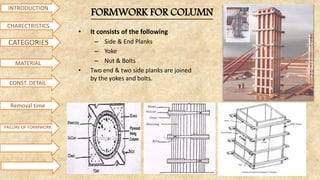
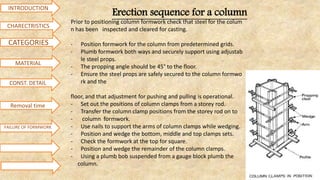
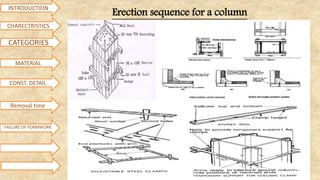
Formwork is used to create structures out of concrete that is poured into molds. It can be made from materials like steel, wood, aluminum, or prefabricated forms. Construction of formwork takes up 20-25% of total structure costs and involves supporting structures and molds. Proper formwork is designed to be easily removable, economical, leakproof, durable, rigid, provide smooth surfaces, be strong, and have adequate supports. Common types include conventional timber formwork, engineered prefabricated formwork, and modern systems like flying forms. Materials used include steel, plywood, plastic, and aluminum. Proper bracing and construction is needed to avoid failures from improper stripping, inadequate bracing, vibration