This document provides an overview of muscle physiology, including:
1. The objectives are to learn about muscle functions, types, structures, contraction mechanisms, and differences between muscle fiber types.
2. Muscles have general functions like body movement, stabilization, substance transport, heat generation, and respiration.
3. Muscles are classified by control (voluntary or involuntary), location, and striation. The three main types are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle.
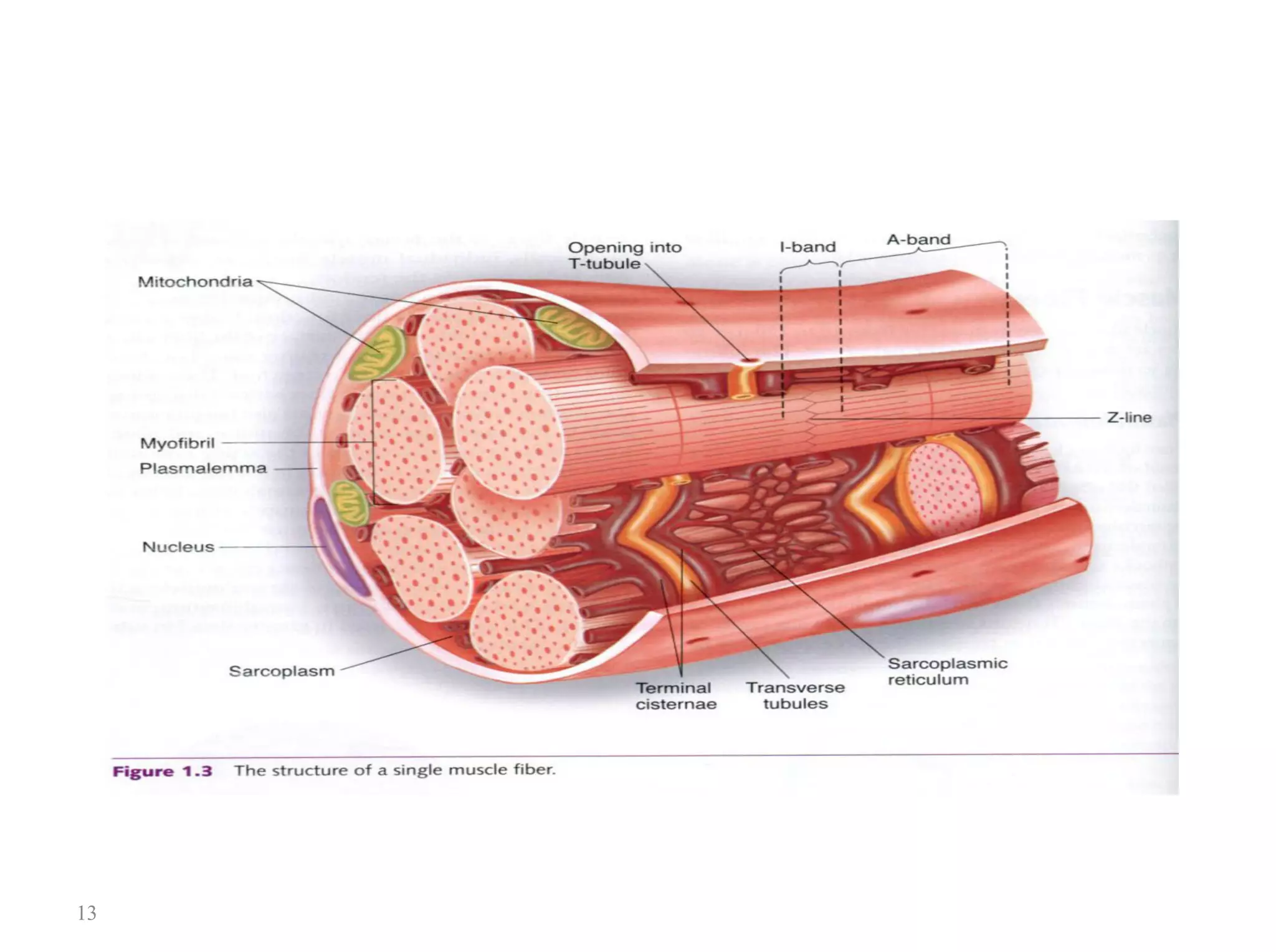
4. Skeletal muscle contraction occurs via the sliding filament theory where the cross-bridge cycling of actin and myosin fibers causes sarcomere shortening and muscle contraction.