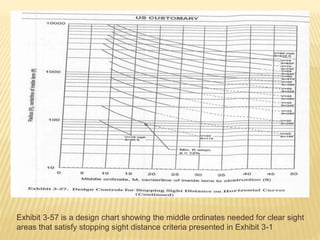
The document discusses the principles of sight distance and road alignment, emphasizing the significance of stopping and passing sight distances in road design. It explains how horizontal and vertical alignments should interact, taking into consideration factors such as speed, curvature, and super elevation to ensure safety and comfort for drivers. Additionally, it outlines various calculations and design techniques to optimize sight distances and road curvature for effective highway and roadway engineering.



















![21
SIGHT DISTANCE FOR HORIZONTAL
CURVES
Location of object along chord length that blocks
line of sight around the curve
m = R(1 – cos [28.65 S])
R
Where:
m = line of sight
S = stopping sight distance
R = radius](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sightdistanceandroadallignment-160914095927/85/Sight-distance-and-road-allignment-21-320.jpg)























