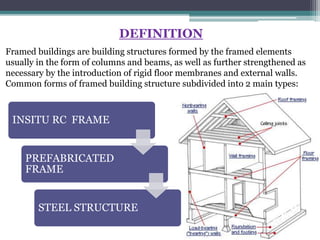
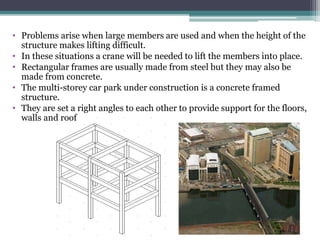
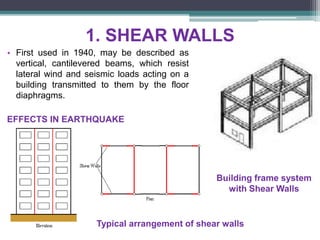
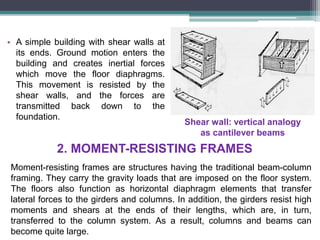
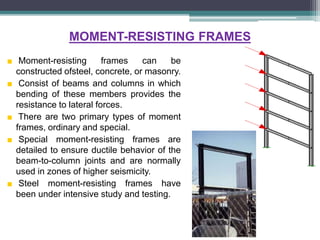
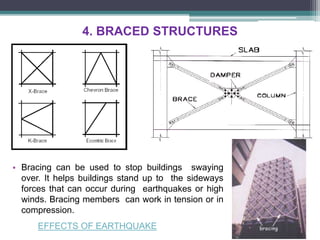
Framed structures are building skeleton frameworks formed by columns and beams. There are two main types: in-situ reinforced concrete frames and prefabricated frames. Rectangular framed structures use columns and beams arranged at right angles to support floors, walls, and roofs. They are commonly used for multi-story buildings like offices, schools, and hospitals. Framed structures provide large open floor plans and are adaptable to different shapes. Earthquake-resistant features in framed structures include shear walls, moment-resisting frames, and braced structures which resist lateral forces during seismic activity.