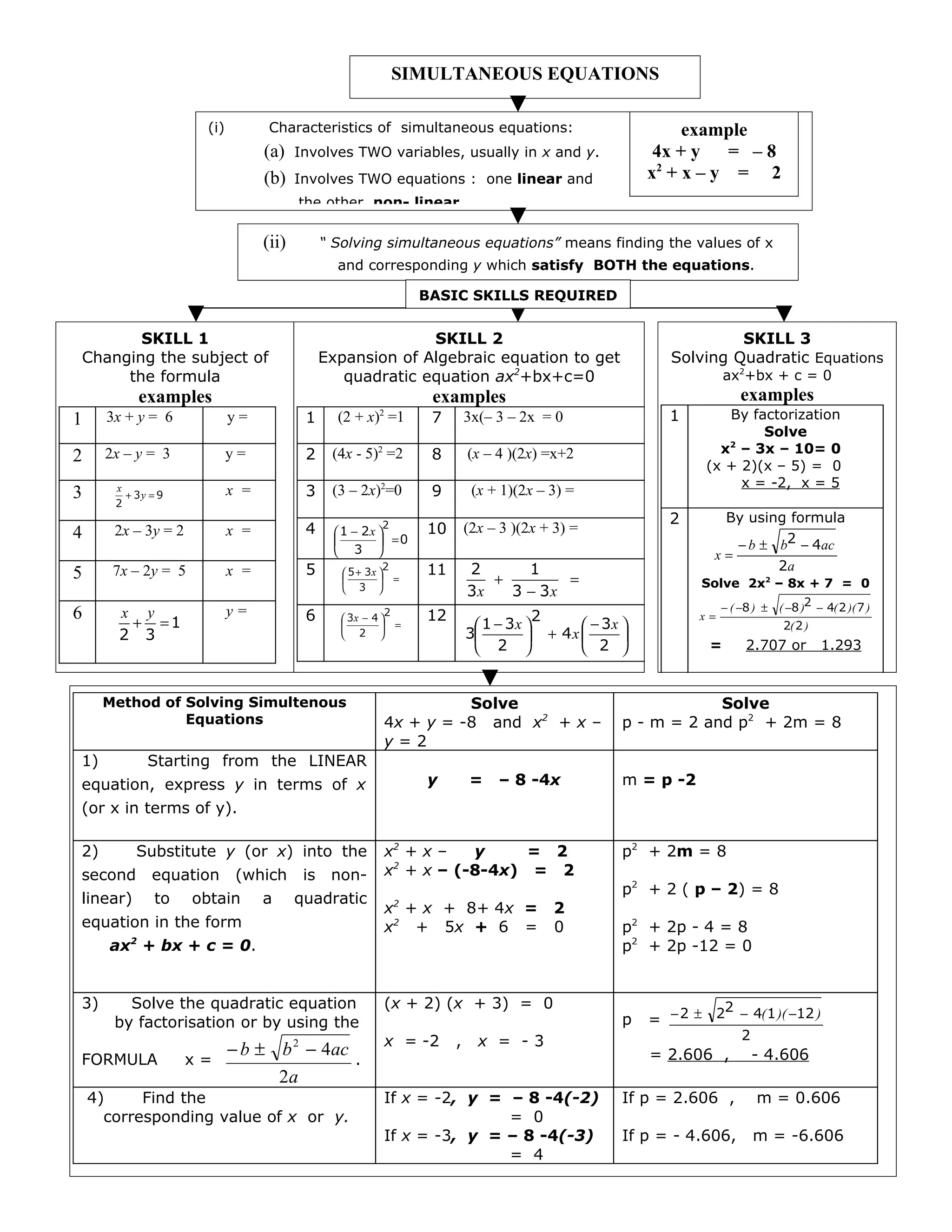
1) Simultaneous equations involve two variables in two equations that are solved simultaneously to find the values of the variables.
2) To solve simultaneous equations, one first expresses one variable in terms of the other by changing the subject of one linear equation, then substitutes this into the other equation to obtain a quadratic equation.
3) This quadratic equation is then solved using factorisation or the quadratic formula to find the values of the variables that satisfy both original equations.