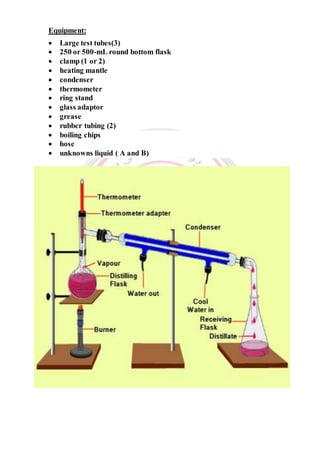
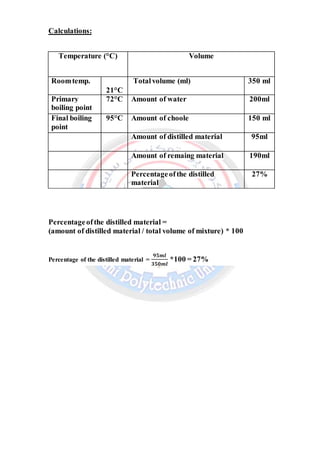
This document summarizes a chemistry laboratory experiment on simple distillation. The experiment aims to separate a mixture of two miscible liquids with a boiling point difference of at least 25°C. The procedure involves heating the liquid mixture in a round-bottom flask attached to a condenser. Vapors form and travel up the condenser where they cool and drip into a collection flask. The temperature is recorded at each stage of distillation. The results show the primary boiling point, final boiling point, amounts distilled and remaining, and percentage of distilled material.