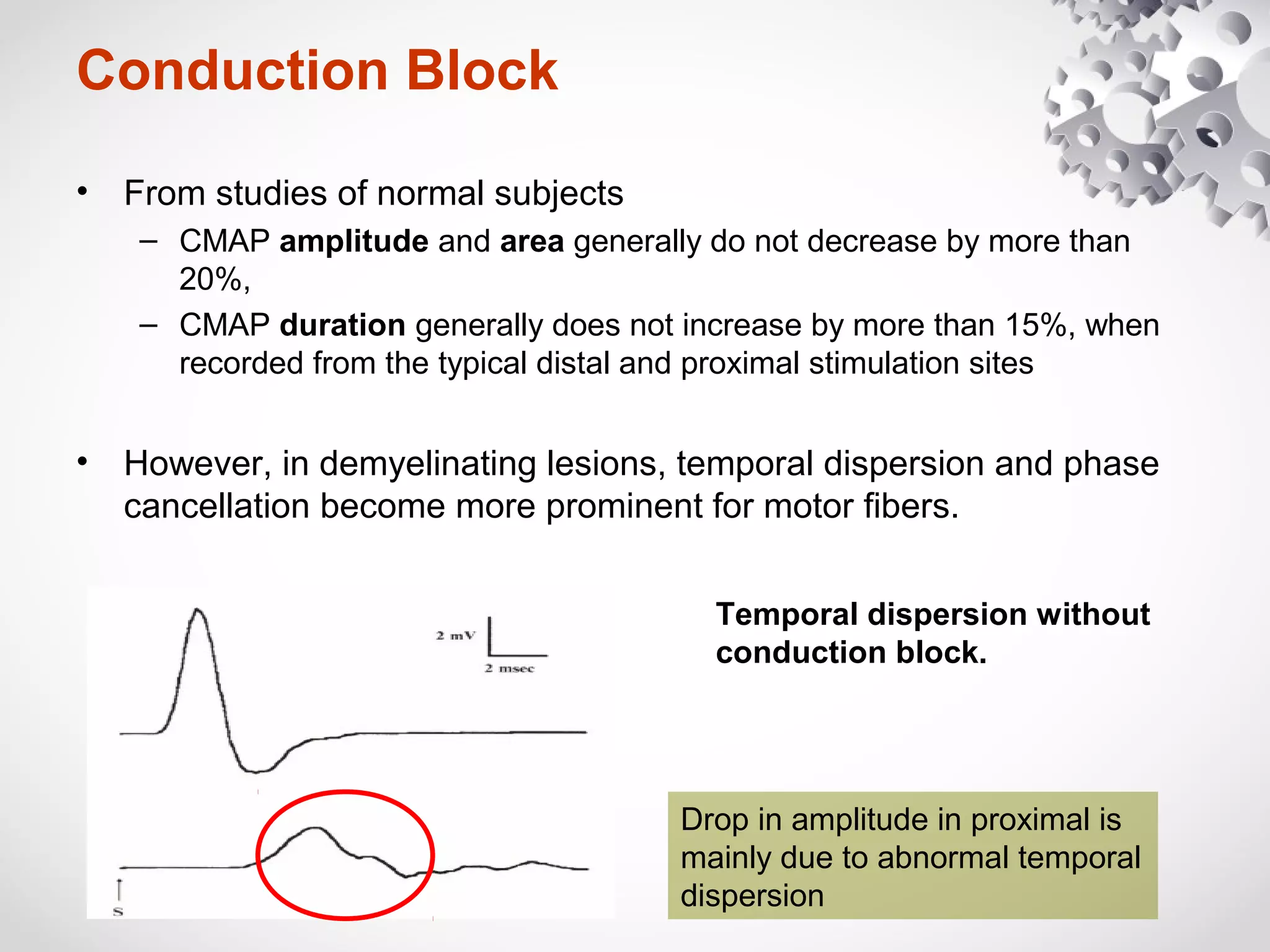
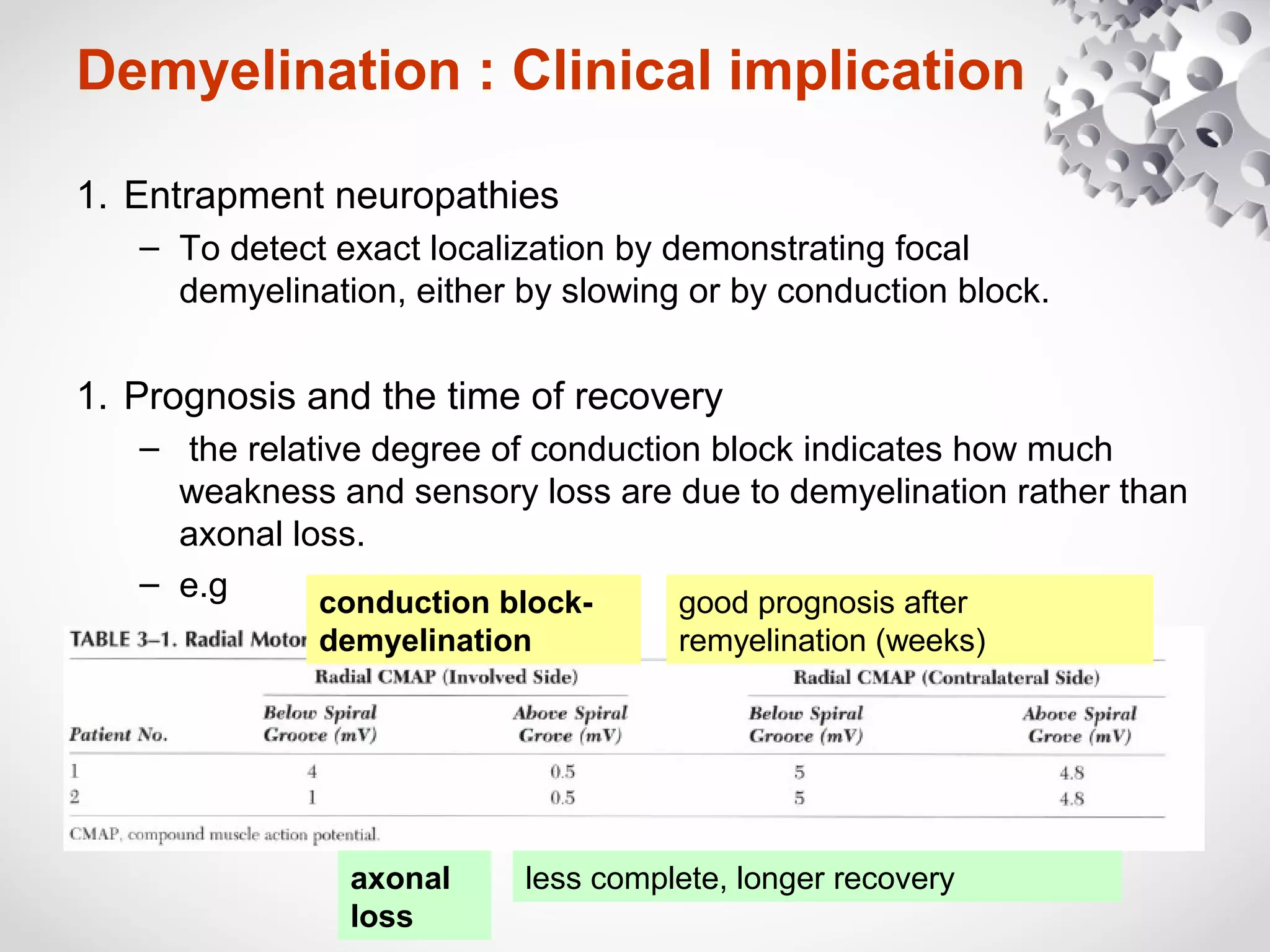
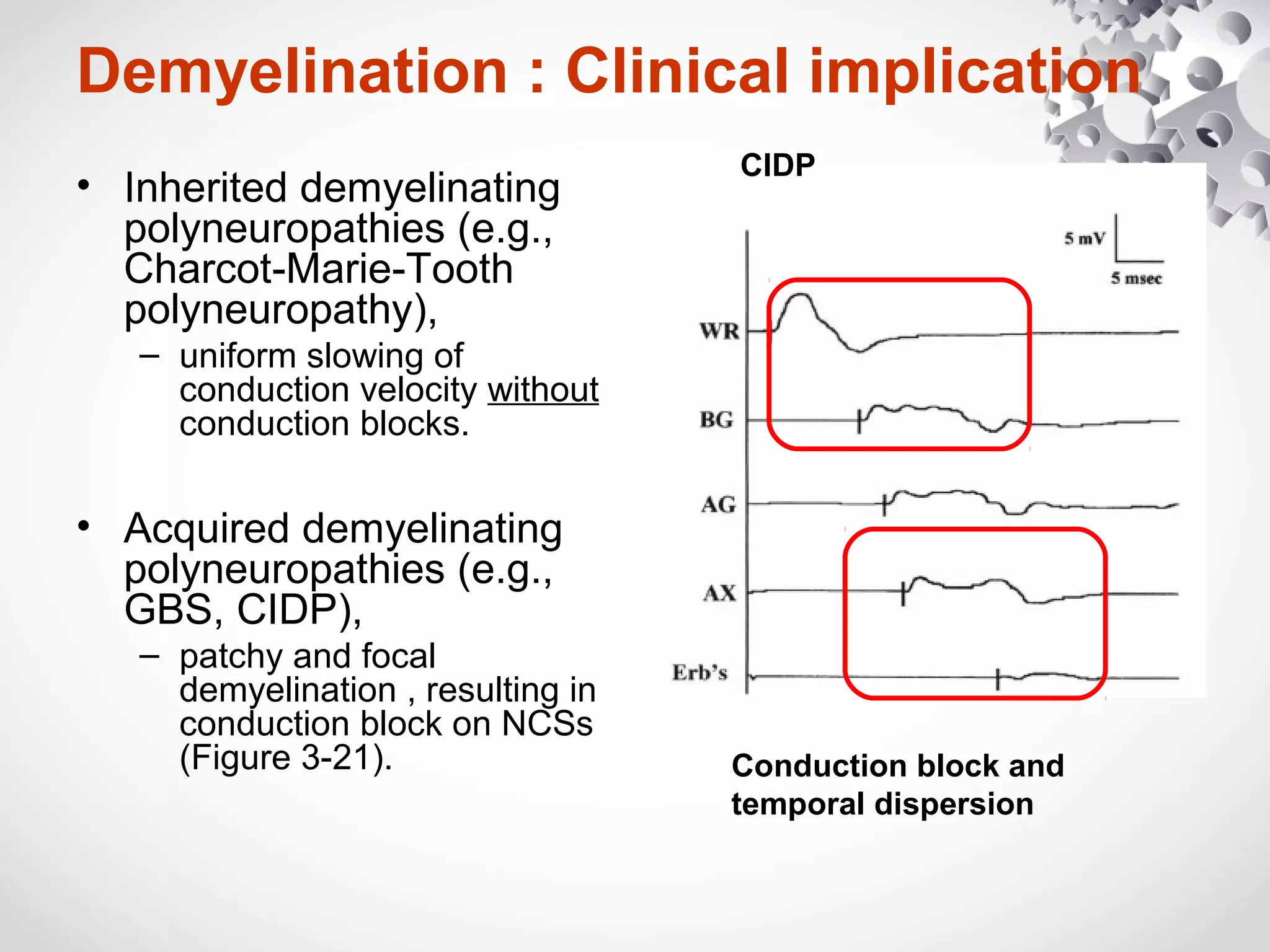
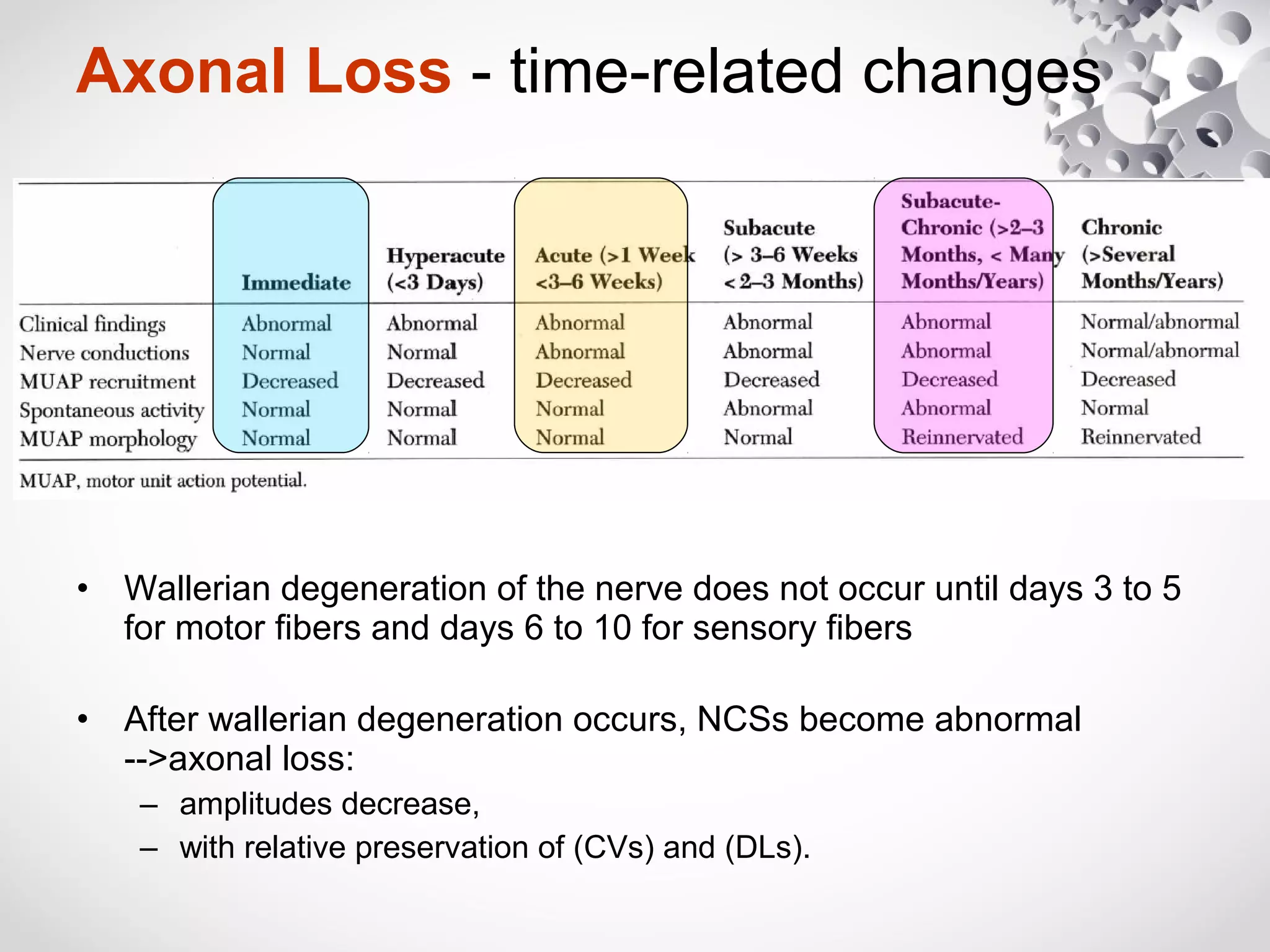
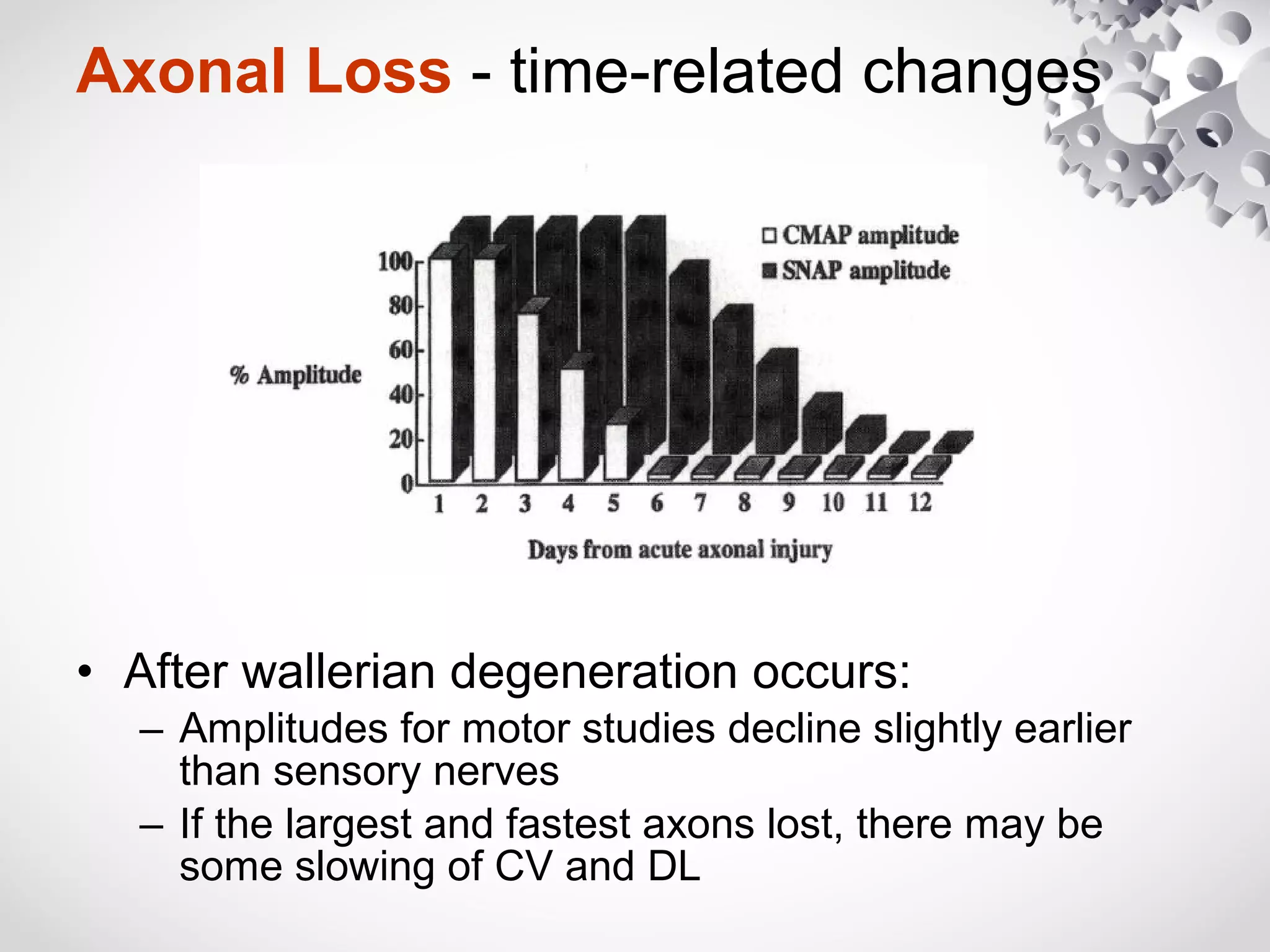
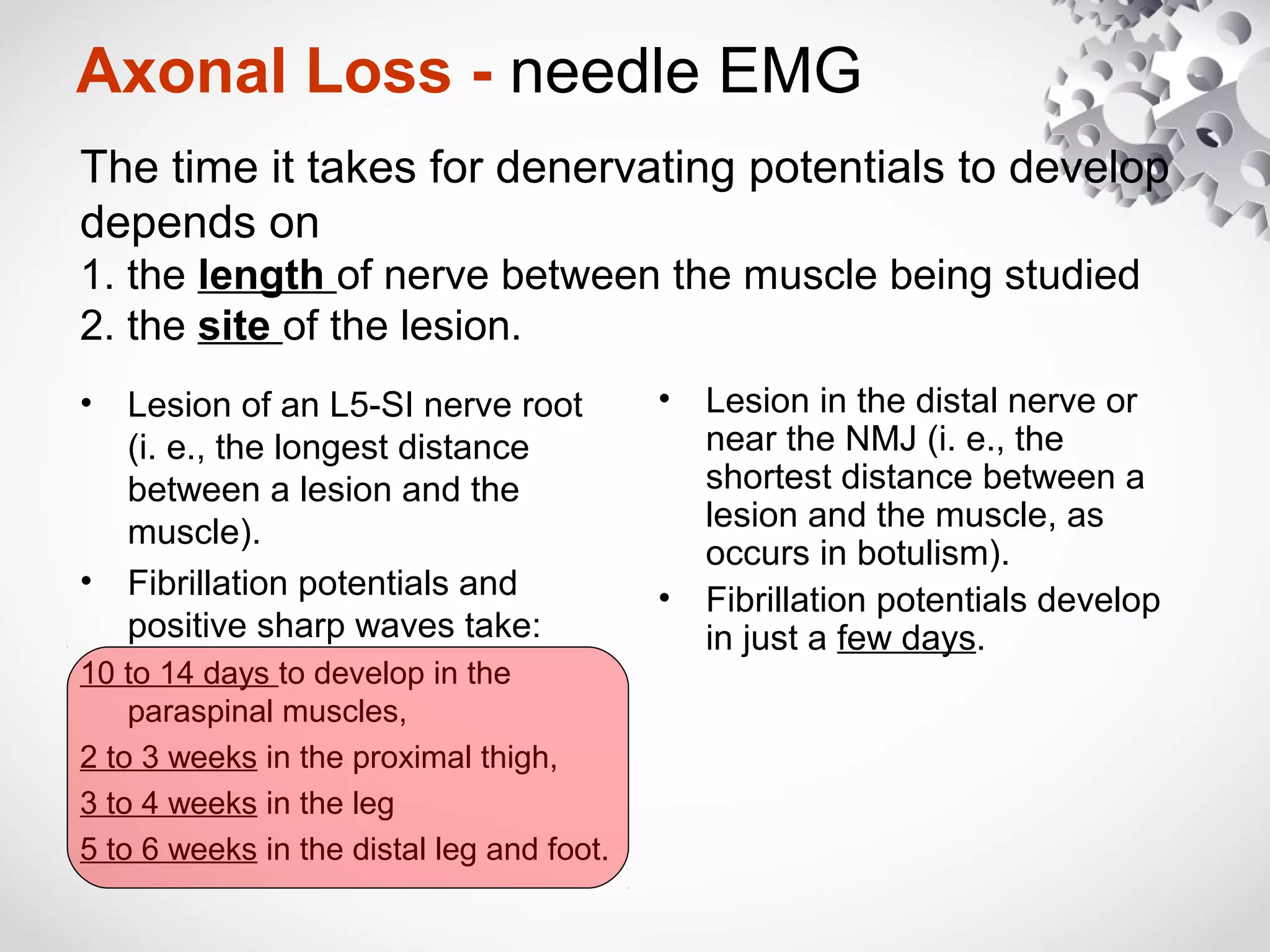
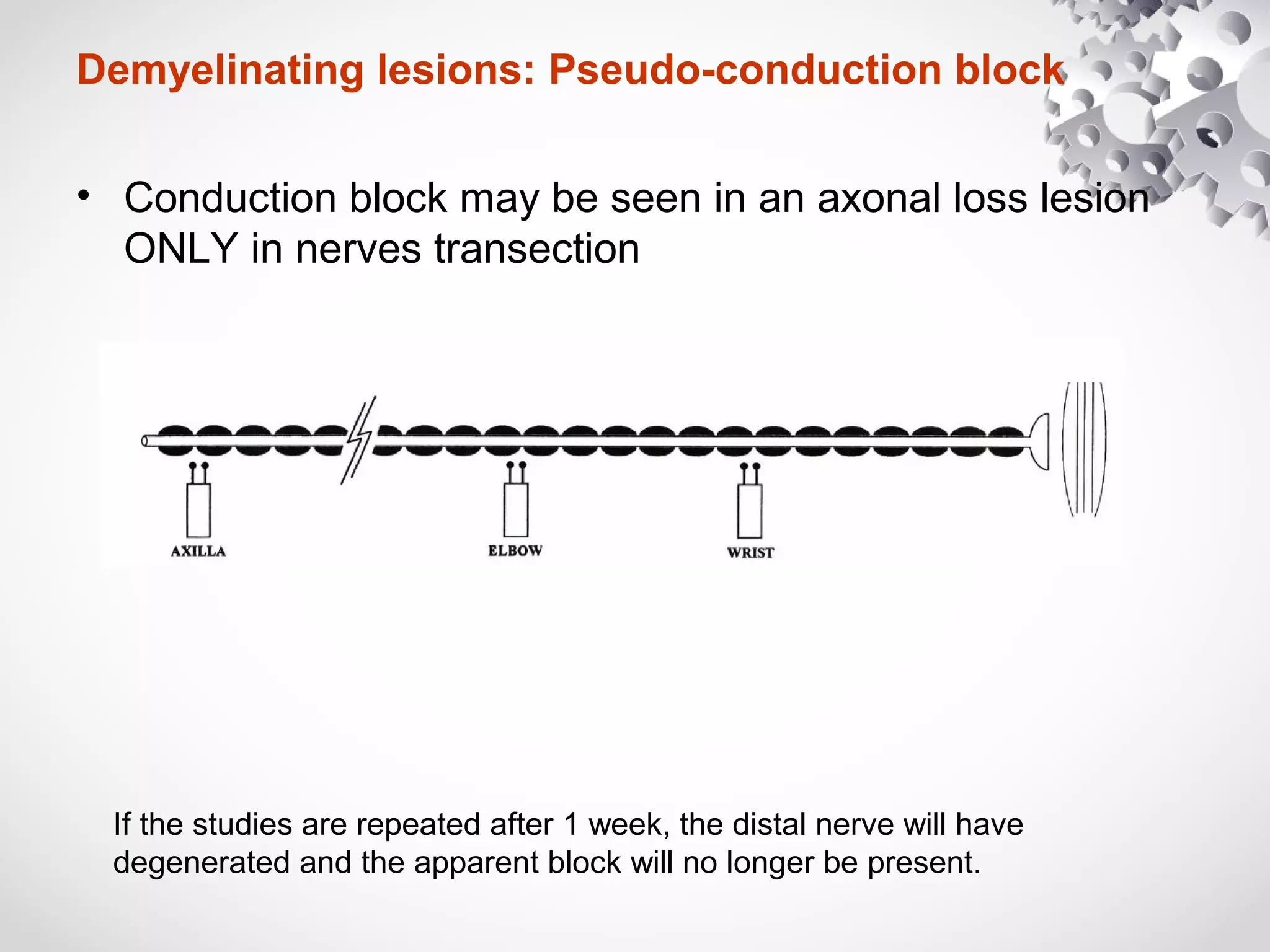
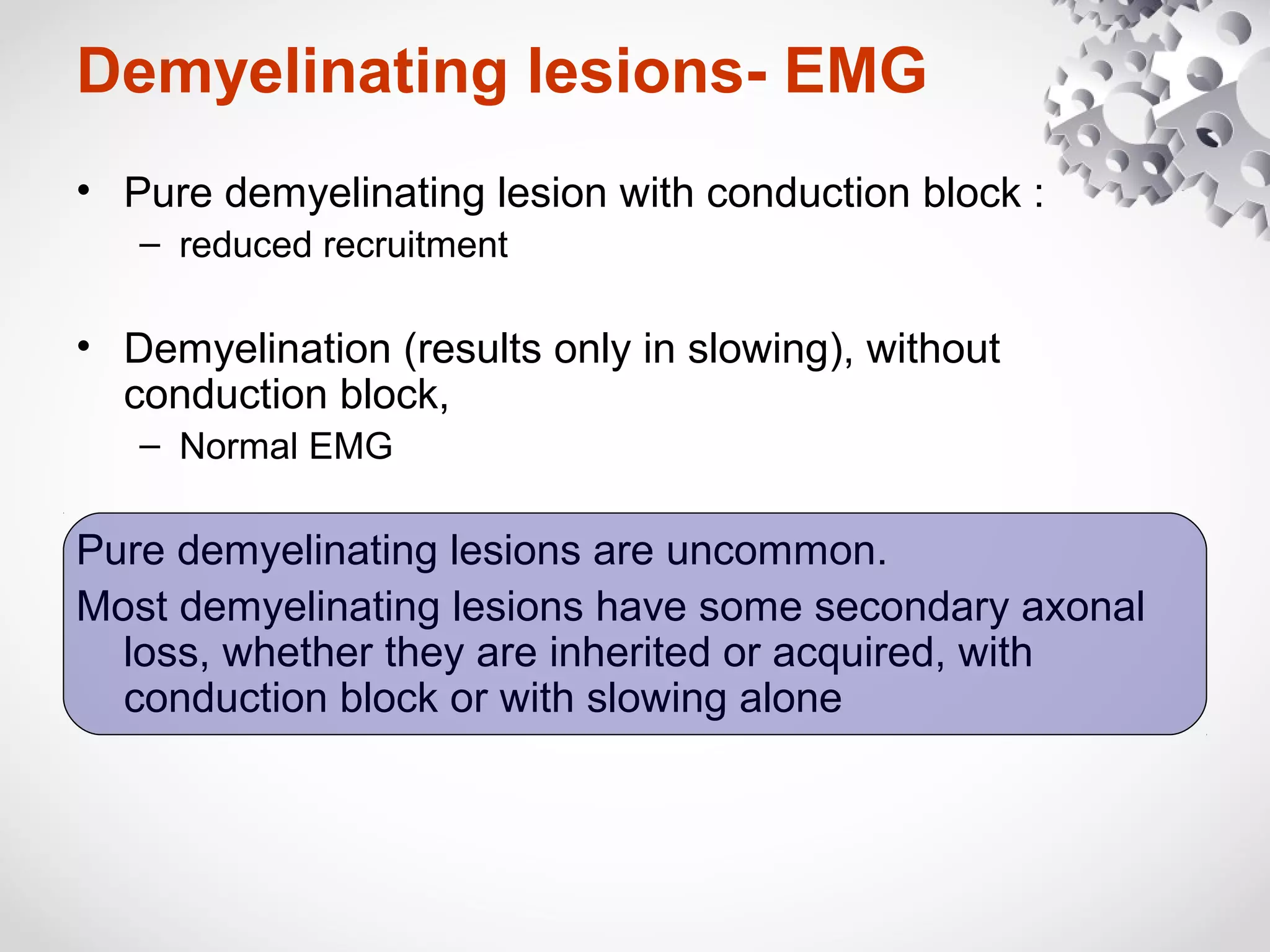
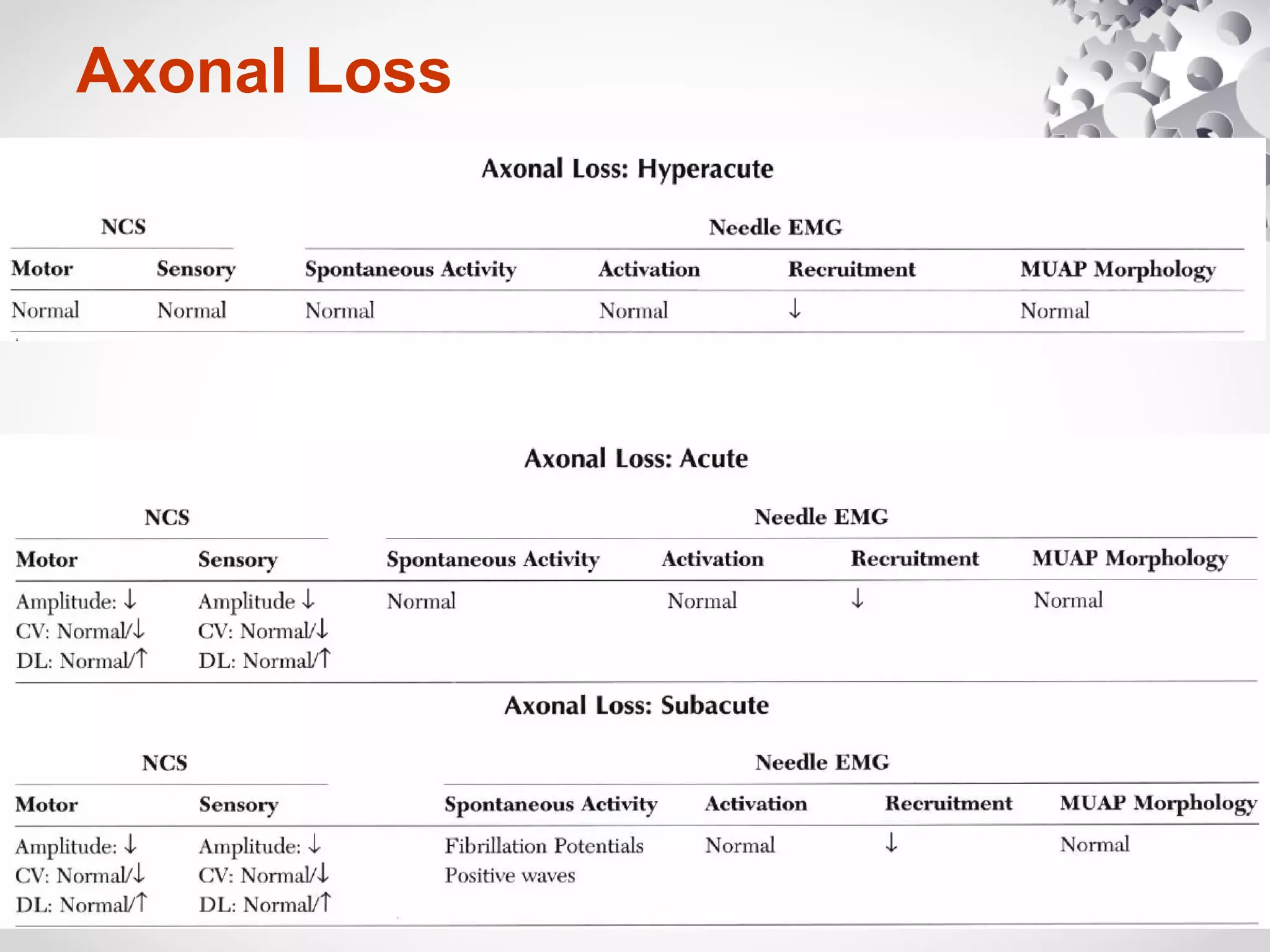
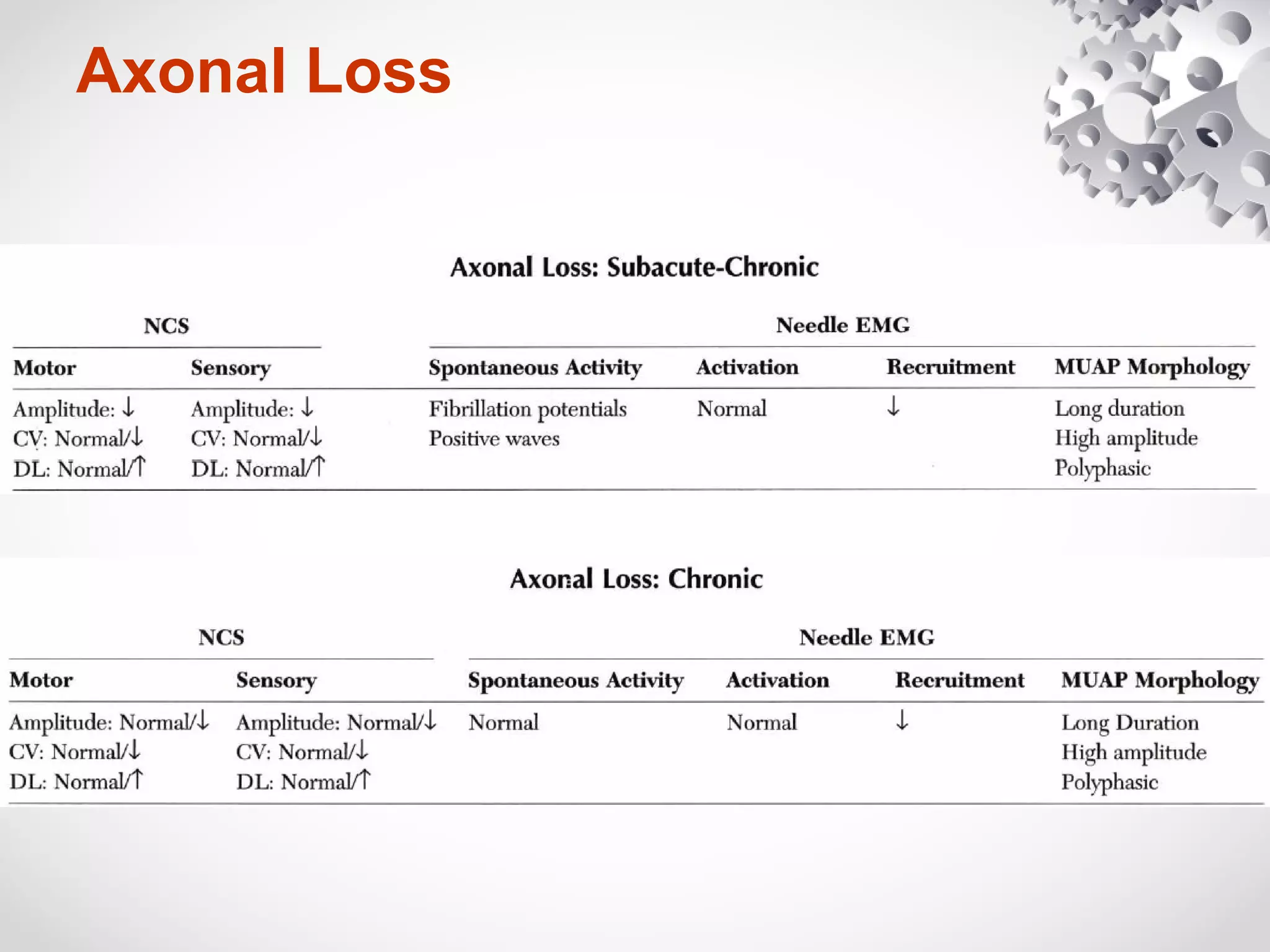
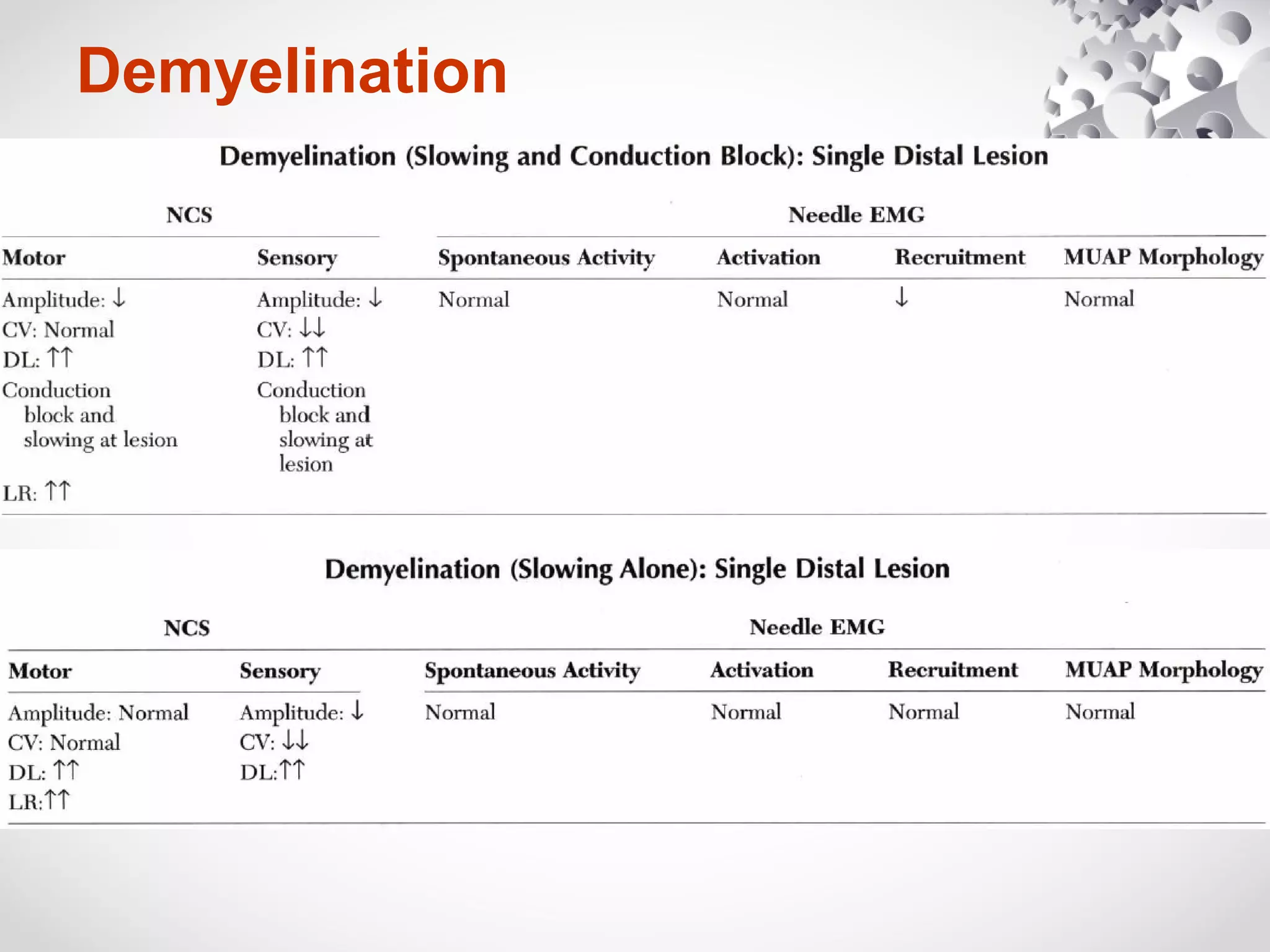
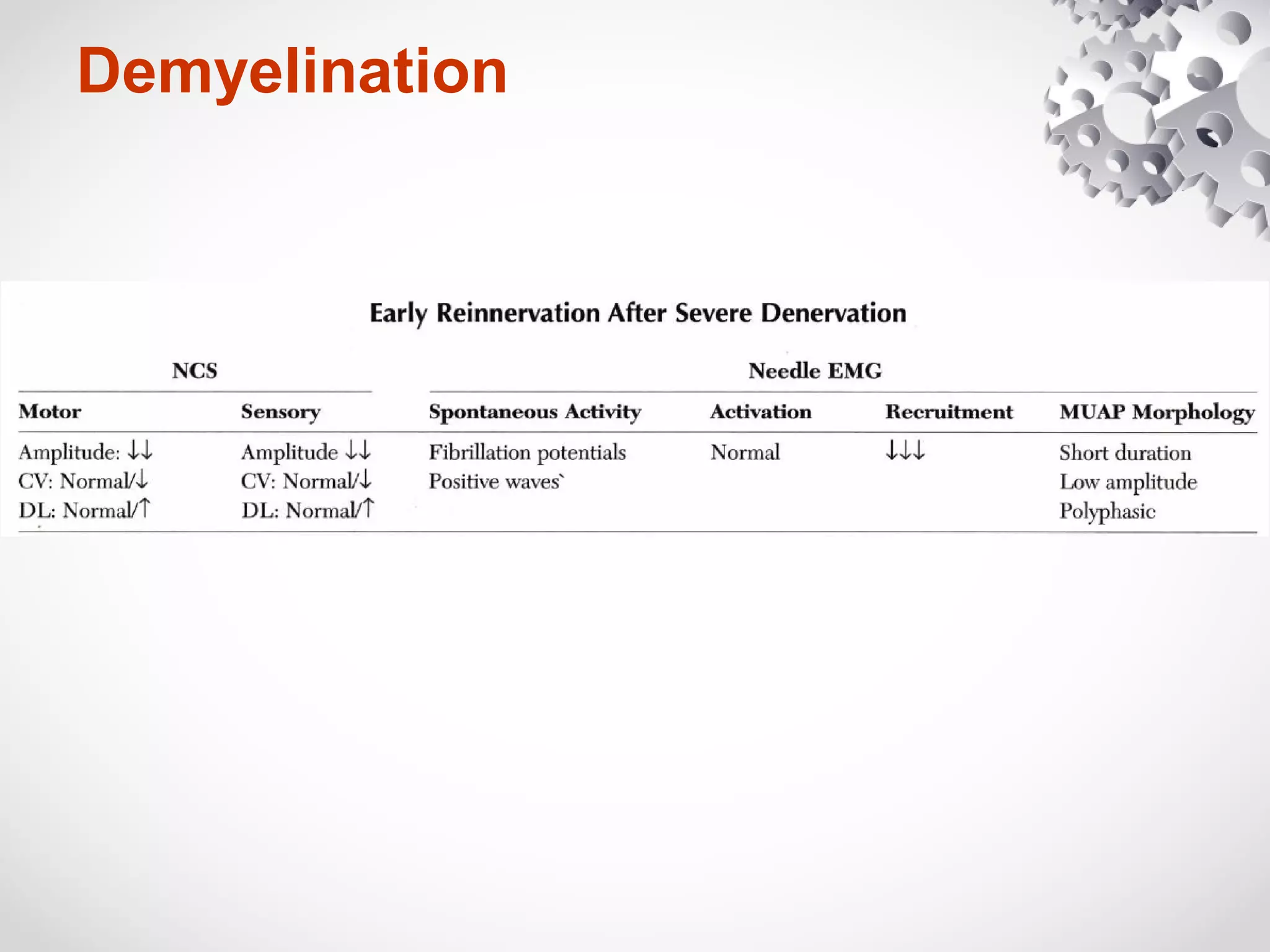
This document summarizes the key differences between axonal loss and demyelination lesions as assessed by nerve conduction studies. Axonal loss lesions typically show decreased amplitudes with normal or slightly slowed conduction velocities and distal latencies. Demyelination lesions are characterized by markedly slowed conduction velocities below 75% of the lower limit of normal or prolonged distal latencies over 130% of the upper limit, indicating primary demyelination. The document discusses various patterns that can be seen on nerve conduction studies for both types of lesions and their clinical implications.