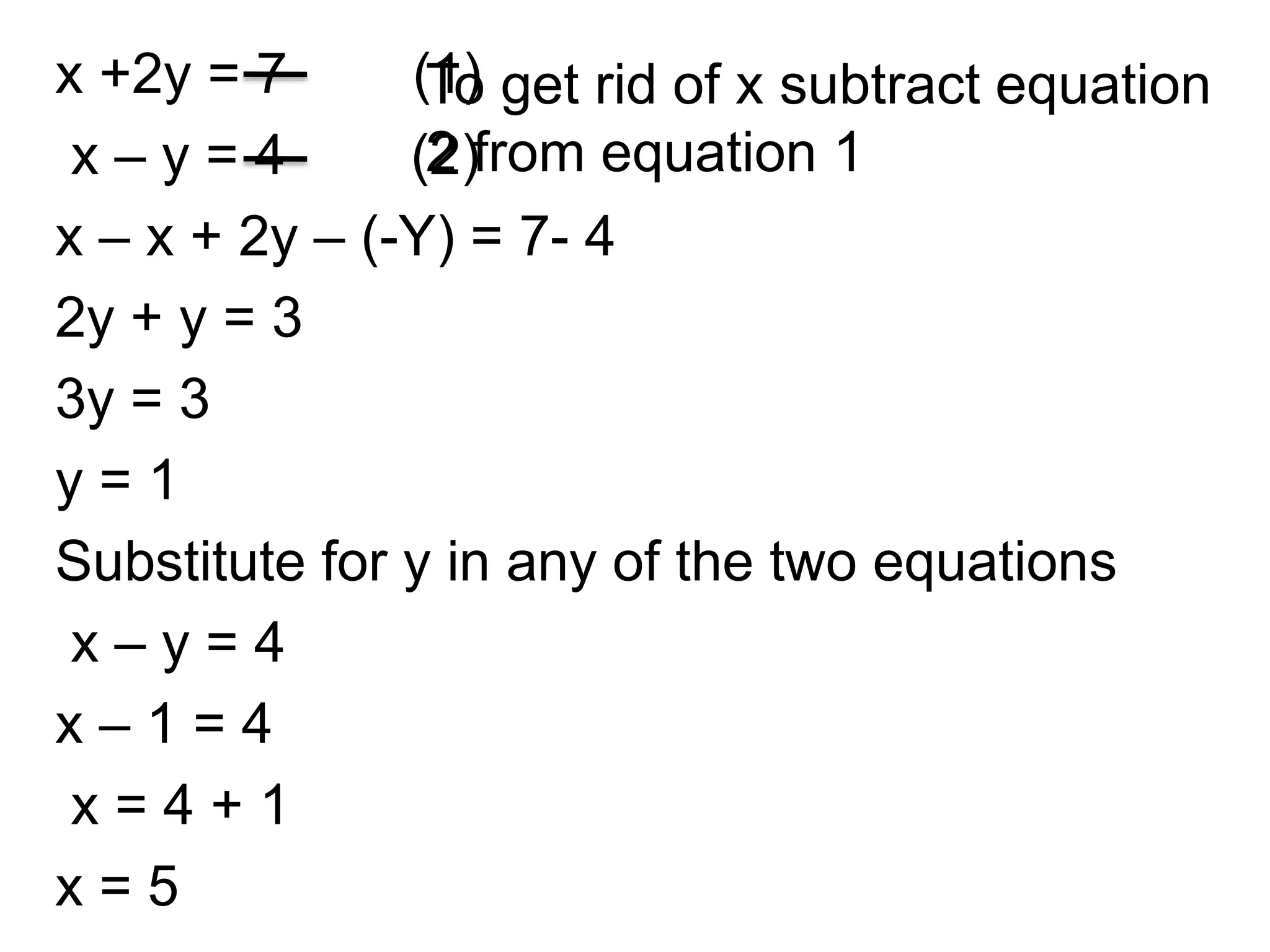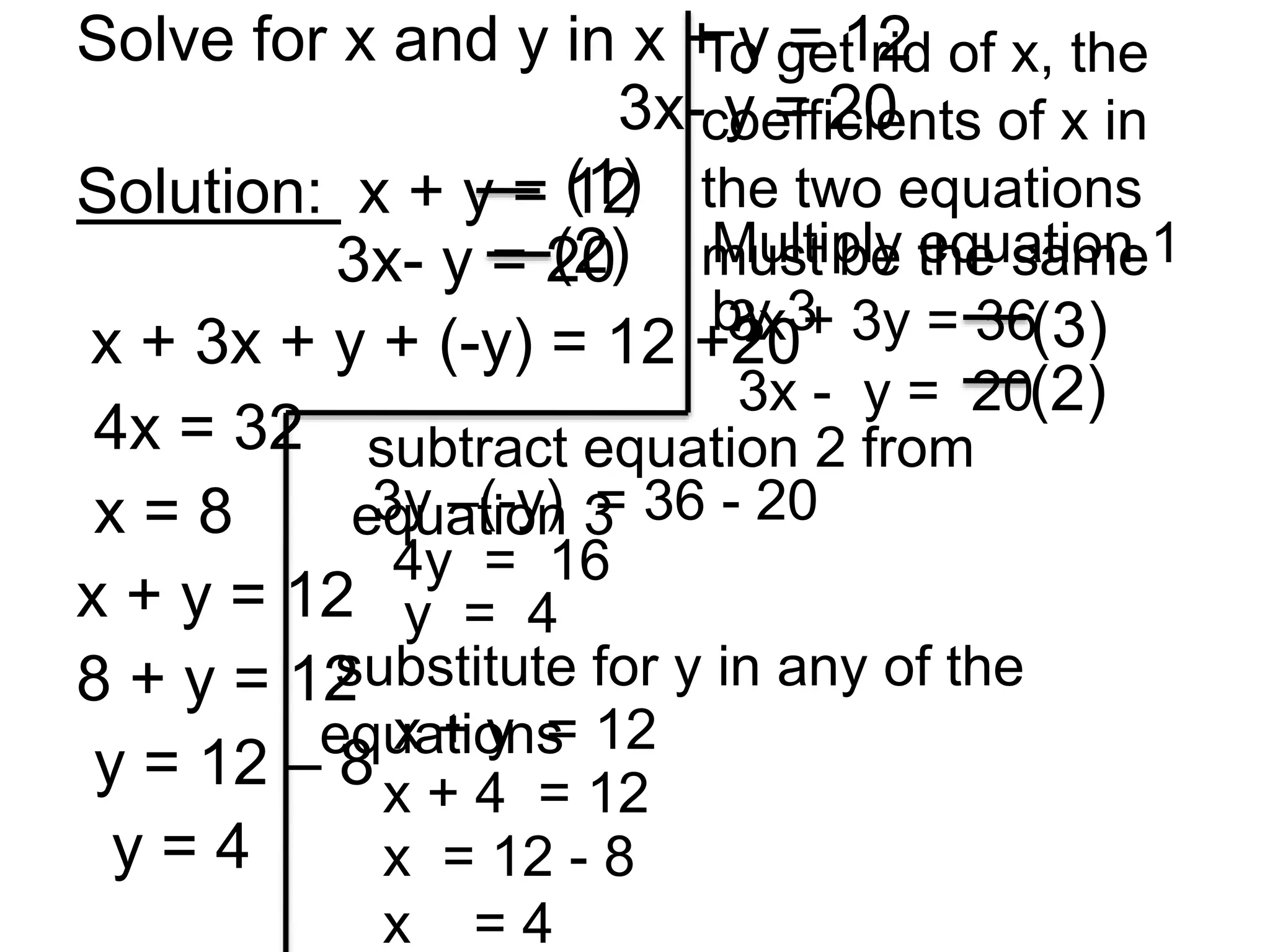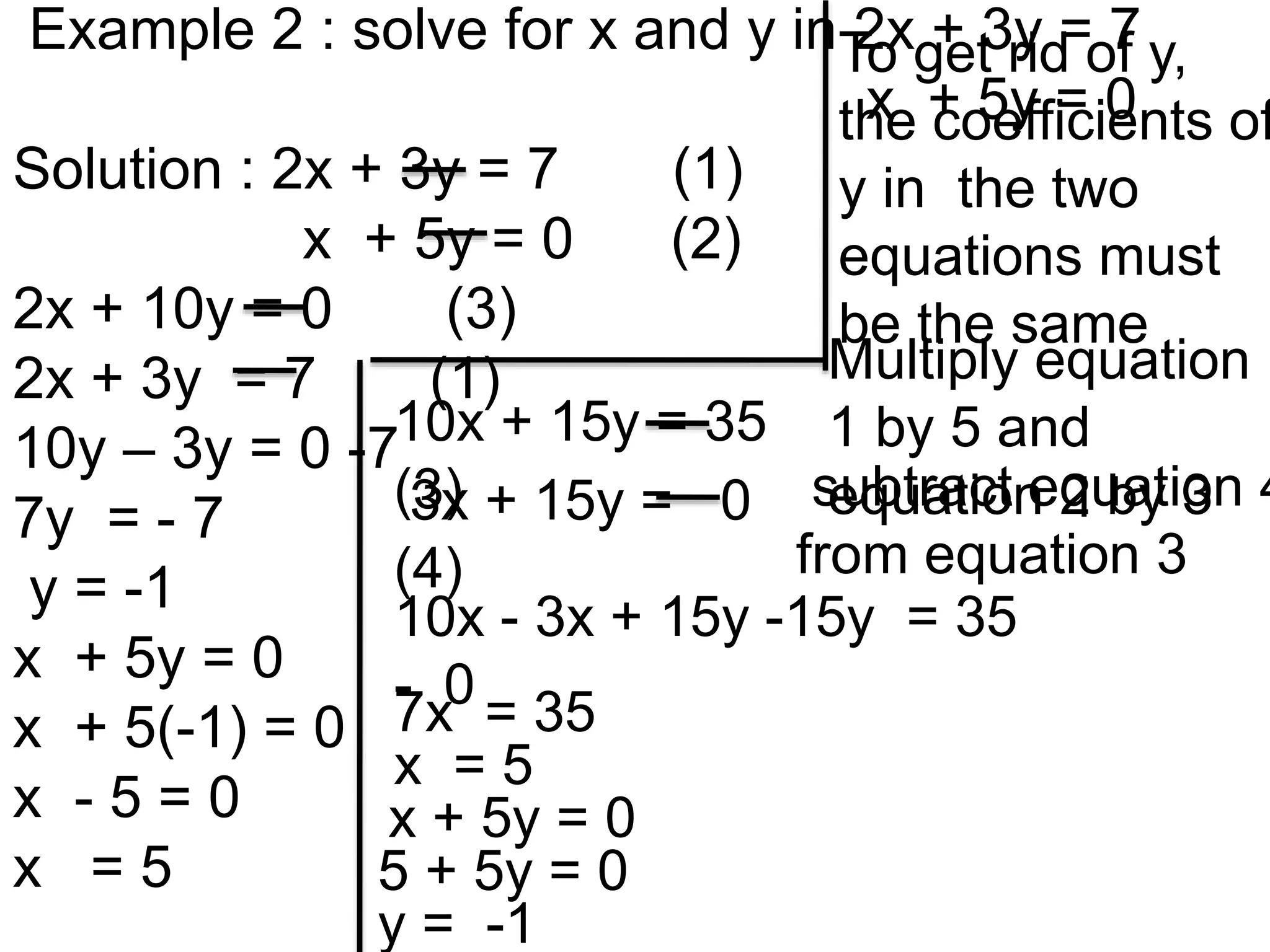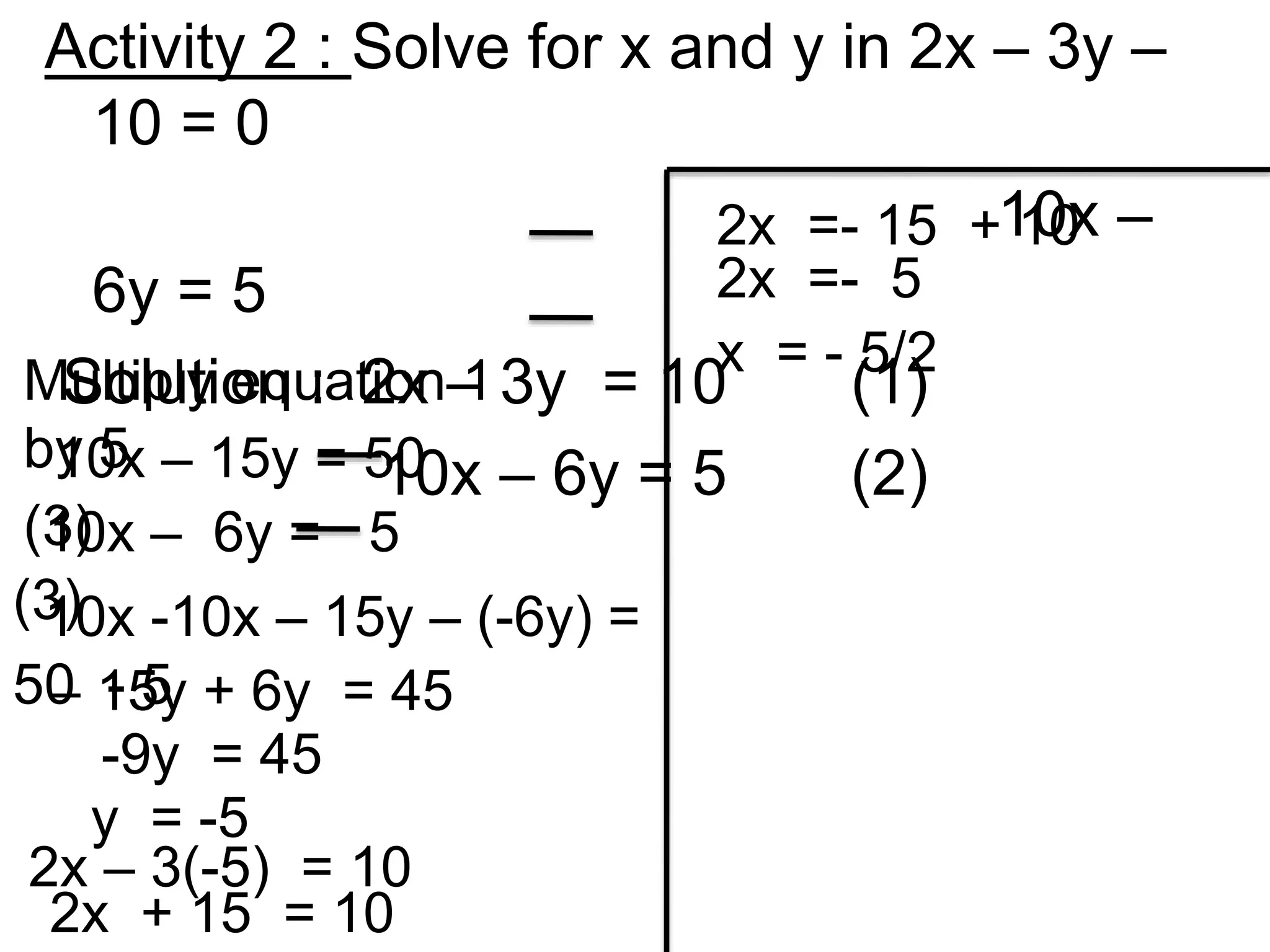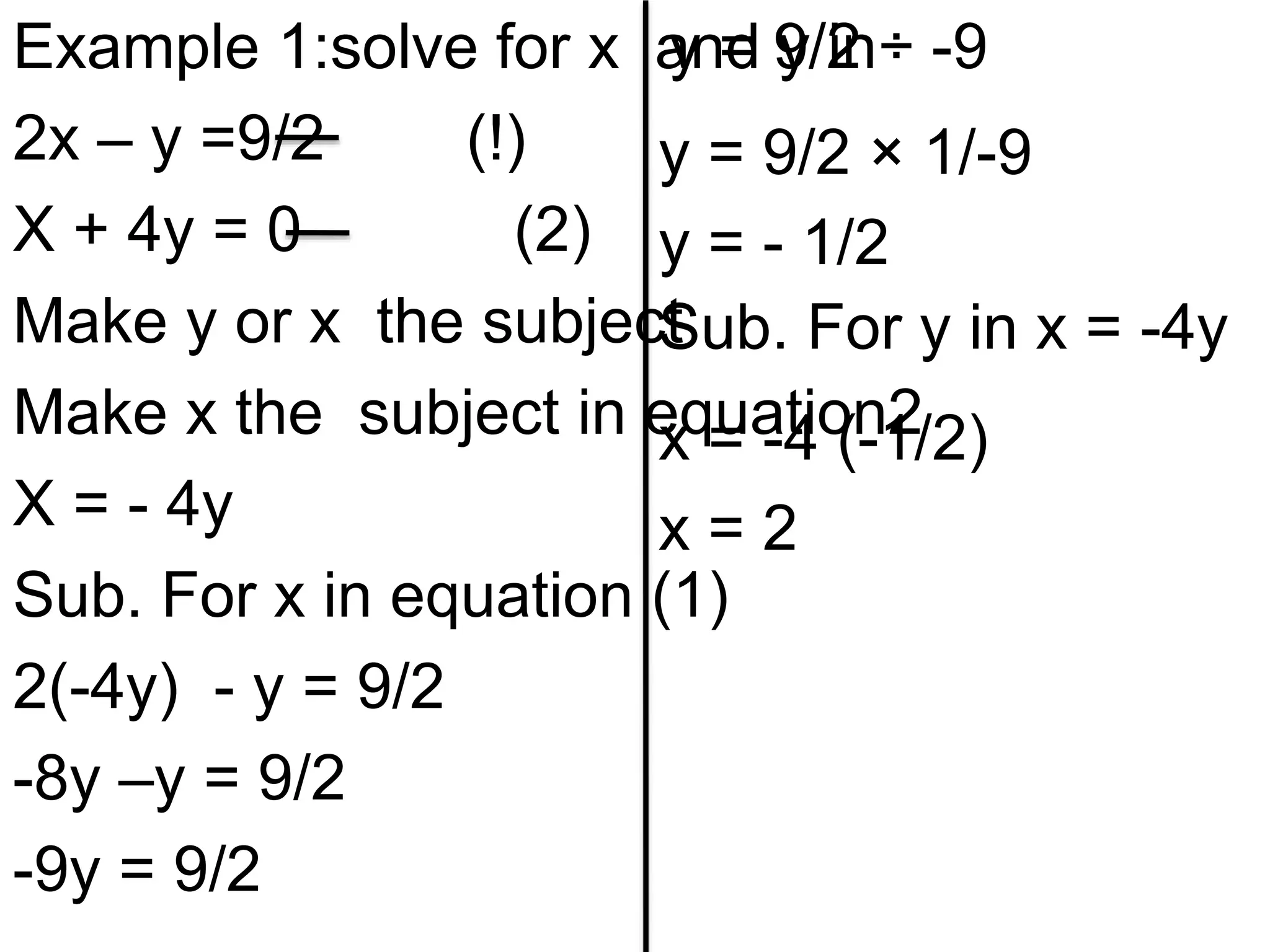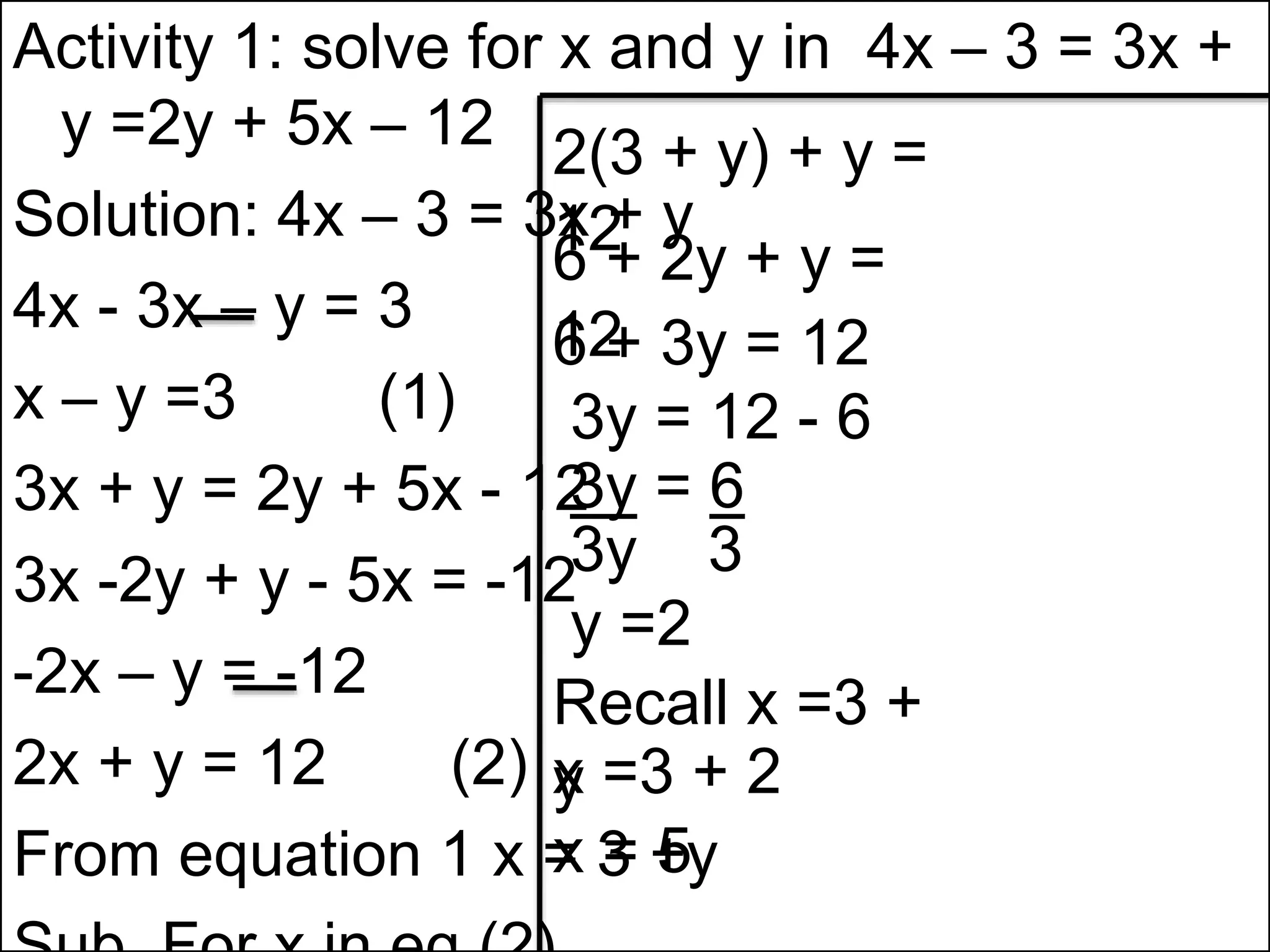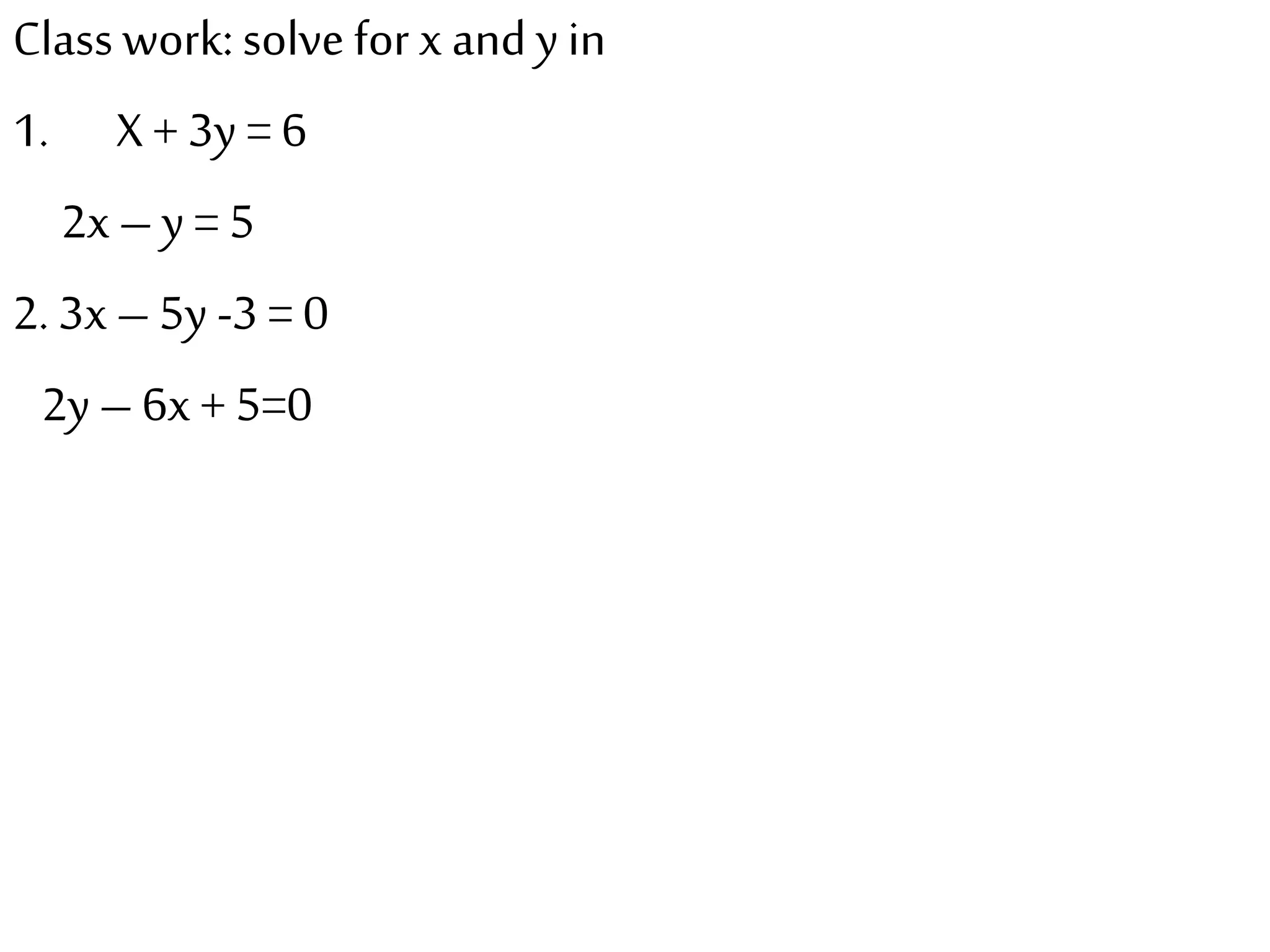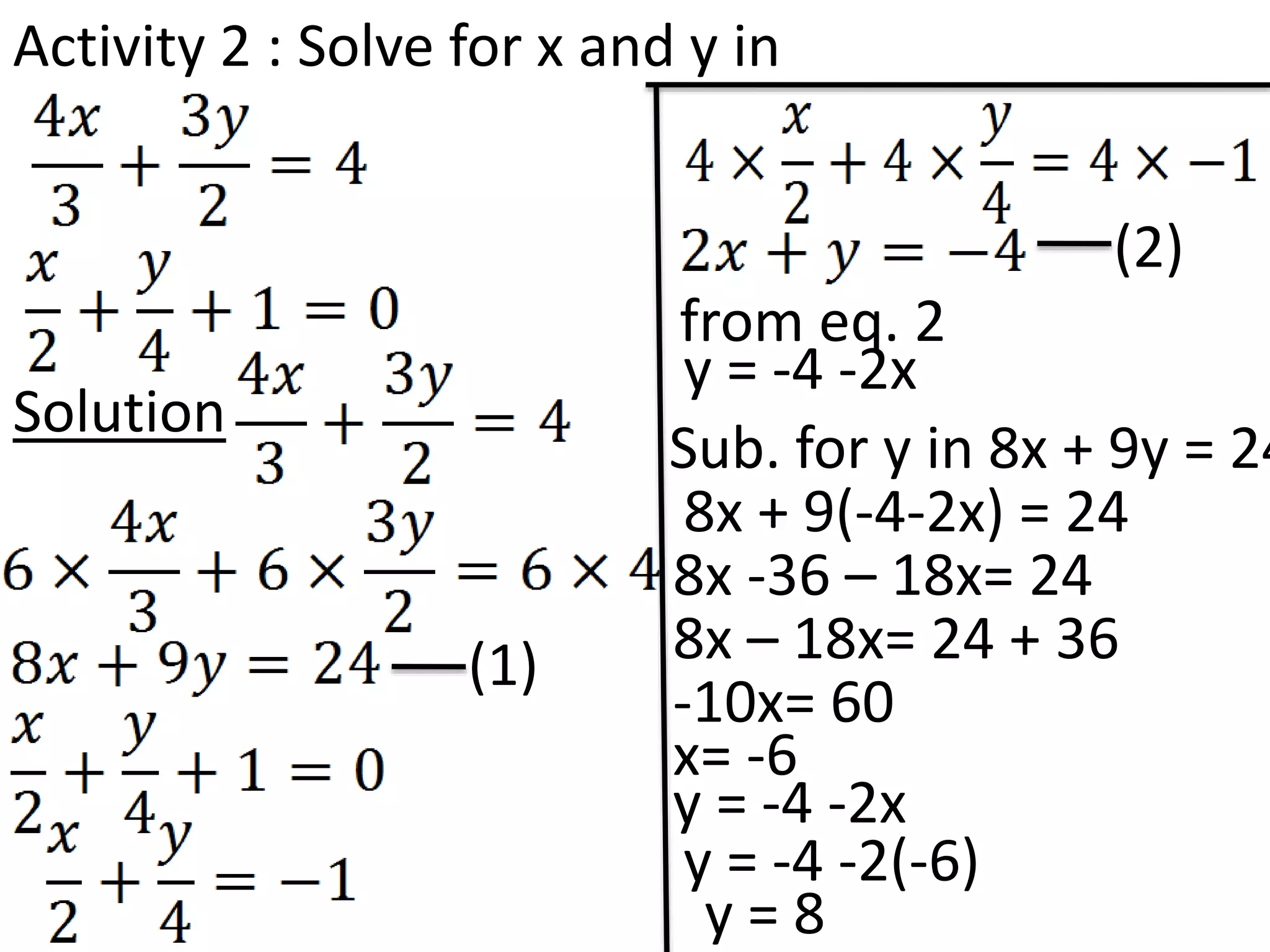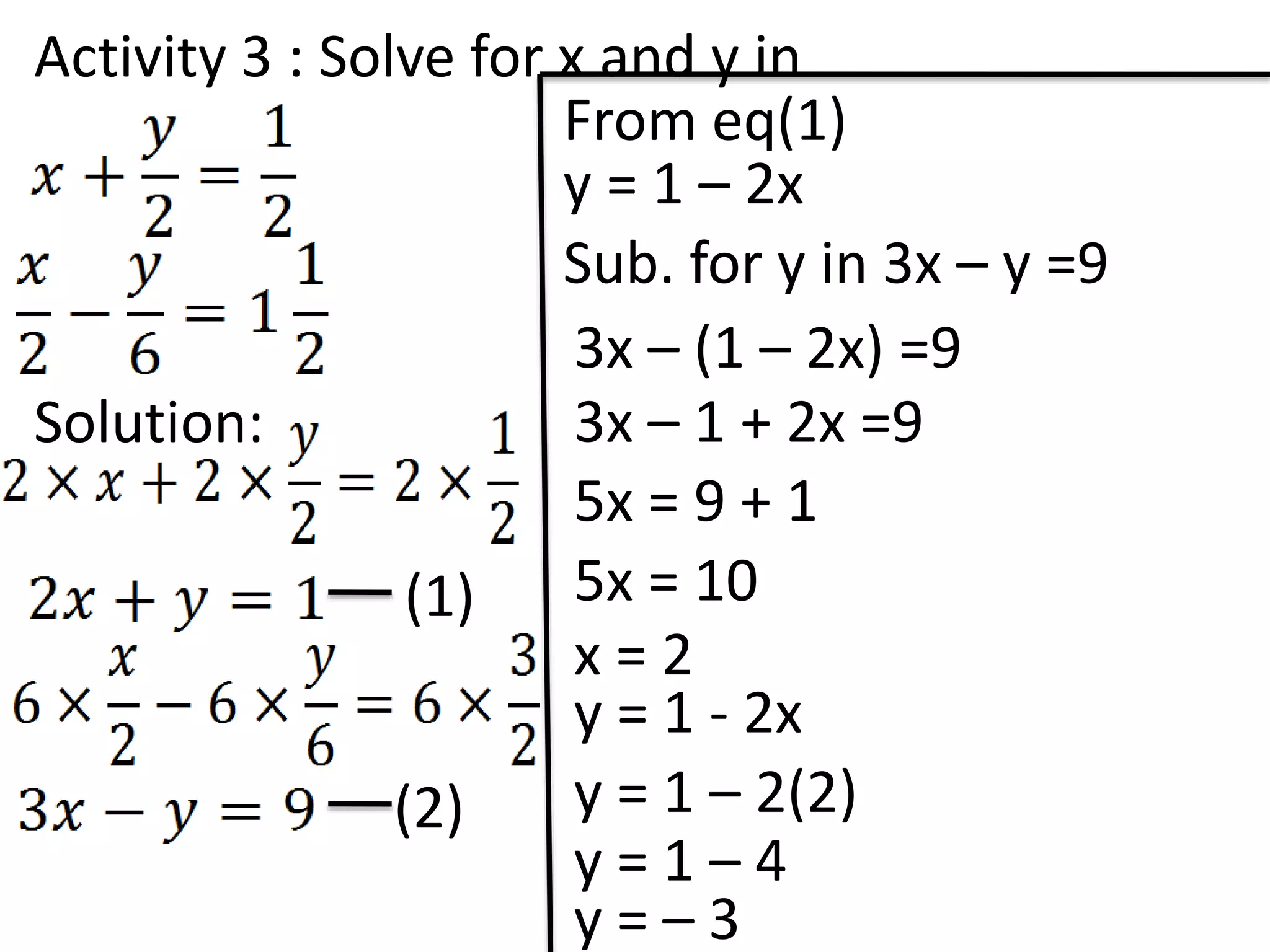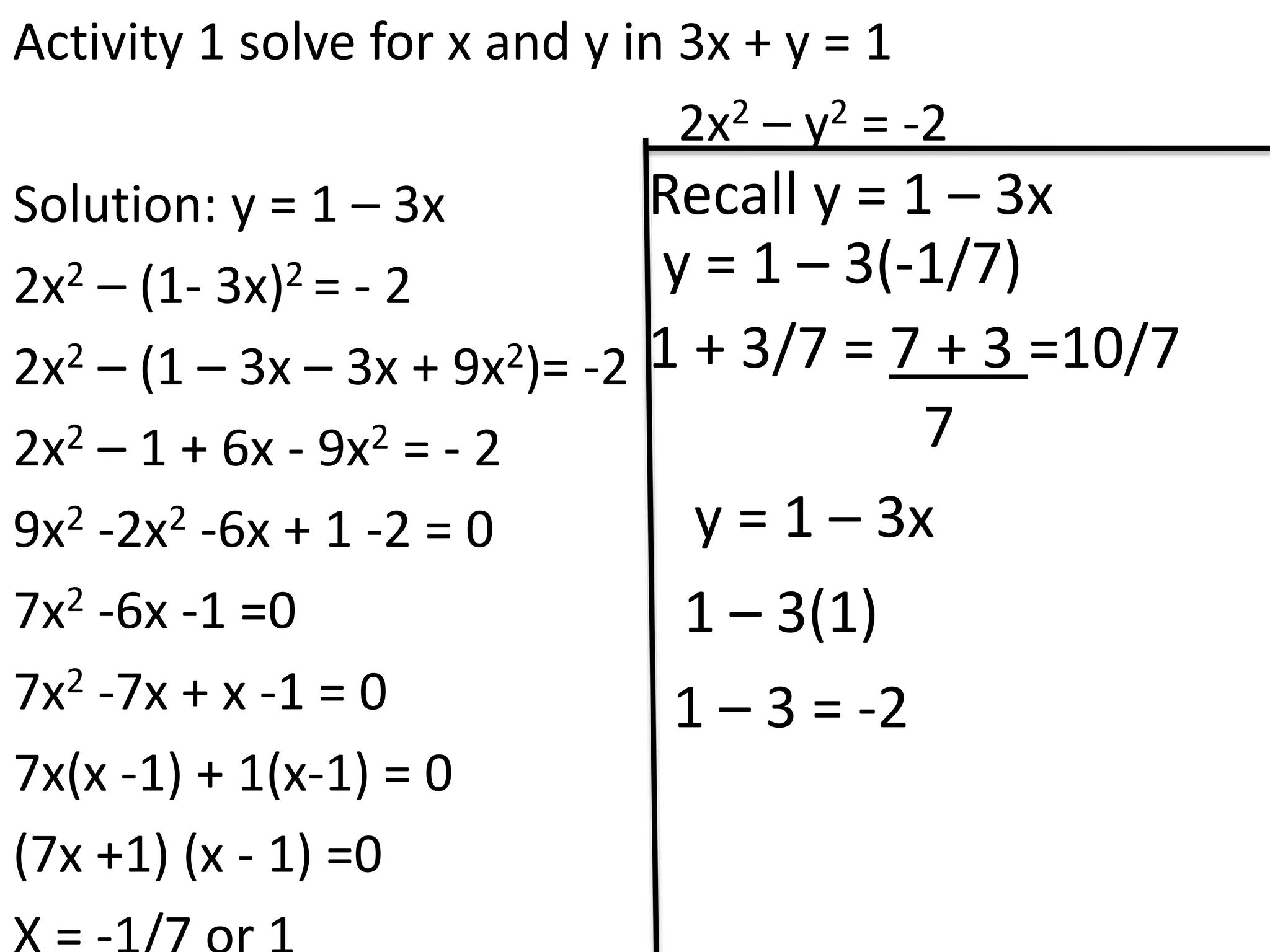The document discusses methods for solving simultaneous linear equations, including elimination and substitution.
It provides examples of using elimination by adding or subtracting equations to remove a variable, and substitution by making one variable the subject of an equation and substituting it into the other equation. Fractions are converted to simple linear equations by finding a common denominator. The document also covers solving simultaneous equations when one equation is quadratic using substitution after making one variable the subject of the linear equation.