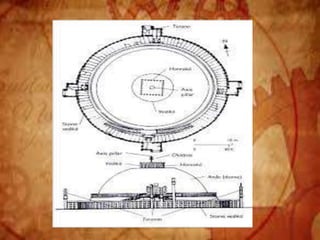
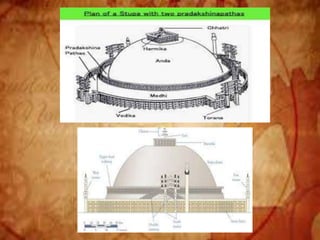
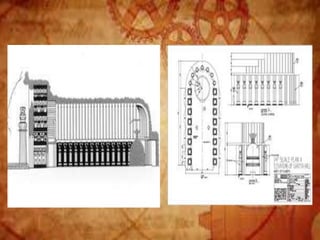
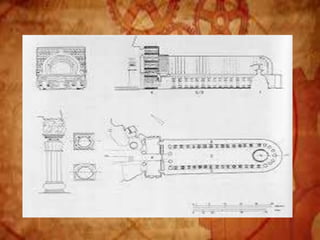
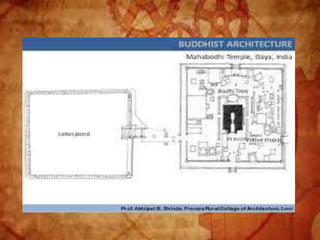
Buddhist architecture originated in the Indian subcontinent and comprises three main structures: monasteries, relic veneration places, and prayer halls, evolving from symbols of Buddha's life. Key elements include stupas, stambhas, chaityas, and viharas, showcasing unique architectural features and examples like the Sanchi Stupa and the Iron Pillar of Delhi. Important sites such as the Ajanta and Ellora caves, as well as the Mahabodhi Temple, reflect the rich cultural and artistic heritage of Buddhism.