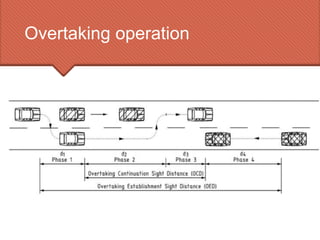
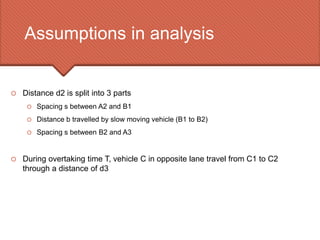
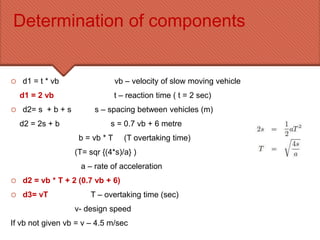
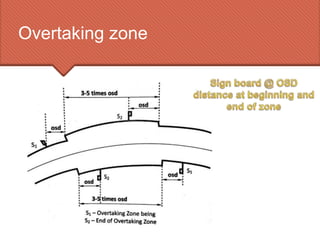
The document discusses the essential requirement for overtaking sight distance (OSD) for vehicles, outlining the factors affecting it and analyzing the components of OSD on a two-way road. It emphasizes the importance of providing adequate overtaking zones at frequent intervals where there is potential for overtaking, and details the necessary calculations for determining OSD, including driver reaction time and spacing between vehicles. Additionally, it mentions the concept of intermediate sight distance (ISD) when OSD cannot be accommodated.