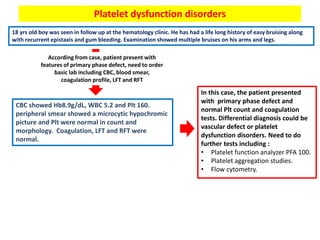
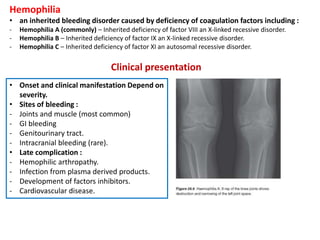
This document discusses bleeding disorders and provides details on specific disorders such as von Willebrand disease, hemophilia, and immune thrombocytopenia. It describes the pathophysiology of hemostasis and the coagulation cascade. Signs and symptoms of bleeding disorders are outlined depending on whether they affect the primary or secondary phase of hemostasis. The diagnostic approach and differential diagnosis for evaluating bleeding disorders is also summarized.
































![Thrombotic microangiopathy syndromes (TMA):
• specific pathologic lesion in which abnormalities in the vessel wall of arterioles
and capillaries lead to microvascular thrombosis. TMA syndromes include :
1- thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura (TTP).
2- Shiga toxin-mediated HUS (hemolytic-uremic syndrome [ST-HUS]).
3- drug-induced TMA (DITMA) syndromes.
4- complement-mediated TMA.
• TTP associated with Deficiency of
ADAMTS13 which can be hereditary or
acquired. This enzyme break down
ultra large von willrbrand factor
multimers (ULVWF) which become
inactive. Once reduce ADAMTS13 will
lead to increase ULVWF causing more
Plt aggregation and form large
occlusive platelet thrombi which are
capable of embolizing to microvessels
contributing to organ ischemia.
• HUS associated with direct affect of
toxin (Shiga toxin producing E. Coli )
into Plt and RBC.
Once
this
occur,
will
cause
Microangiopathic hemolytic
anemia (MAHA) :
• intravascular red blood cell
fragmentation that produces
schistocytes on the peripheral
blood smear including small
arterioles and capillaries.
thrombocytopenia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bleedingdisorders-190213172852/85/Bleeding-disorders-34-320.jpg)







![Heparin induce thrombocytopenia (HIT)
58 yrs old lady with history of HTN and DM II, was admitted with a hip fracture that she sustained following a fall at
home. Plain Xray showed a sub-trochanteric right hip fracture. After stabilization , she underwent open reduction
and internal fixation. 12hrs following surgery, she was started on LWMH enoxaparin 40mg subcutaneously daily. On
the 6th day post-op, CBC showed Hb 9, WBC8, Plt 98. further investigation didn’t reveal any other abnormality. Her
Plt count improved over the subsequent few days.
From the case, Plt drop after administration of
LWMH with no significant symptoms. Possible
causes
HIT :
• is a life-threatening complication of
exposure to heparin (ie, unfractionated
heparin, low molecular weight [LMW]
heparin) regardless of the dose,
schedule, or route of administration.
• More occur in exposure of
unfractionated heparin.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bleedingdisorders-190213172852/85/Bleeding-disorders-42-320.jpg)