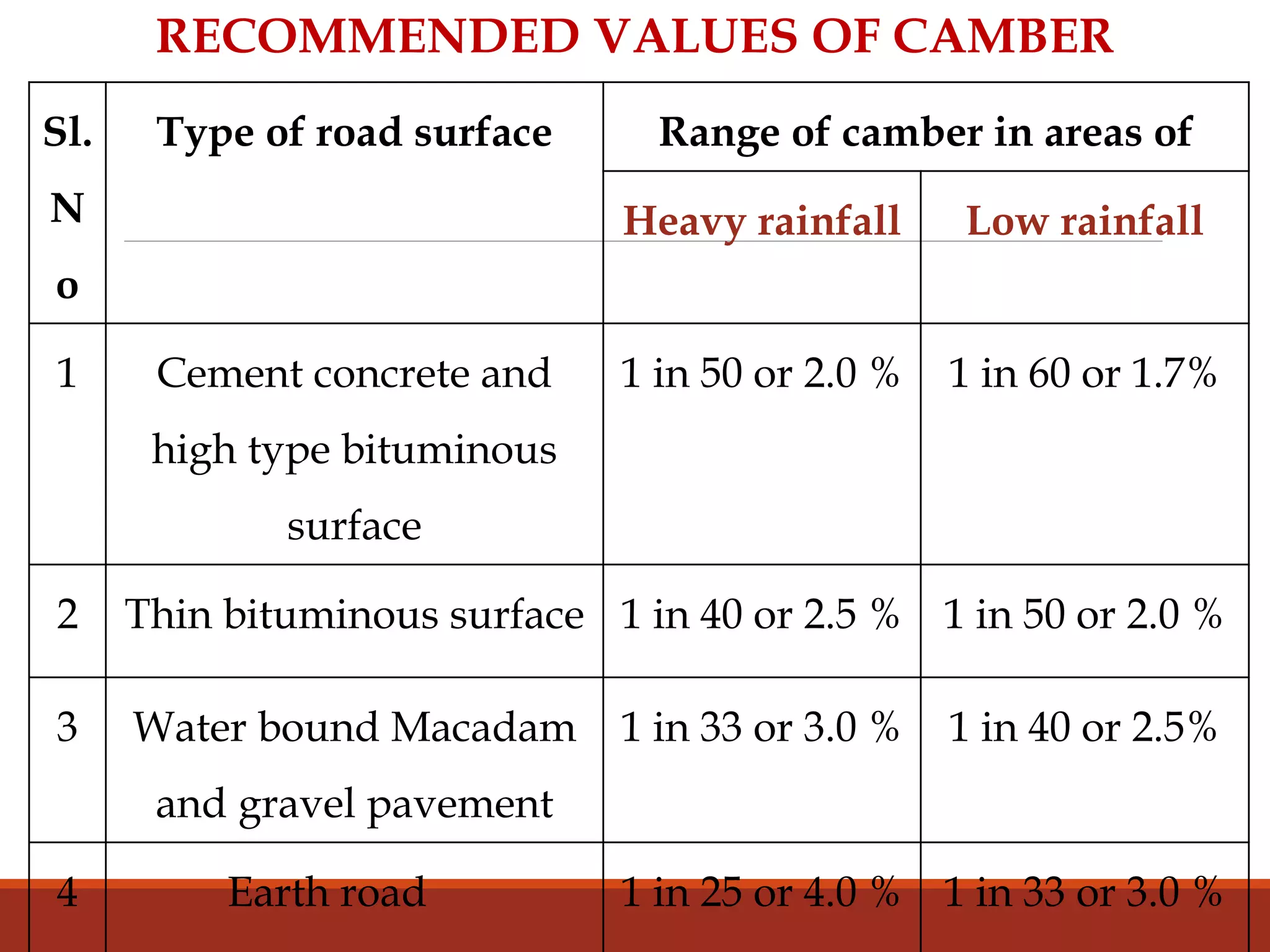
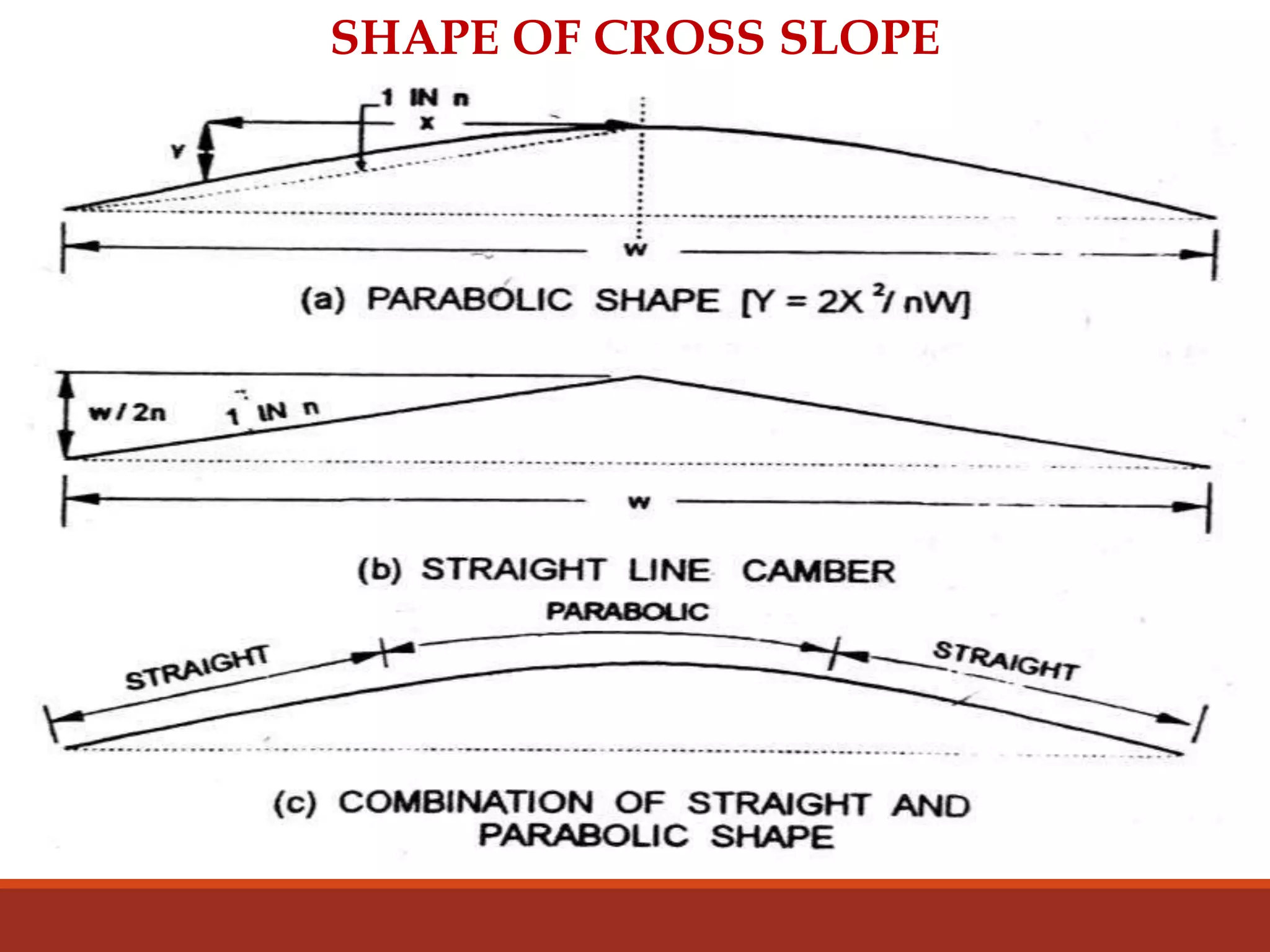
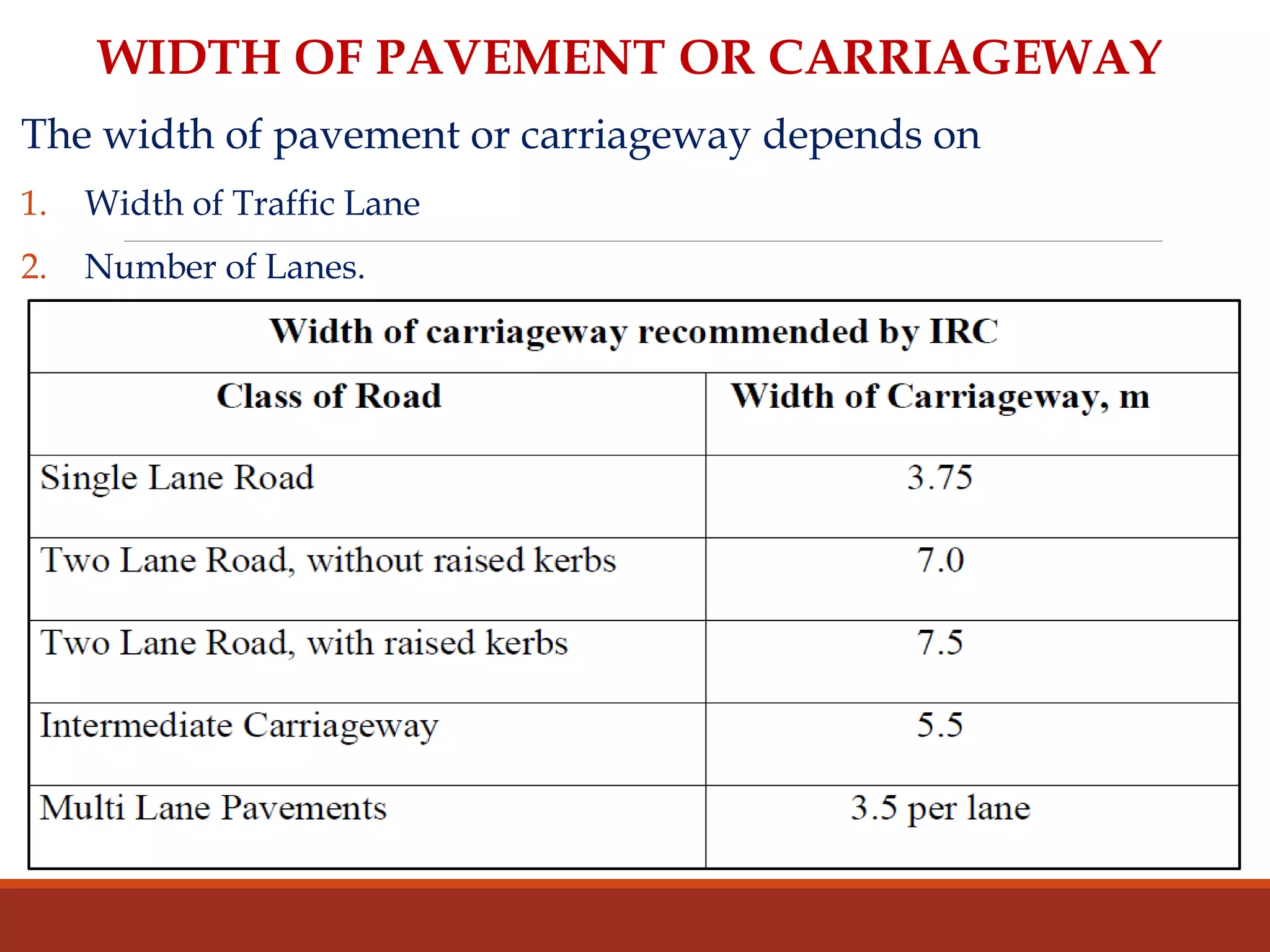
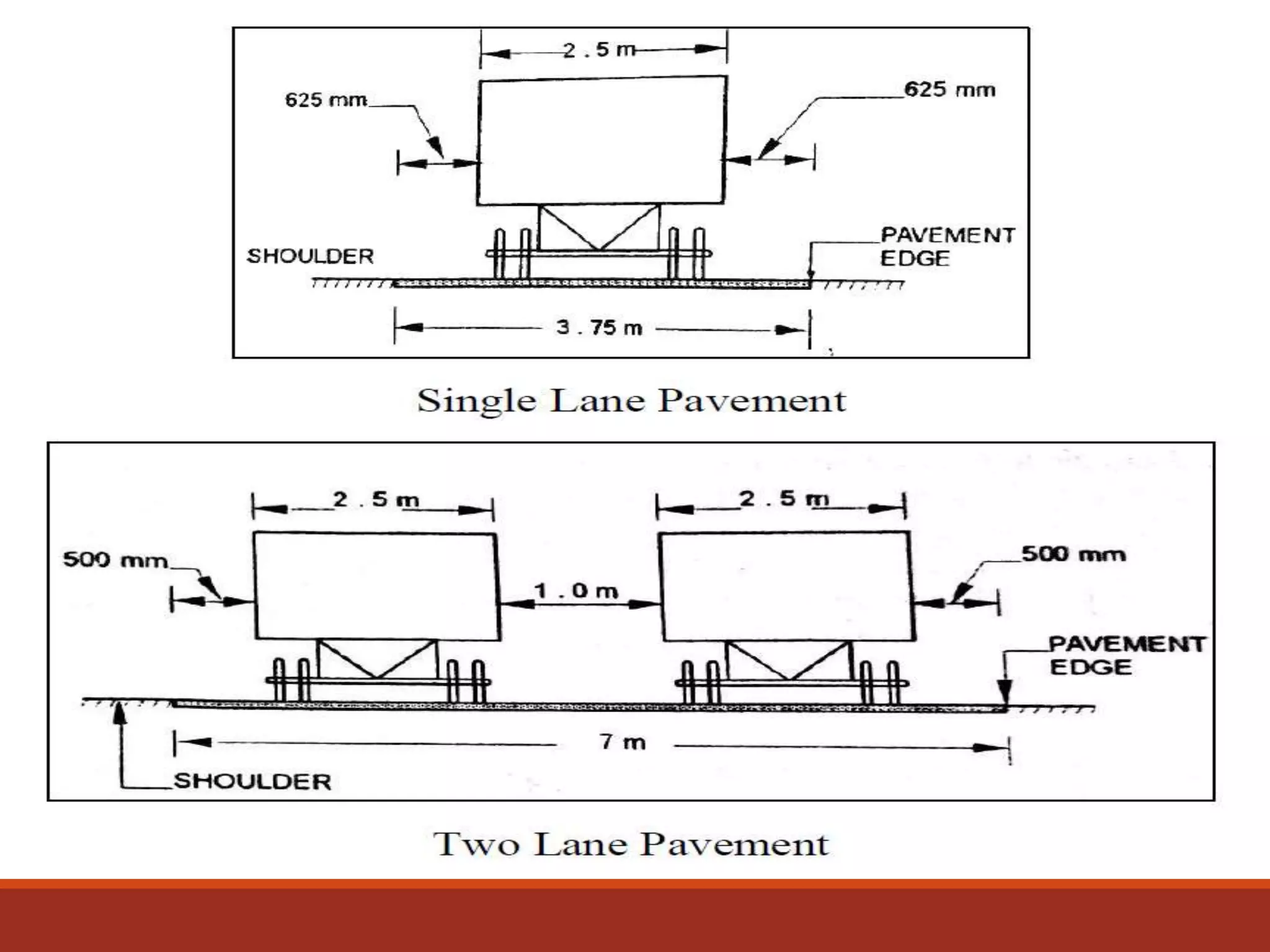
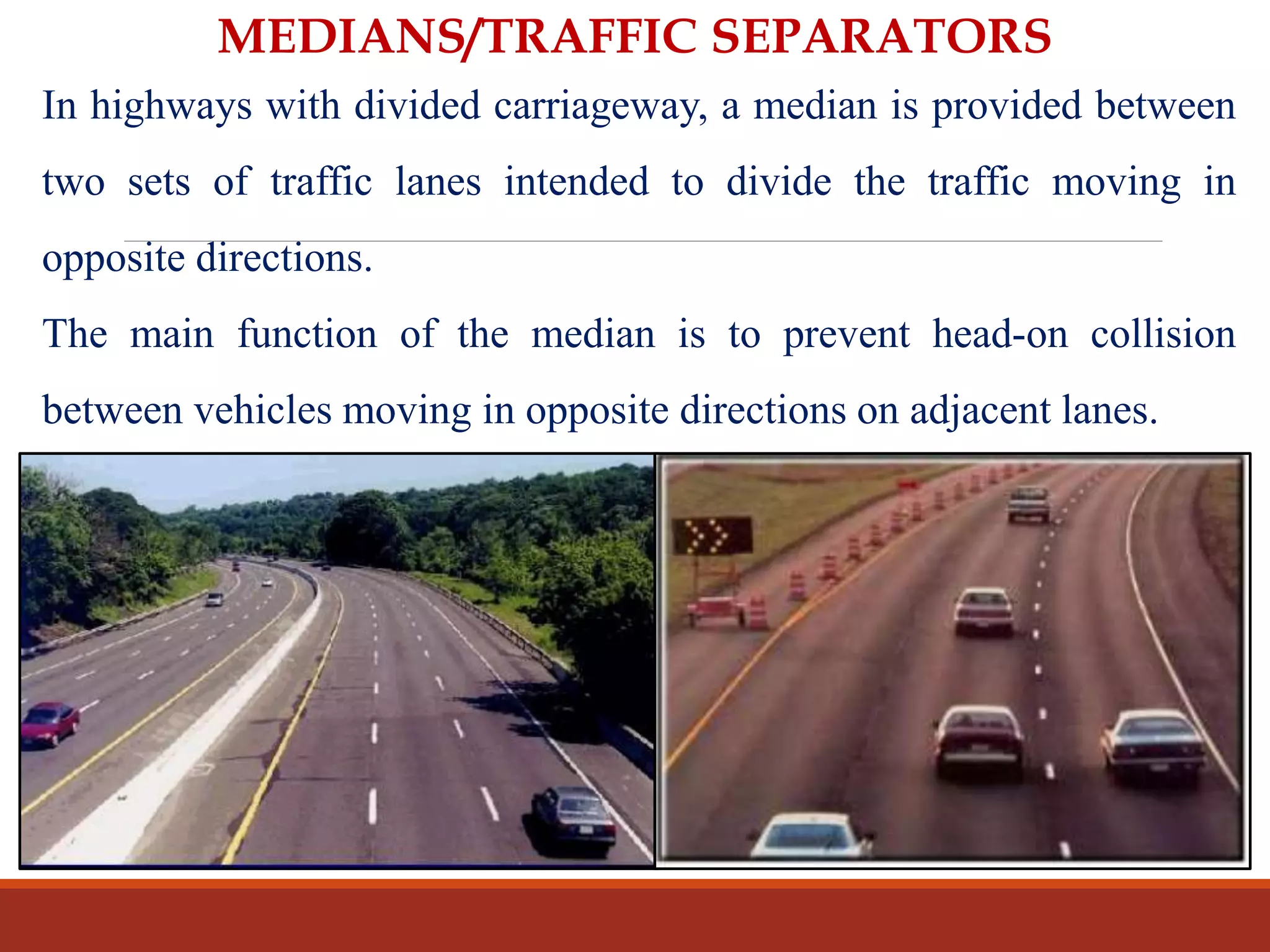
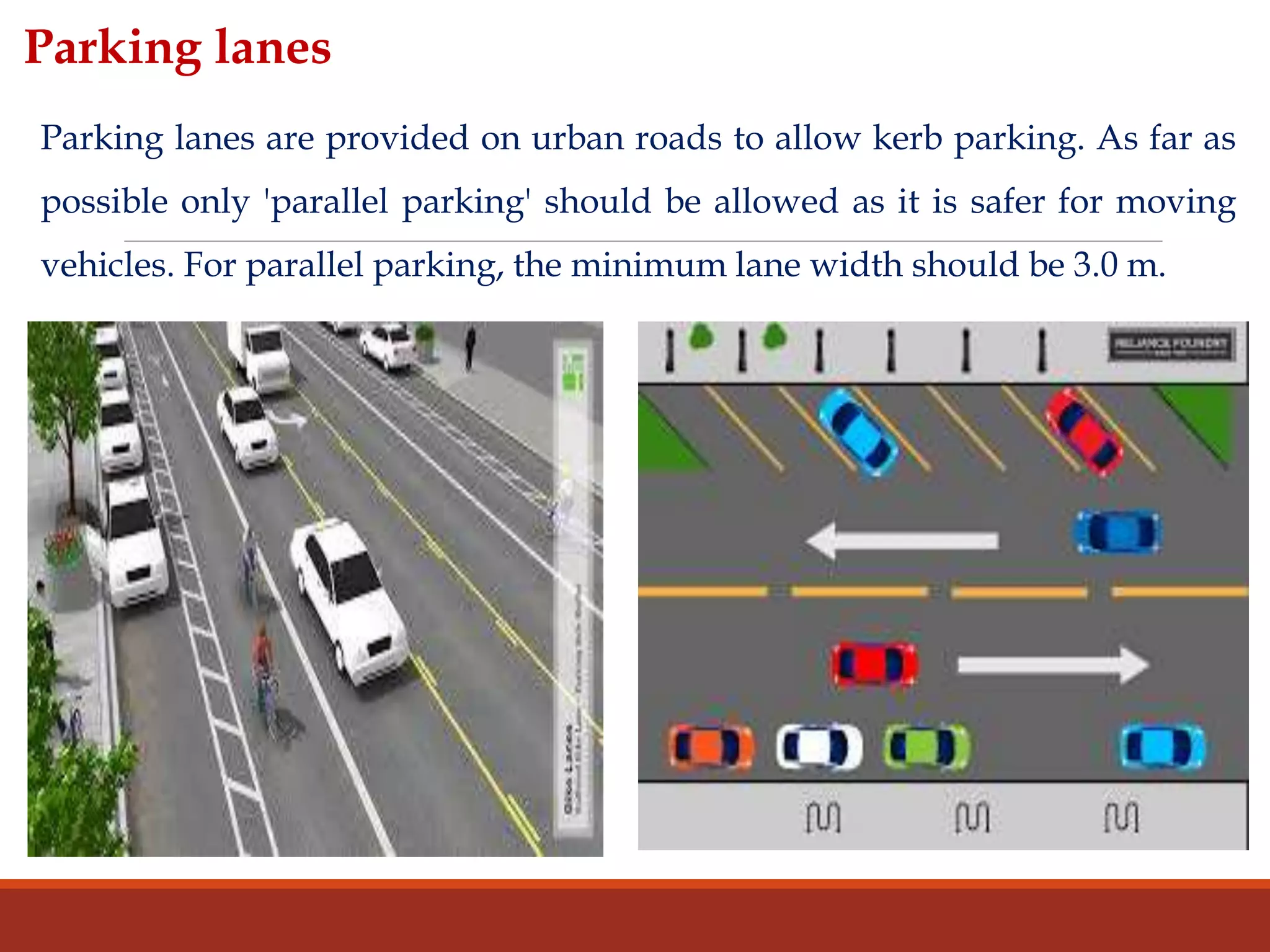
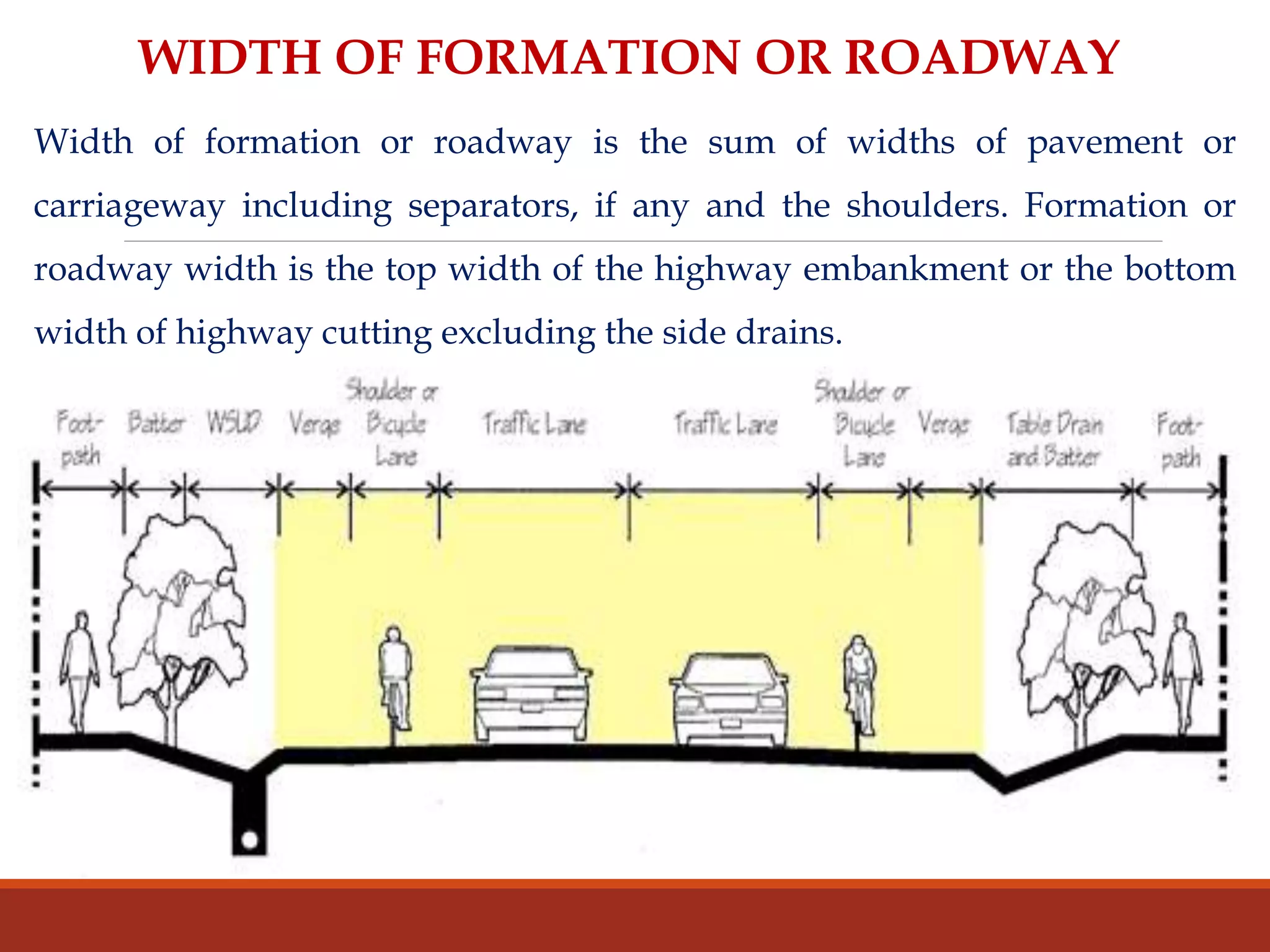
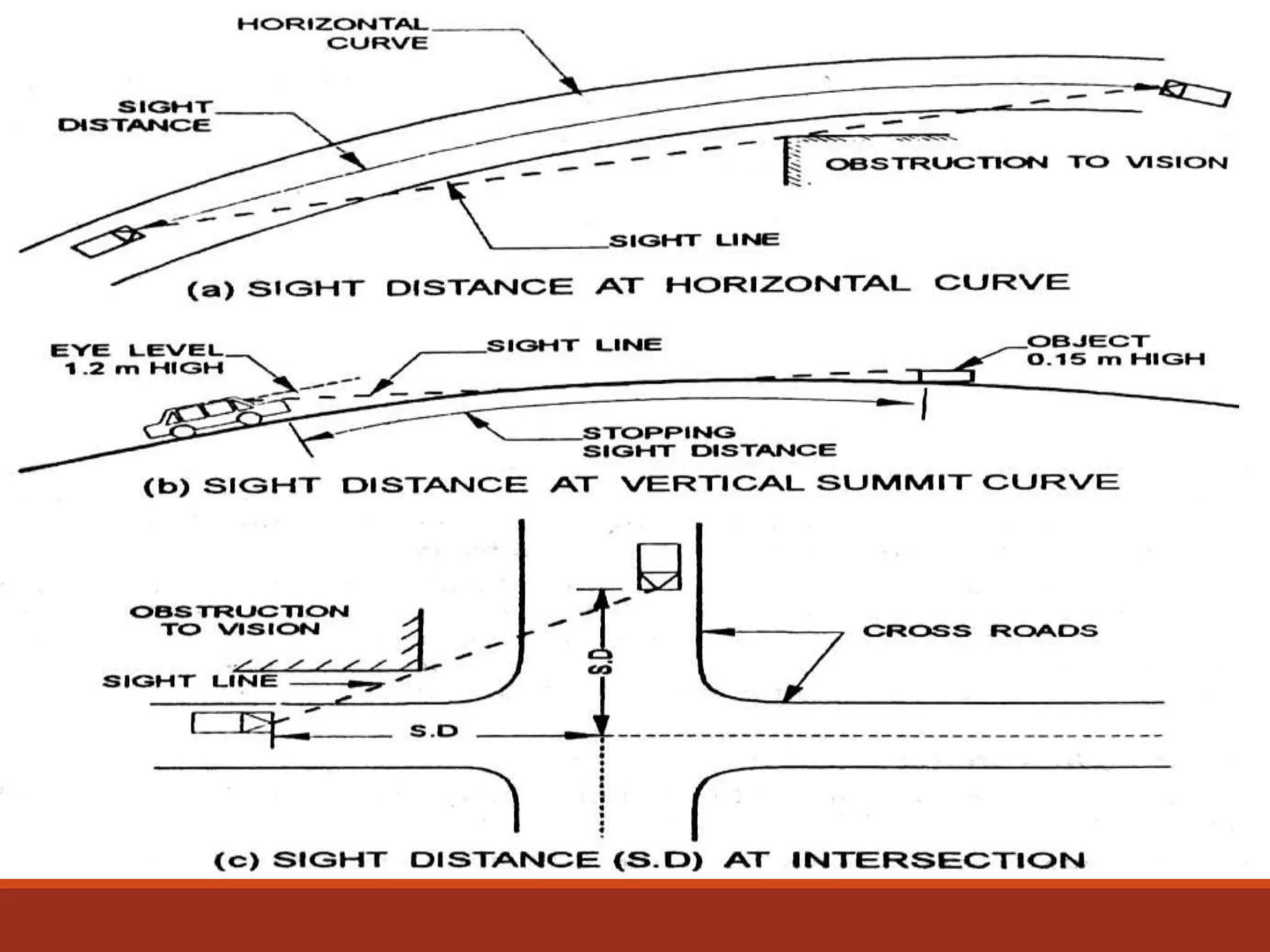
The document covers various aspects of highway cross-section elements, including factors like friction considerations, unevenness, light reflecting characteristics, and drainage. It discusses the design of road elements such as cross slopes, medians, kerbs, road margins, footpaths, driveways, and parking lanes, emphasizing their importance for safety and efficiency. Additionally, it explains the concepts of right of way and sight distance in highway engineering.